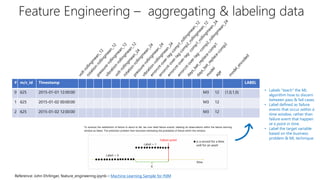
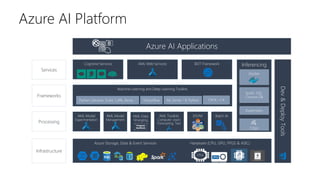
The document discusses predictive maintenance using Azure AI. It describes key concepts of predictive maintenance including predicting failures in advance to schedule timely repairs. It shows the architecture of a predictive maintenance solution template in Azure, including ingesting sensor data, training and testing models, and deploying models for online predictions. The template aims to help reduce operational risks, increase asset utilization, and lower maintenance costs.