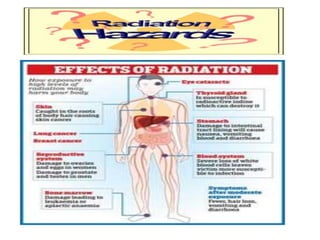
Occupational health focuses on the safety and well-being of workers by addressing potential hazards in the workplace, including ergonomic, physical, chemical, biological, and psychological risks. The objective is to prevent work-related injuries and improve overall health for enhanced productivity. Occupational hazards can lead to various health issues such as fatigue, heart disease, and impact from exposure to radiation.