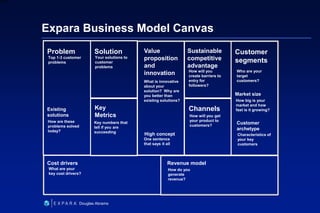
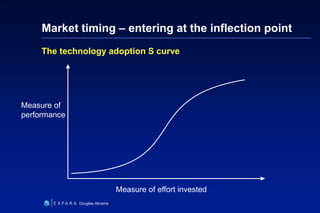
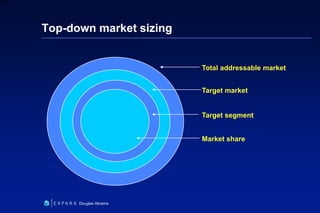
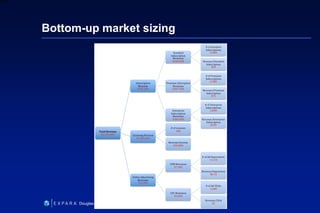
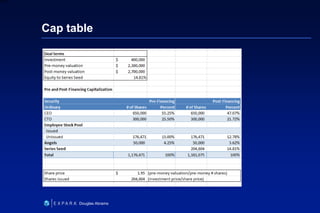
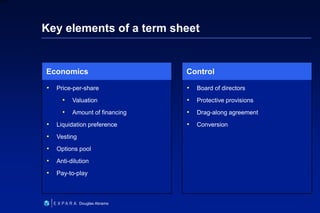
This document summarizes Douglas Abrams' presentation on "From Idea to Investment". It provides an overview of business models and how to prepare an idea for investment. Key elements for success include developing an innovative product, identifying customers, and making money. The presentation addresses questions investors will ask about the value proposition, market, marketing strategy, competitive advantage, and financials. It also discusses funding stages and sources, as well as effective entrepreneur-investor communication.