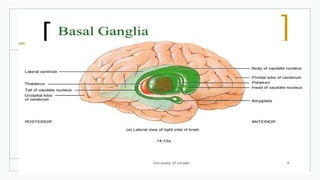
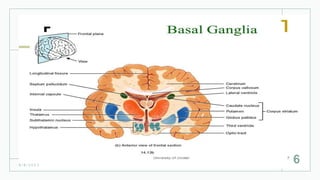
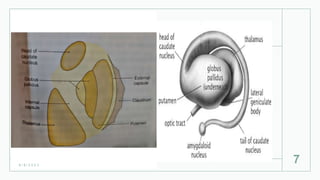
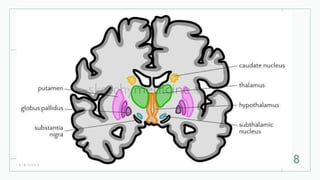
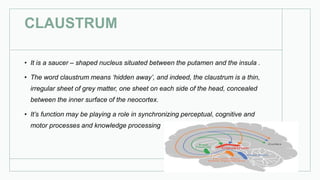
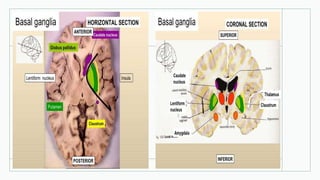
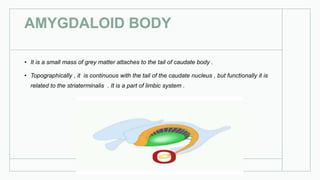
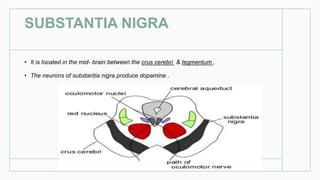
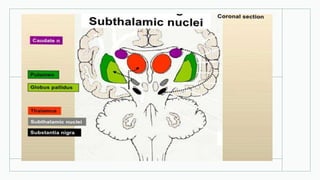
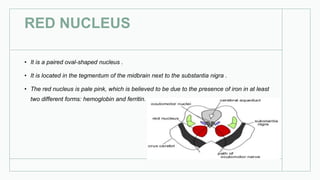
The basal ganglia are masses of grey matter located at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. Anatomically, the basal ganglia consist of the corpus striatum, claustrum, and amygdaloid body, while functionally they also include the substantia nigra, subthalamus, and red nucleus. The basal ganglia are involved in controlling voluntary motor activity, timing and scaling movement intensity, and decreasing unwanted muscle activity. Disorders of the basal ganglia include Parkinson's disease, ballismus, chorea, athetosis, Wilson's disease, and Huntington's disease.