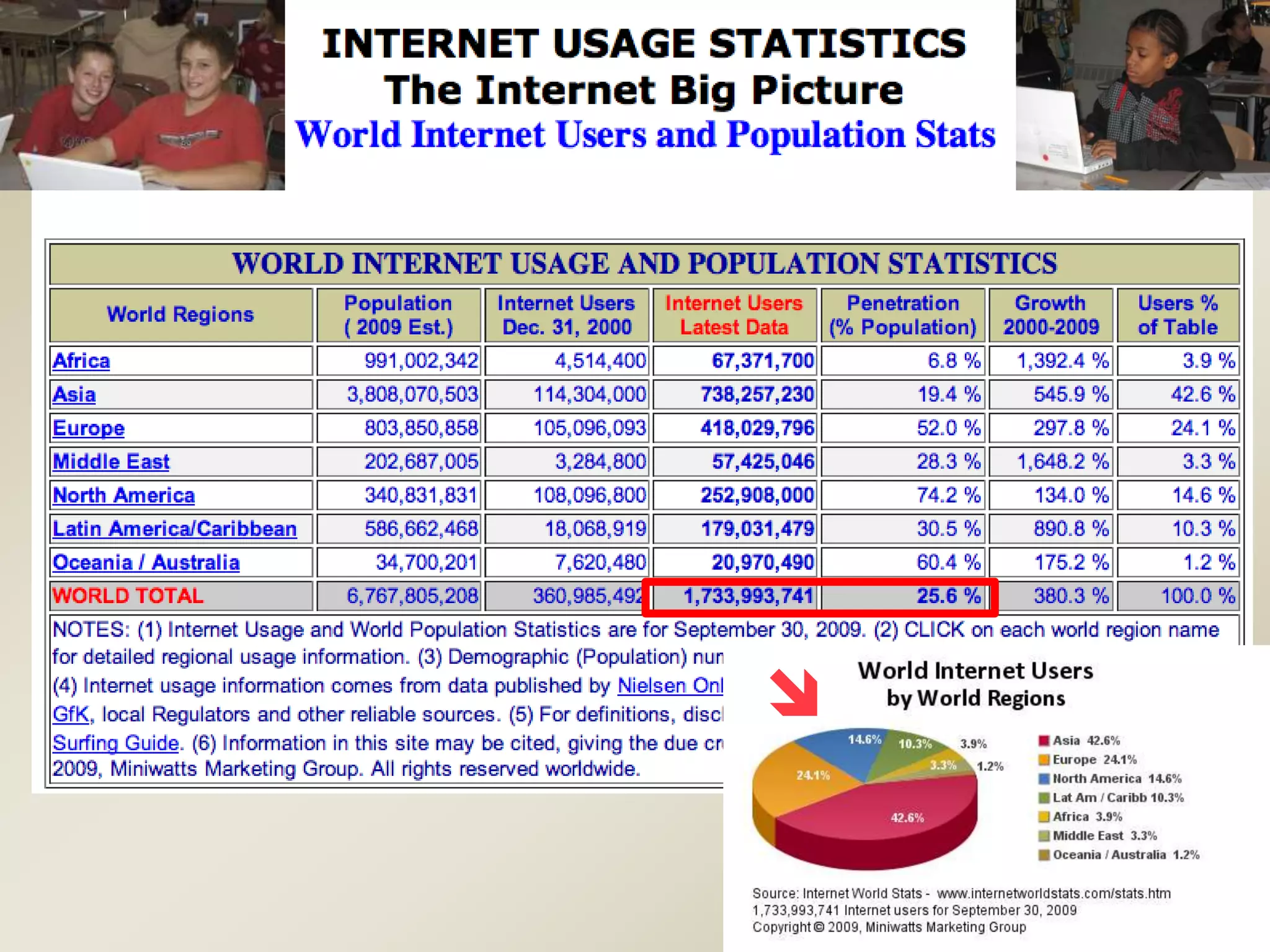
1. Conceptions of reading comprehension are shifting due to new online literacies that require new skills, strategies, and social practices for full participation in a global community.
2. Online reading comprehension involves constructing problems, locating, evaluating, synthesizing, and communicating information through links, and differs somewhat from offline reading.
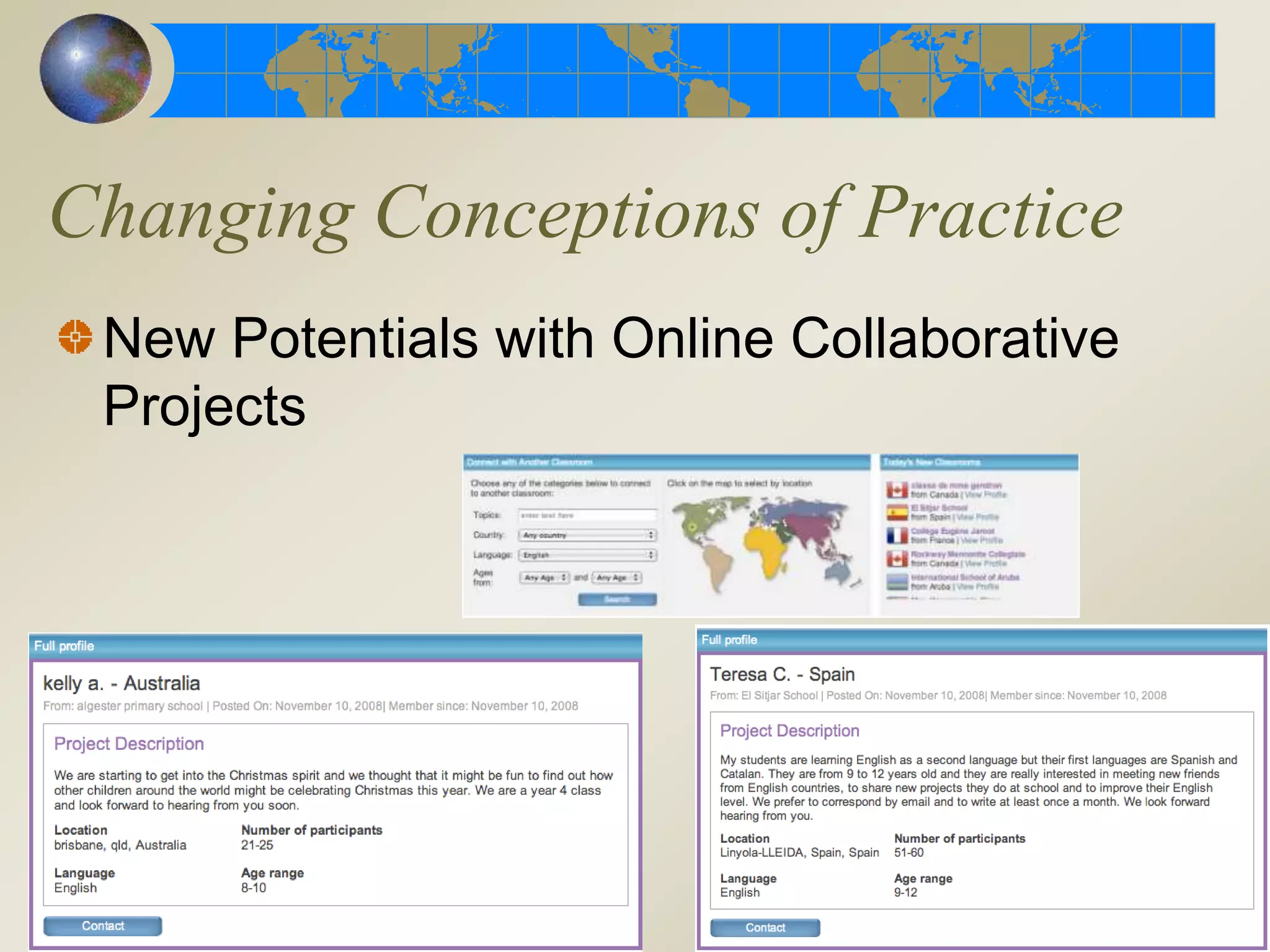
3. Changing instructional practices for online reading comprehension include 1:1 computing, collaborative projects, and new models of professional development delivered through technology.