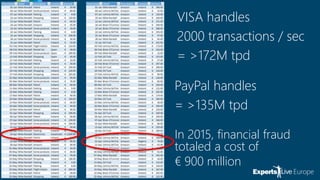
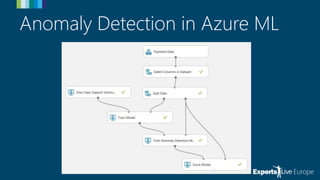
The document discusses the use of Azure Machine Learning for online payment fraud detection, detailing the process of training, scoring, and evaluating models while emphasizing the importance of anomaly detection. It highlights the limitations of traditional fraud detection methods and the advantages of machine learning, including self-learning models and feature engineering with historical data. Various techniques and tools available in Azure ML for anomaly detection are also mentioned.