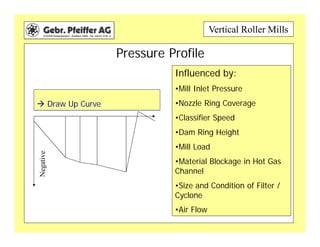
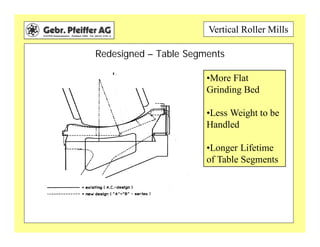
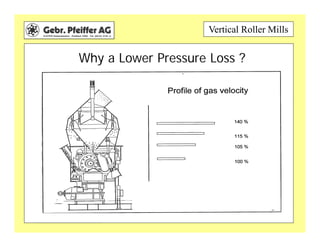
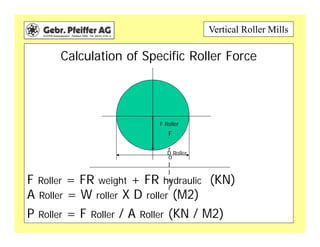
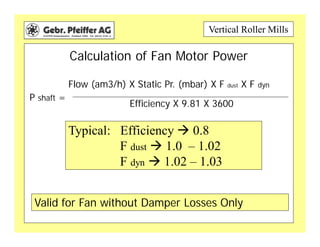
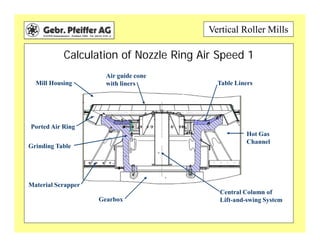
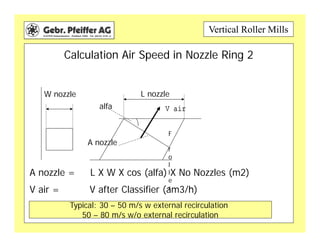
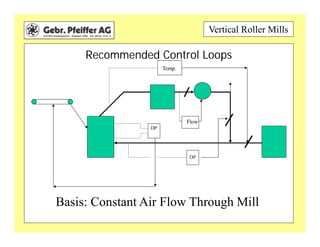
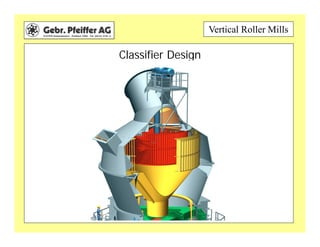
The document provides information on optimizing the operation of vertical roller mills (VRMs). It discusses monitoring relevant process parameters like product rate, fineness, classifier speed, grinding force, power consumption, air flow, and availability. The optimum settings are the highest capacity at lowest power. It emphasizes finding the optimum settings through continuously changing parameters and documenting results. Basic calculations for parameters like specific roller force, fan motor power, and air speed in the nozzle ring are also presented.