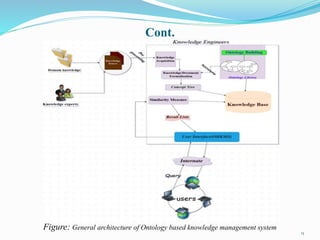
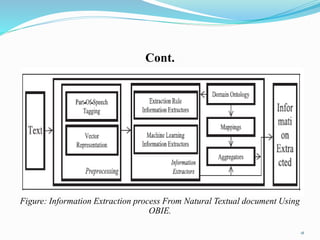
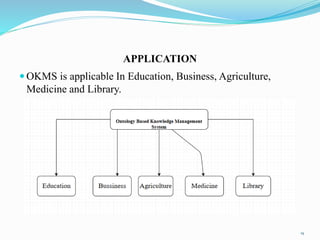
The document outlines an ontology-based knowledge management system. It discusses how traditionally keyword systems cannot understand query meanings, while ontology systems provide a content-oriented approach. It then defines knowledge management and knowledge management systems, and how ontologies can classify knowledge and define vocabularies to facilitate searching, sharing, and integrating related resources. Finally, it discusses using ontologies and information extraction to extract concepts from natural language texts.