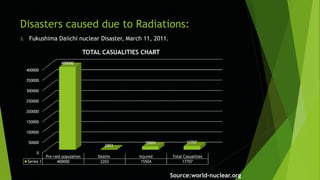
This document provides information about radiation hazards and prevention. It defines radiation and lists examples. Nuclear radiation can ionize molecules and cause cell death, leading to both short and long term health effects like cancer. Sources of radiation include natural (cosmic, radon, earth's crust) and artificial (environmental, industries) sources. Several nuclear disasters are described along with charts showing deaths and injuries. Prevention methods are outlined like minimizing exposure, shielding, surveillance, and protective equipment. Radiation safety is important for diagnostic and nuclear facilities.