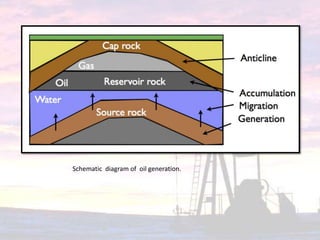
The document discusses the origin of oil. It states that oil is formed from organic matter from ancient marine organisms that accumulated on ocean floors. Bacteria transformed this organic matter into oil through biochemical changes. Further geochemical changes from heat, pressure, and radioactivity over long periods of time converted the organic material into liquid oil and gas. For oil deposits to form, the oil must migrate from its source rock into porous reservoir rocks and be trapped by an impermeable cap rock.