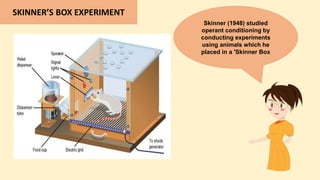
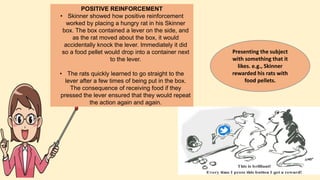
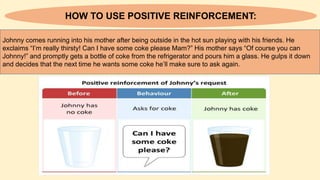
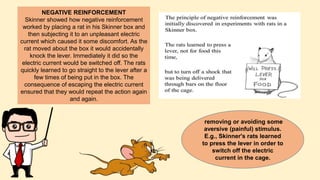
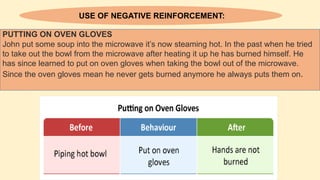
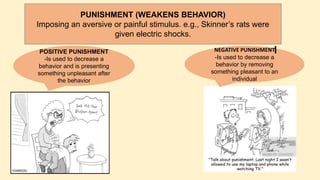
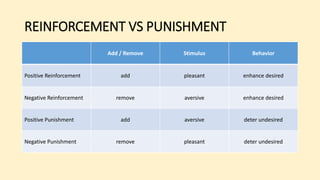
The document discusses operant conditioning, a learning method developed by B.F. Skinner, which emphasizes the relationship between behavior and its consequences through rewards and punishments. It explains positive and negative reinforcement with examples, showing how behavior can be shaped by adding or removing stimuli. Additionally, it covers punishment methods aimed at decreasing undesirable behaviors by introducing aversive stimuli or removing pleasant ones.