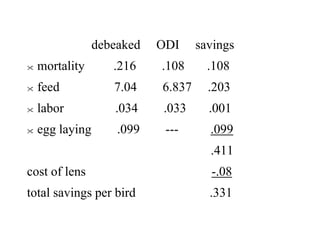
This document presents an analysis of the costs and savings of debeaking versus using Optical Debeaking Instruments (ODI) for chickens. Some key points:
- Debeaking results in savings of $0.331 per bird compared to ODI due to lower mortality, feed costs, labor costs, and egg laying costs.
- The total variable cost per pair of ODI lenses is $0.03448, including manufacturing, injection, and box costs.
- Total fixed costs for ODI are estimated at $955,000 annually, including payments, facilities, staffing, marketing, and trade shows.
- For ODI to be profitable, the lens price would need to be