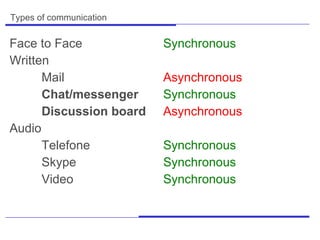
This document discusses various theoretical concepts and practical techniques related to online moderation. It covers types of communication, models of mass communication, the roles of moderators, competencies for moderators, tools for moderation, legal issues, and theories related to online communication and moderation. Key points include different asynchronous and synchronous communication methods, the importance of understanding online communication processes and technical skills for moderators, and techniques like using questions, summaries, and ensuring discussions stay on topic.