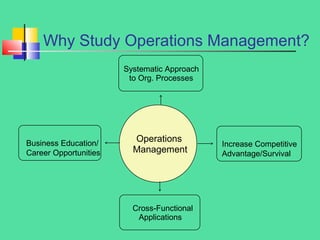
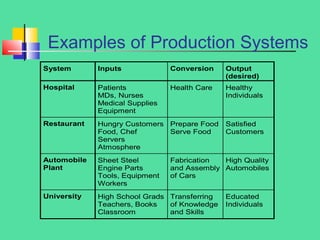
Operations management involves the design, operation, and improvement of systems for delivering a firm's products and services. Key concepts include efficiency, effectiveness, value, and various transformation types, alongside competitive dimensions such as cost, quality, and delivery. The document highlights the importance of a systematic approach for enhancing organizational processes and career opportunities in operations management.