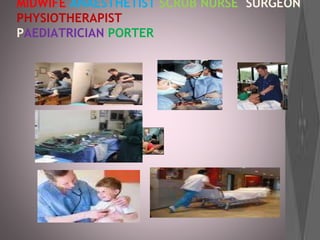
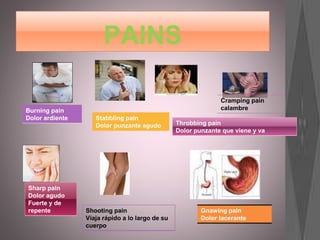
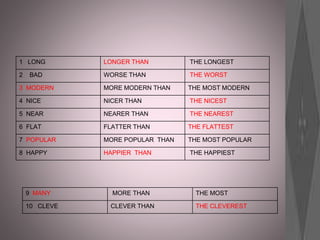
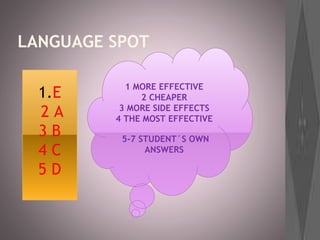
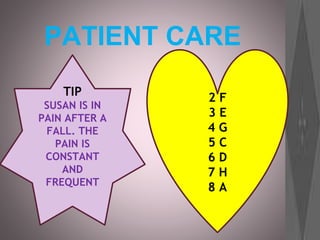
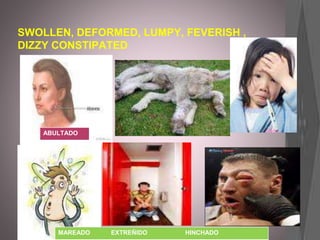
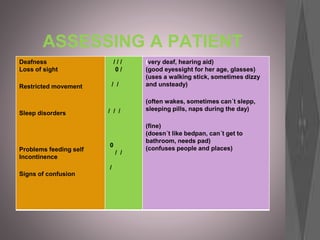
This document provides information about various roles in the nursing profession. It lists 14 different jobs/roles followed by short descriptions of what 3 of the roles involve. It then discusses what an anesthetist does in 5 sentences. The document aims to inform about different types of jobs that exist within the nursing profession.