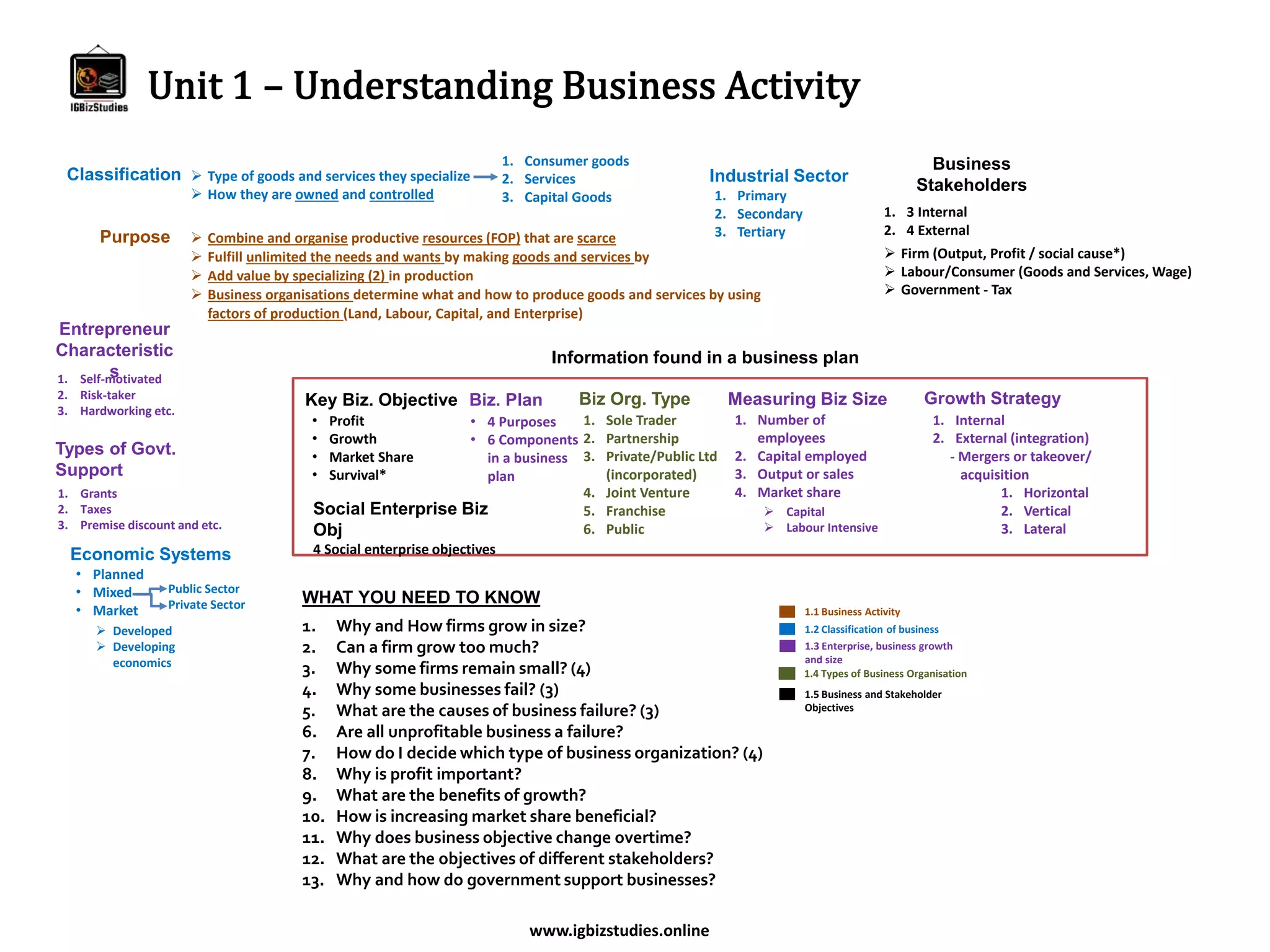
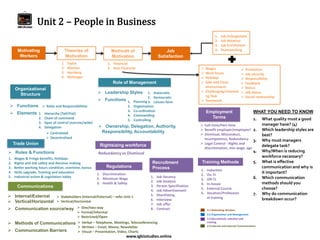
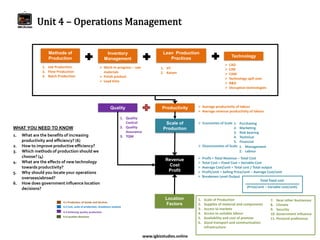
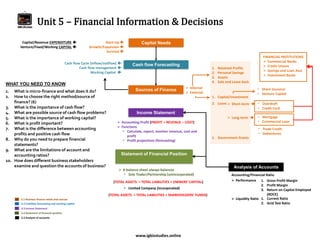
The document provides an overview of business studies topics including:
- The purpose of business organizations and how they use resources to produce goods and services.
- The different sectors of industry and types of government support.
- Key topics in business studies like growth strategies, types of business organizations, and objectives of different stakeholders.
- Questions students should know about topics like competition, marketing, operations, finance, and external influences on business.
It covers a wide range of concepts in business organization, production, marketing, finance, and the external environment in a comprehensive but concise manner.