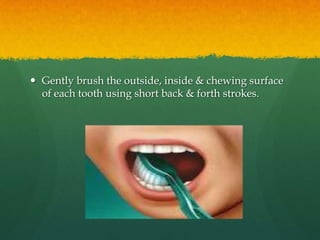
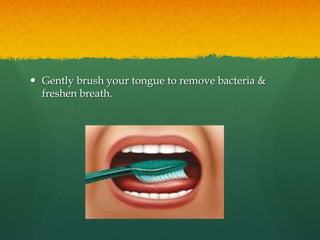
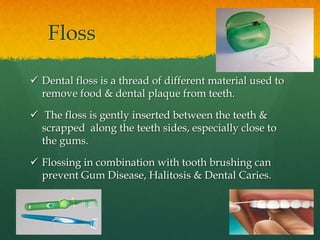
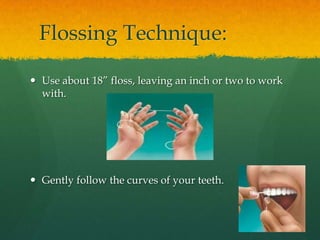
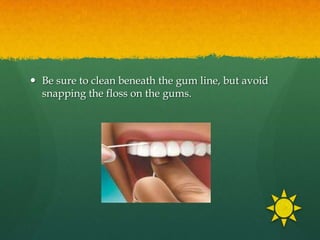
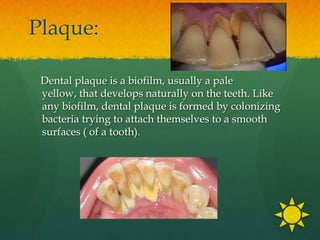
This document discusses proper oral hygiene and dental health. It defines oral hygiene as keeping the mouth clean to prevent disease and increase comfort. Maintaining good oral hygiene involves brushing teeth twice daily, flossing daily, eating a balanced diet, and using fluoride toothpaste. Proper brushing and flossing techniques are described. Replacing toothbrushes every 3 months or after illness is recommended. Dental plaque, caries, and halitosis are explained as are natural solutions used for mouthcare like potassium permanganate and sodium chloride. The importance of calcium, limiting sugars, and practicing good oral hygiene from an Islamic perspective are highlighted.