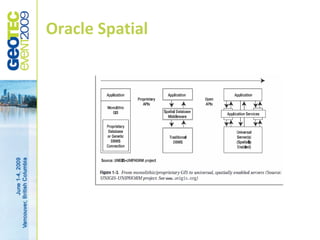
Oracle Spatial Databases allow for the integration of CAD and GIS data into Oracle technologies by treating spatial data as just another data type. As part of a universal information repository, Oracle Spatial provides a common format for various GIS content to ensure application independence and accessibility. It exposes location data to the entire enterprise in a reliable, scalable, and secure manner.