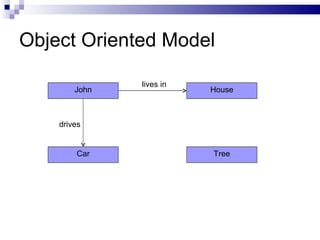
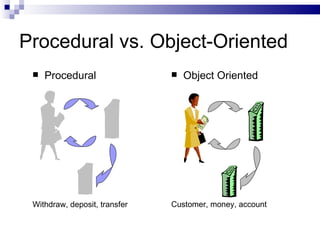
Object-oriented concepts involve modeling real-world entities as objects that have states (attributes) and behaviors (operations). An object is an instance of a class, which defines common properties and behaviors. The object-oriented approach focuses on objects that encapsulate both data and functions, in contrast to the procedural approach which focuses on standalone procedures and shares all data. Some benefits of the object-oriented approach include being easier to develop and understand, and better mapping to real-world problems.