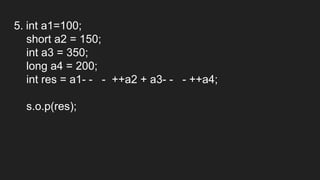
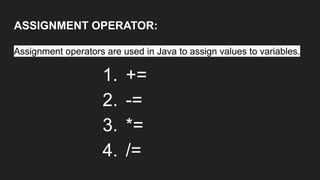
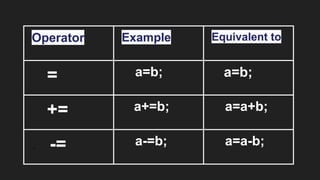
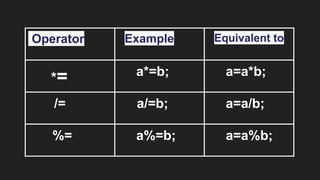
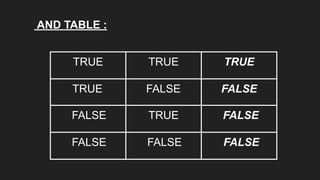
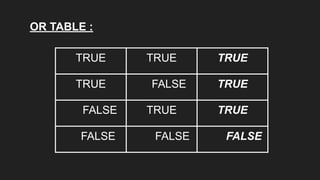
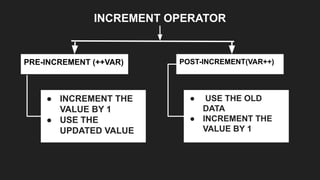
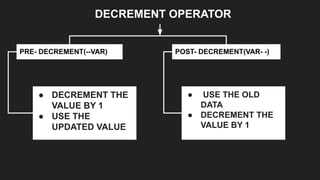
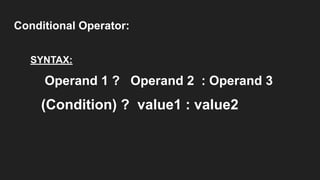
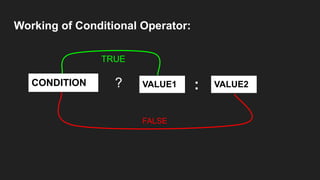
Operators are symbols that perform specific operations on operands. There are unary, binary, and ternary operators classified based on the number of operands they accept. Common operators include arithmetic, assignment, relational, logical, increment/decrement, and conditional operators. The increment and decrement operators can be pre-increment/decrement or post-increment/decrement, affecting whether the operand is updated before or after use in an expression.














![EXAMPLE:
Class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b =20;
int c = (a>b) ? a : b; //Conditional Operator
System.out.println(c); // 20
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10operators-230506093238-7a2e69a5/85/10-OPERATORS-pdf-25-320.jpg)