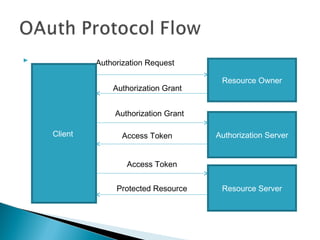
The document discusses OAuth and its roles and flow. OAuth allows clients to access server resources on behalf of resource owners without sharing credentials. It addresses limitations of directly sharing passwords by enabling selective, limited access delegation. The roles in OAuth are resource owner, resource server, client, and authorization server. The OAuth flow involves the client obtaining an authorization grant from the resource owner, exchanging it for an access token at the authorization server, and using the access token to access protected resources from the resource server.