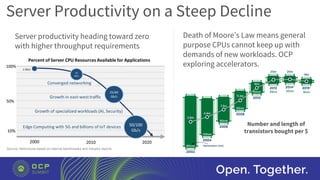
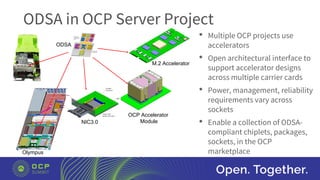
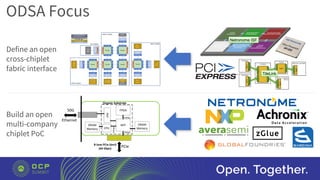
The document discusses the launch of the Open Domain-Specific Architecture (ODSA) sub-project, aiming to create a new server subgroup that utilizes domain-specific accelerators and chiplets to enhance performance while reducing costs. It highlights the shift from monolithic designs to chiplet-based architectures to overcome the limitations of Moore's Law and improve server productivity. Additionally, the document calls for collaboration across companies to develop a standardized open interface for chiplet integration and emphasizes the importance of domain-specific logic and open-source support for successful implementation.