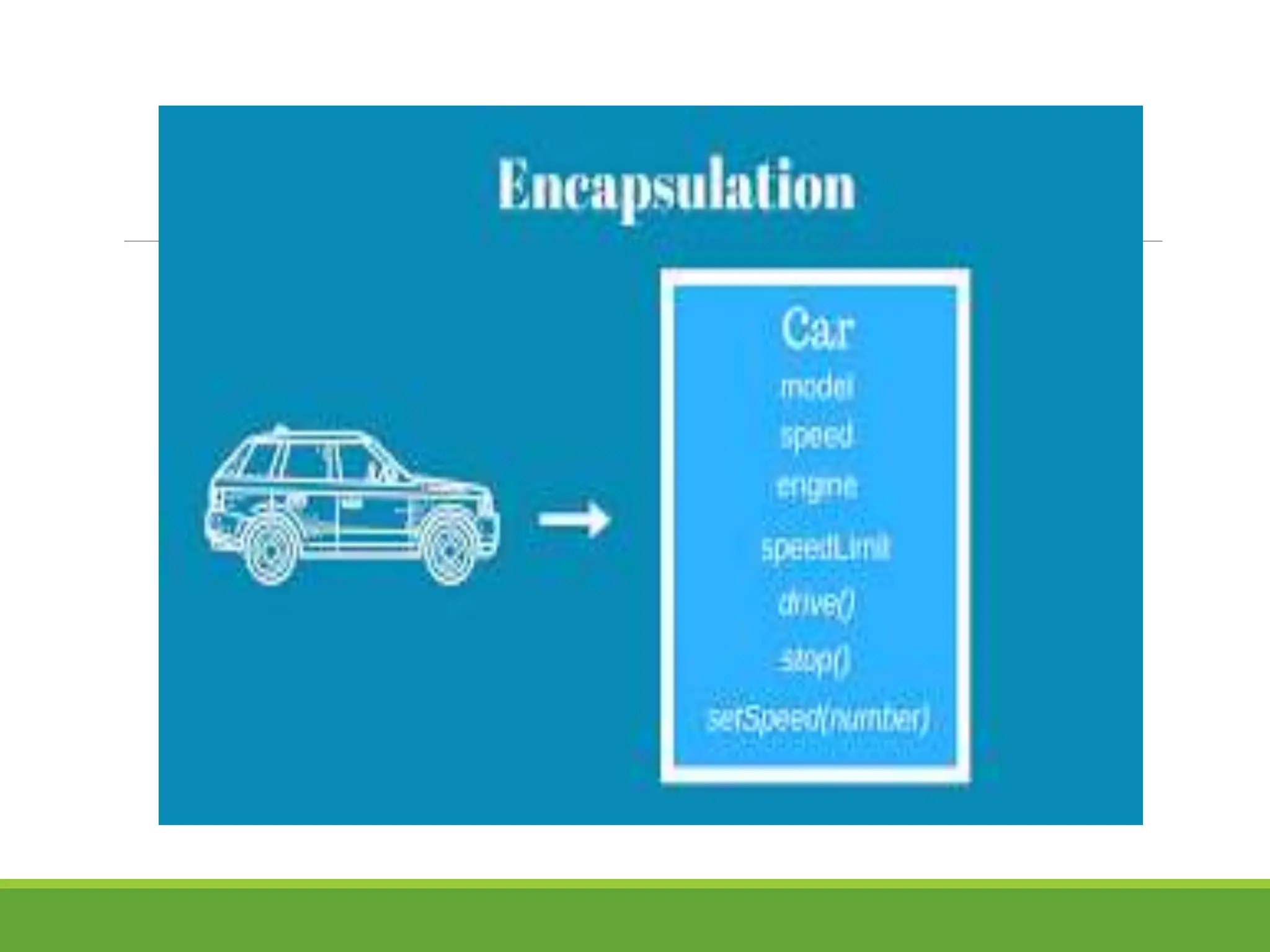
Object-oriented programming (OOP) addresses the limitations of procedural programming by organizing code into classes and objects, focusing on encapsulating data and behavior. A class serves as a blueprint for creating objects, which represent real-world entities and contain attributes (state) and methods (behavior). The four key principles of OOP are encapsulation, abstraction, polymorphism, and inheritance, which enhance program manageability and reusability.