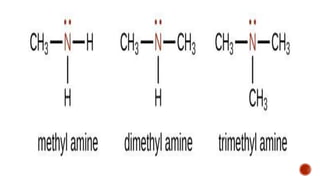
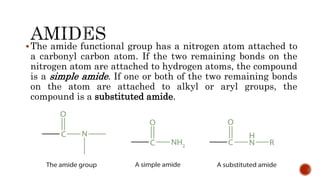
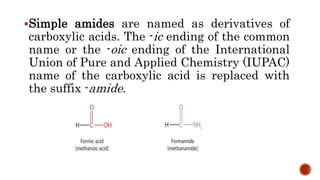
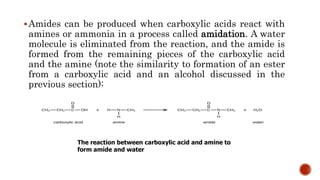
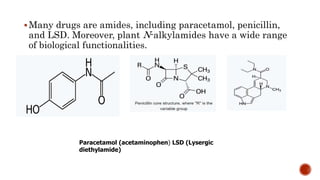
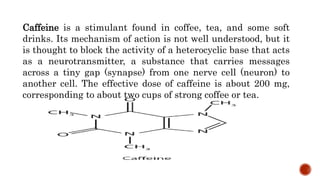
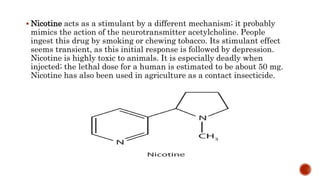
Nitrogen-containing compounds, or amines, include a diverse range of substances from simple molecules like ammonia to complex proteins and nucleic acids. They play crucial roles in biological systems and industrial applications. Amines contain carbon-nitrogen bonds and can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on the number of organic substituents attached to the nitrogen atom. These compounds have various uses including in pharmaceuticals, plastics, solvents, coatings, and agriculture. Heterocyclic amines contain nitrogen atoms within cyclic molecular structures and include important alkaloids like caffeine, nicotine, and cocaine that have physiological effects.