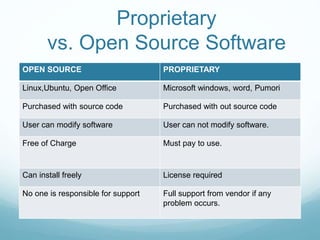
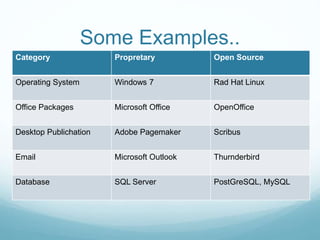
This document provides an introduction to open source technology. It defines open source software as software with available source code that allows users to modify and improve it, in contrast to proprietary software where the source code is not available. Examples of open source software include Linux, Firefox, and OpenOffice, while proprietary software examples include Windows and Microsoft Office. The document then discusses the history of open source software and lists some benefits like free availability and customizability as well as drawbacks like a steeper learning curve. It concludes by discussing Nepal's current status with open source and possibilities for its future use.