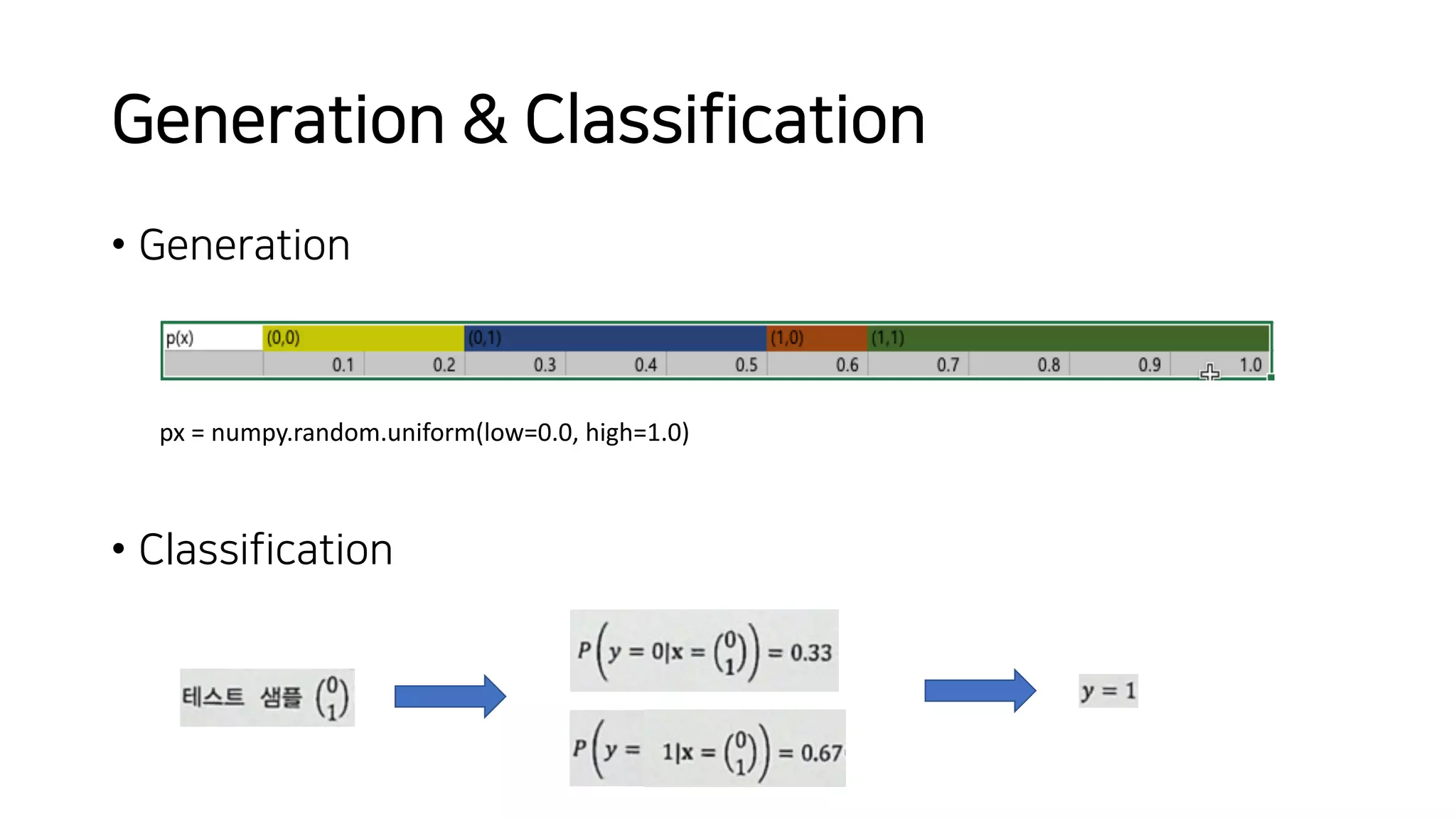
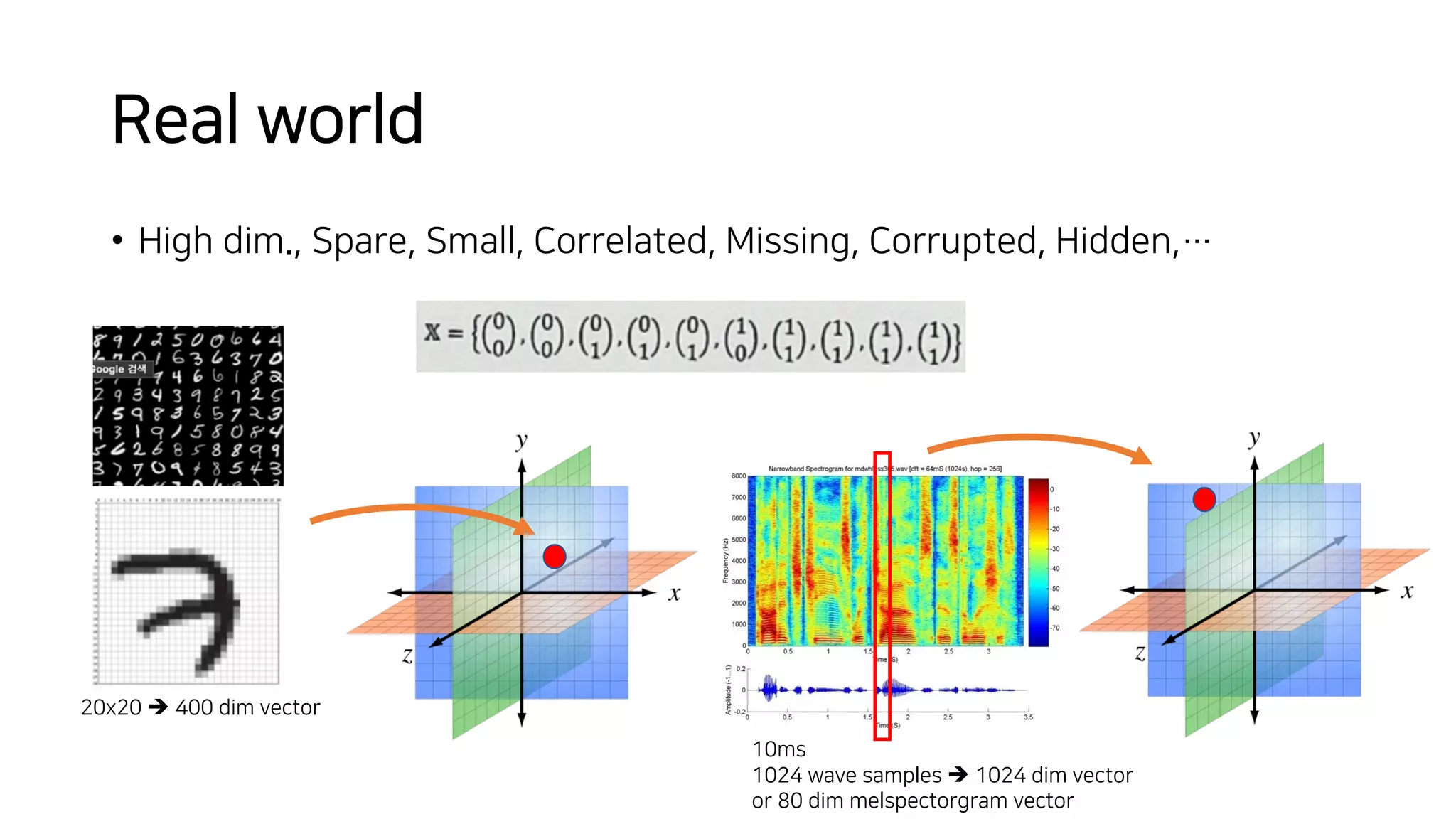
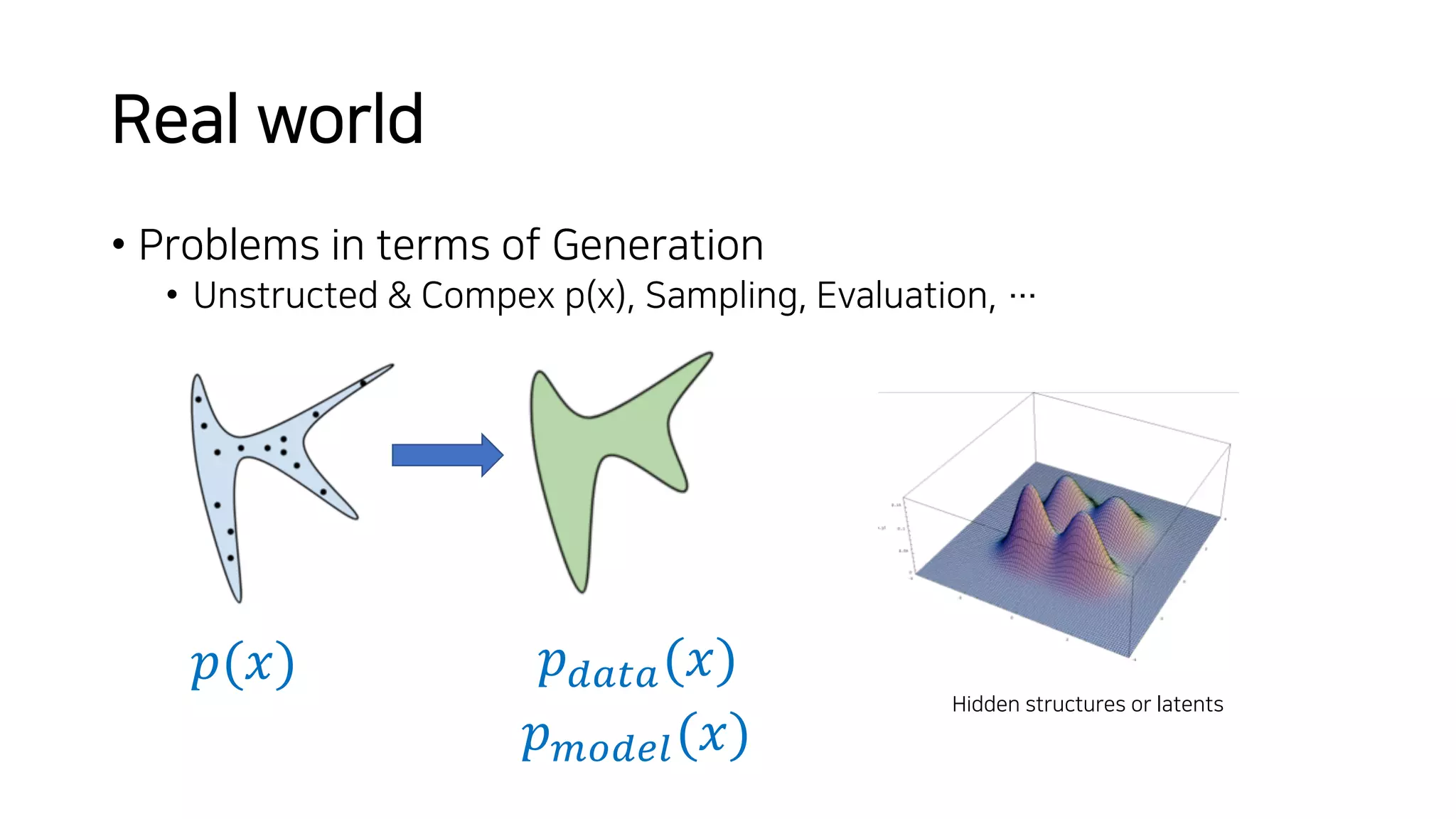
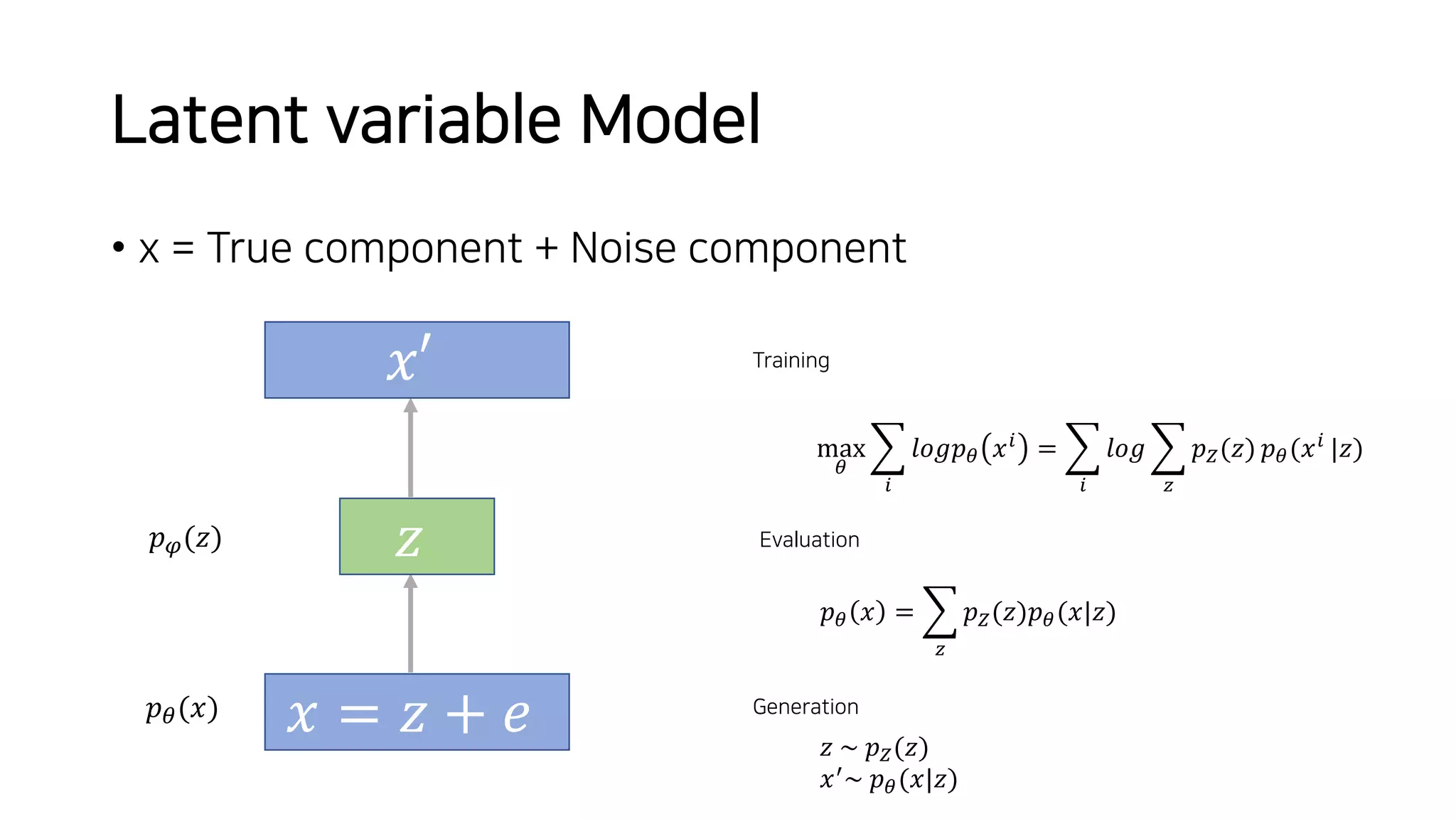
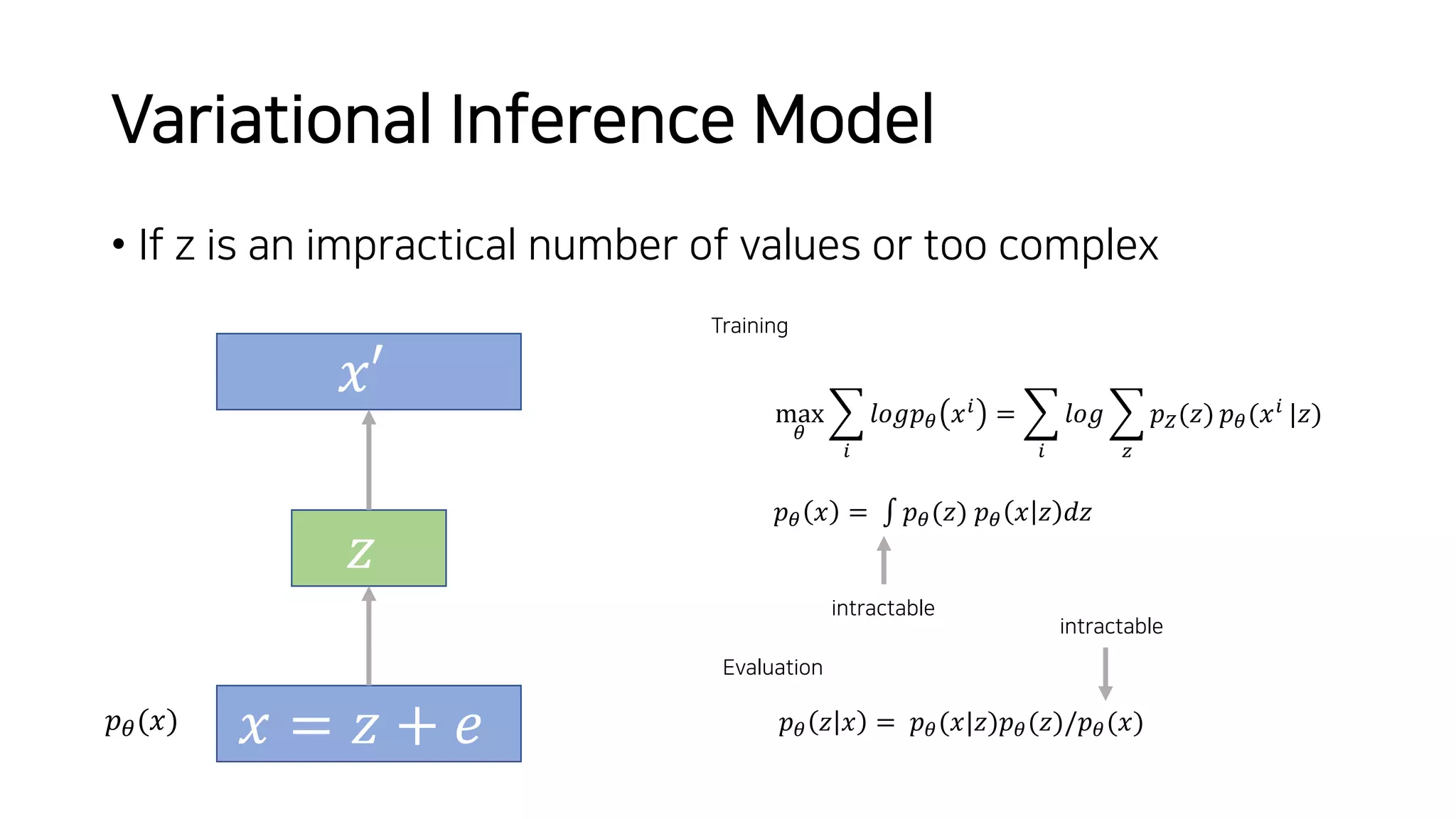
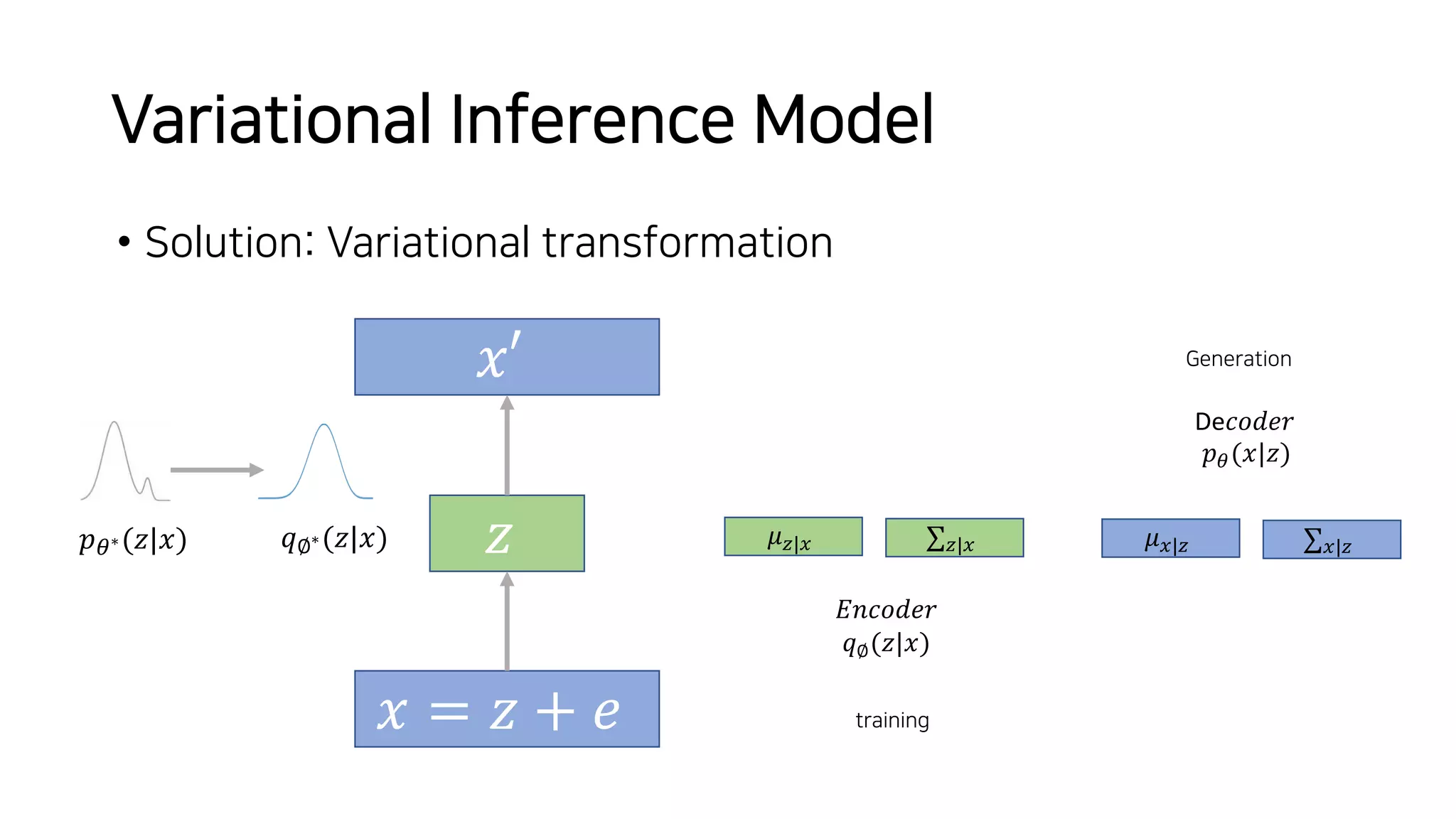
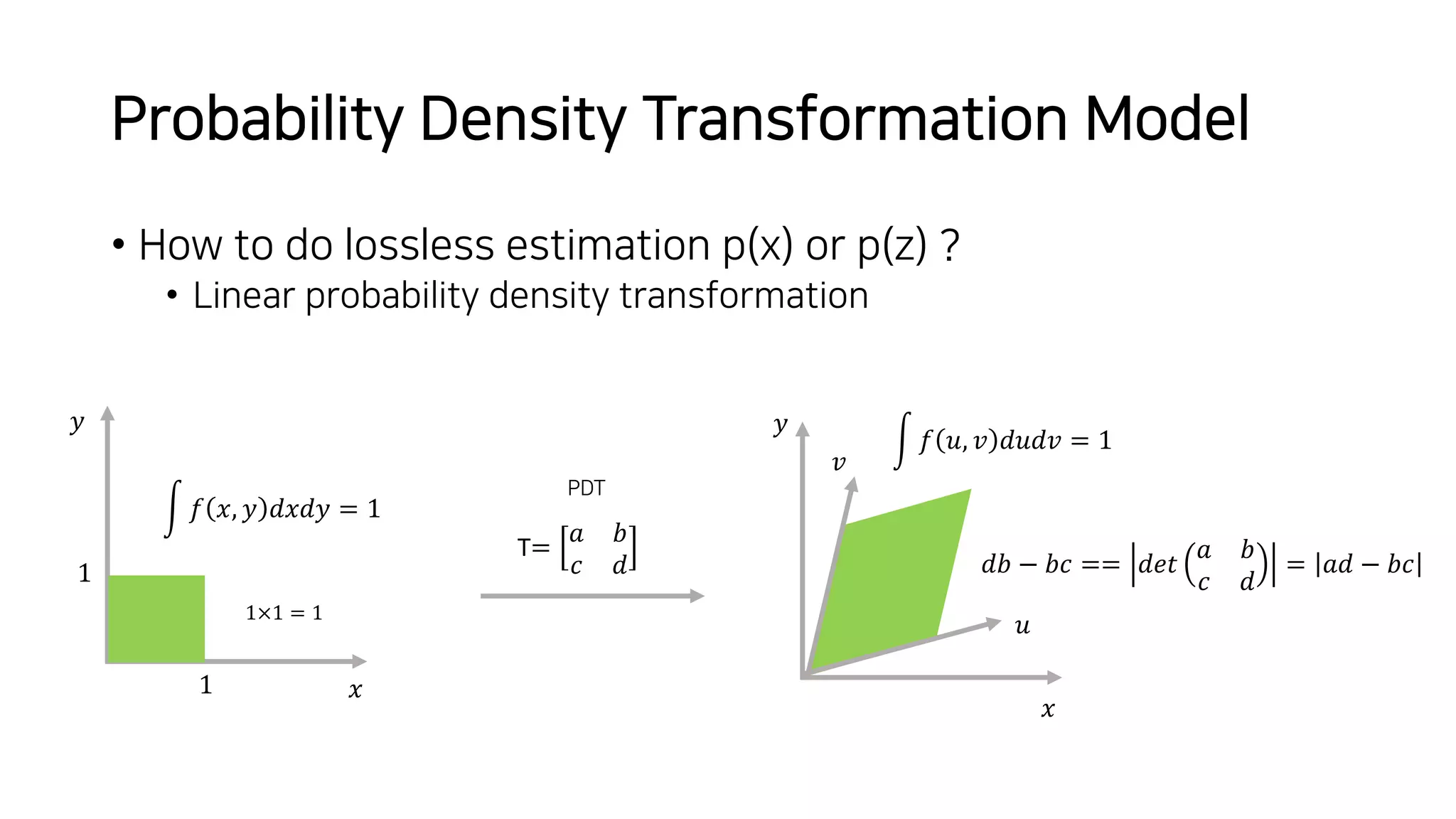
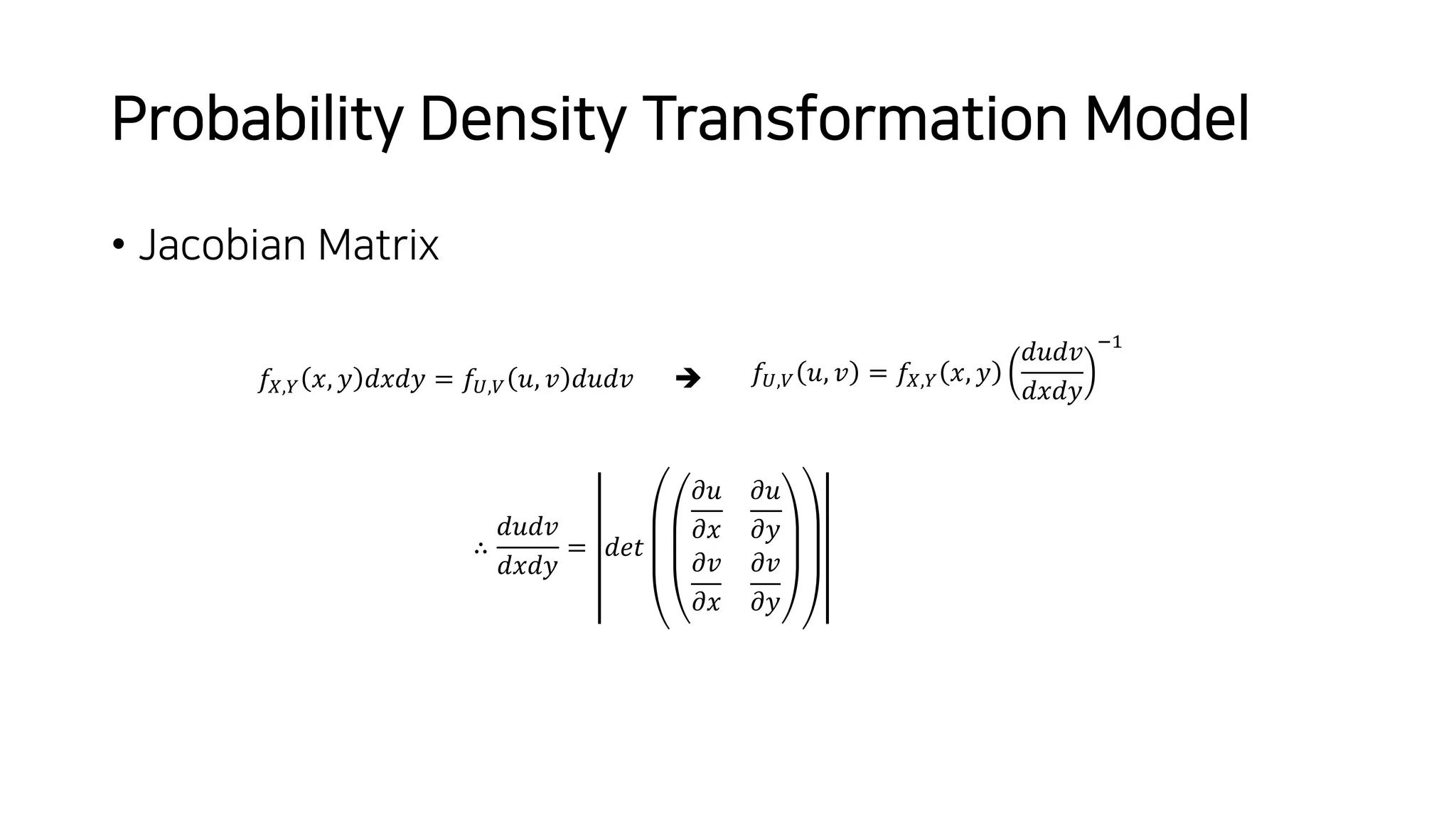
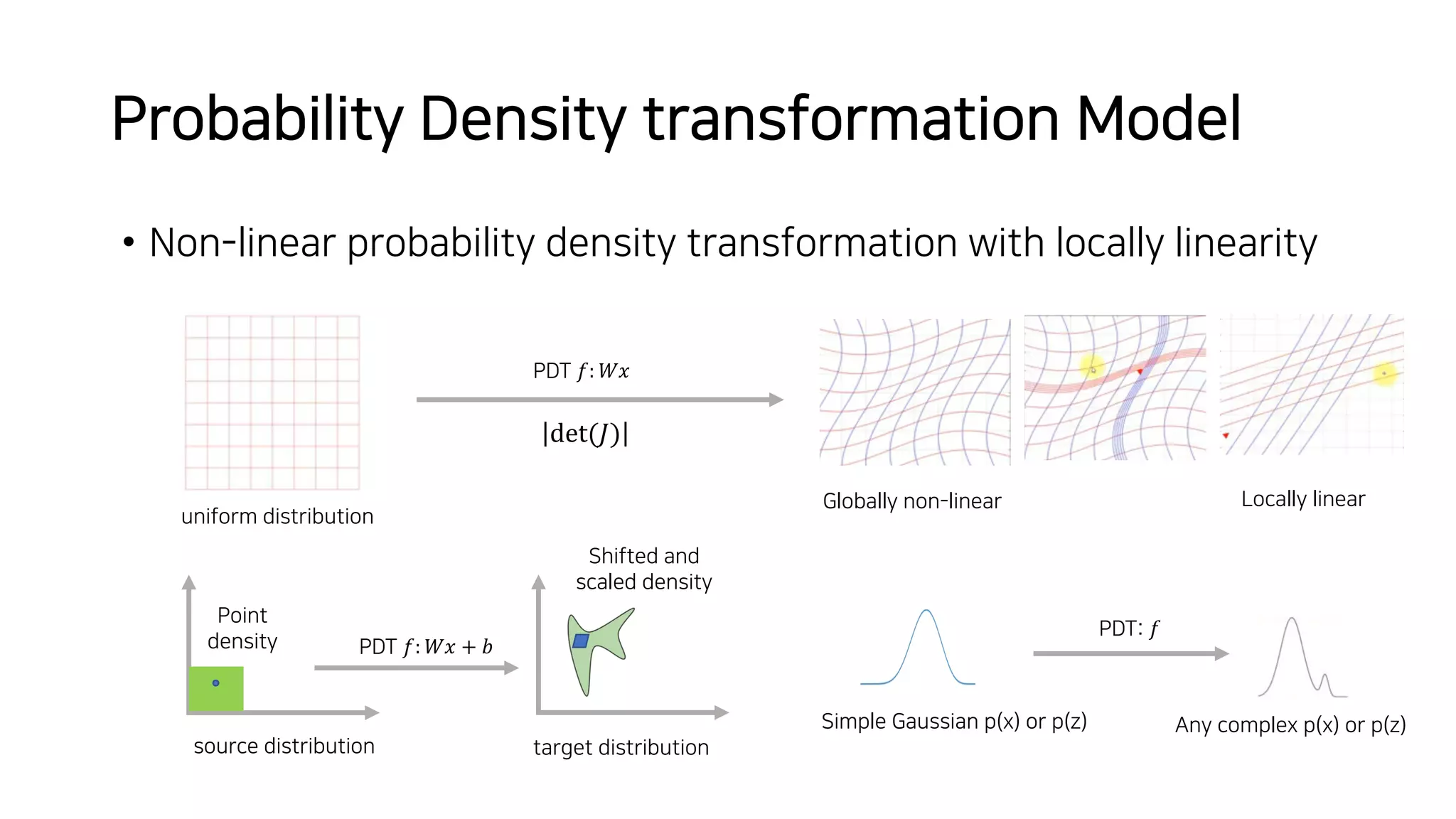
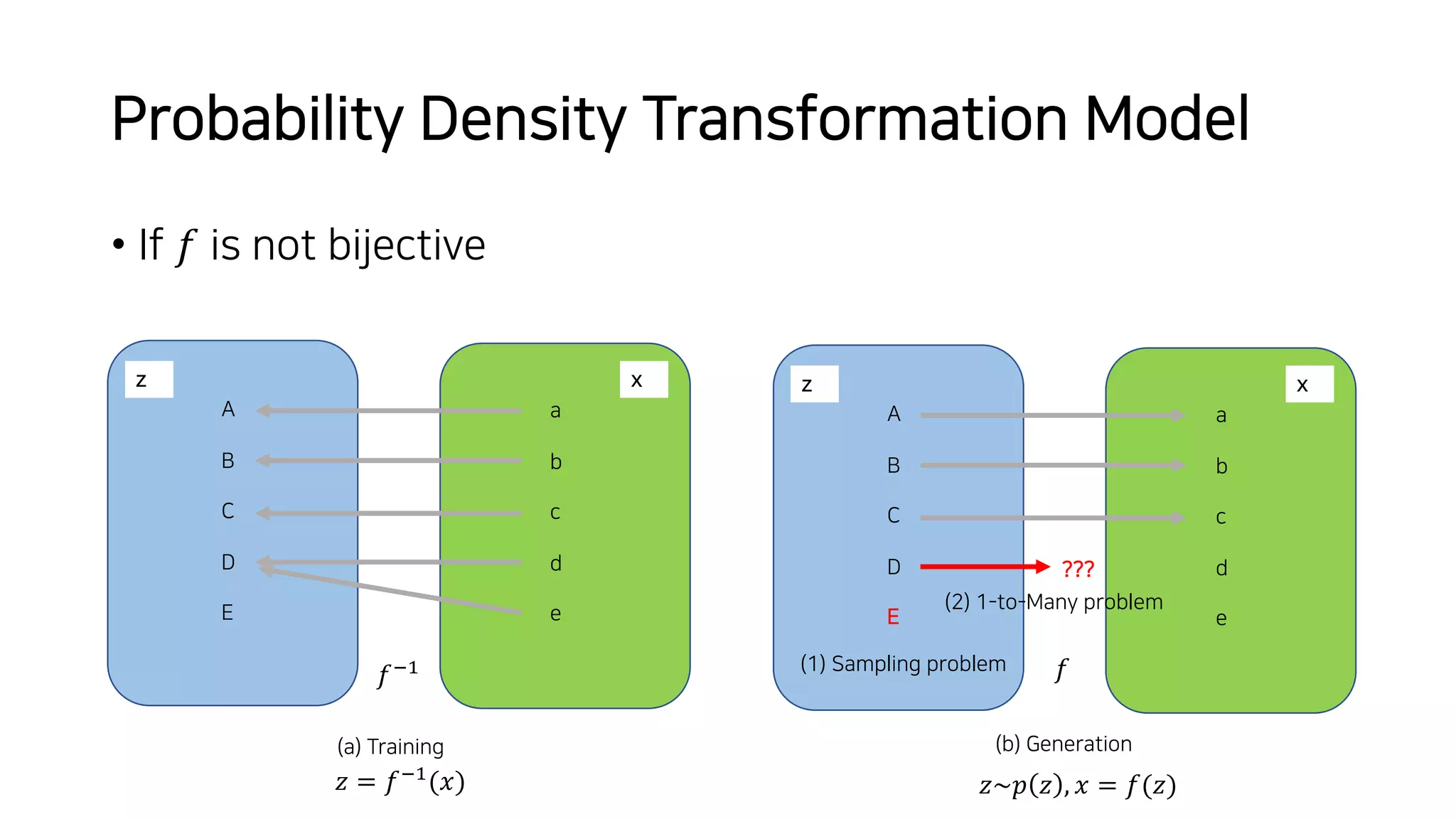
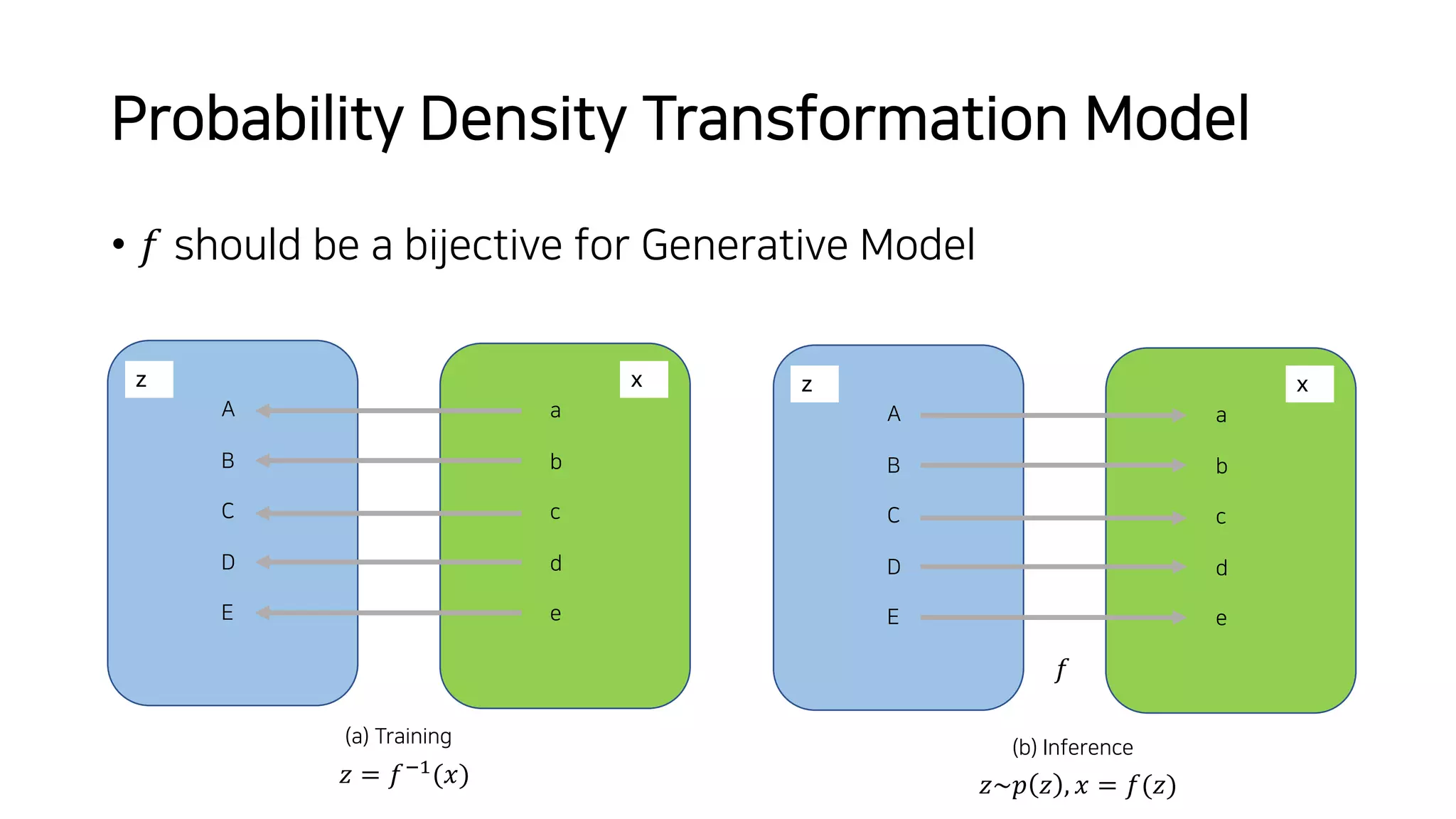
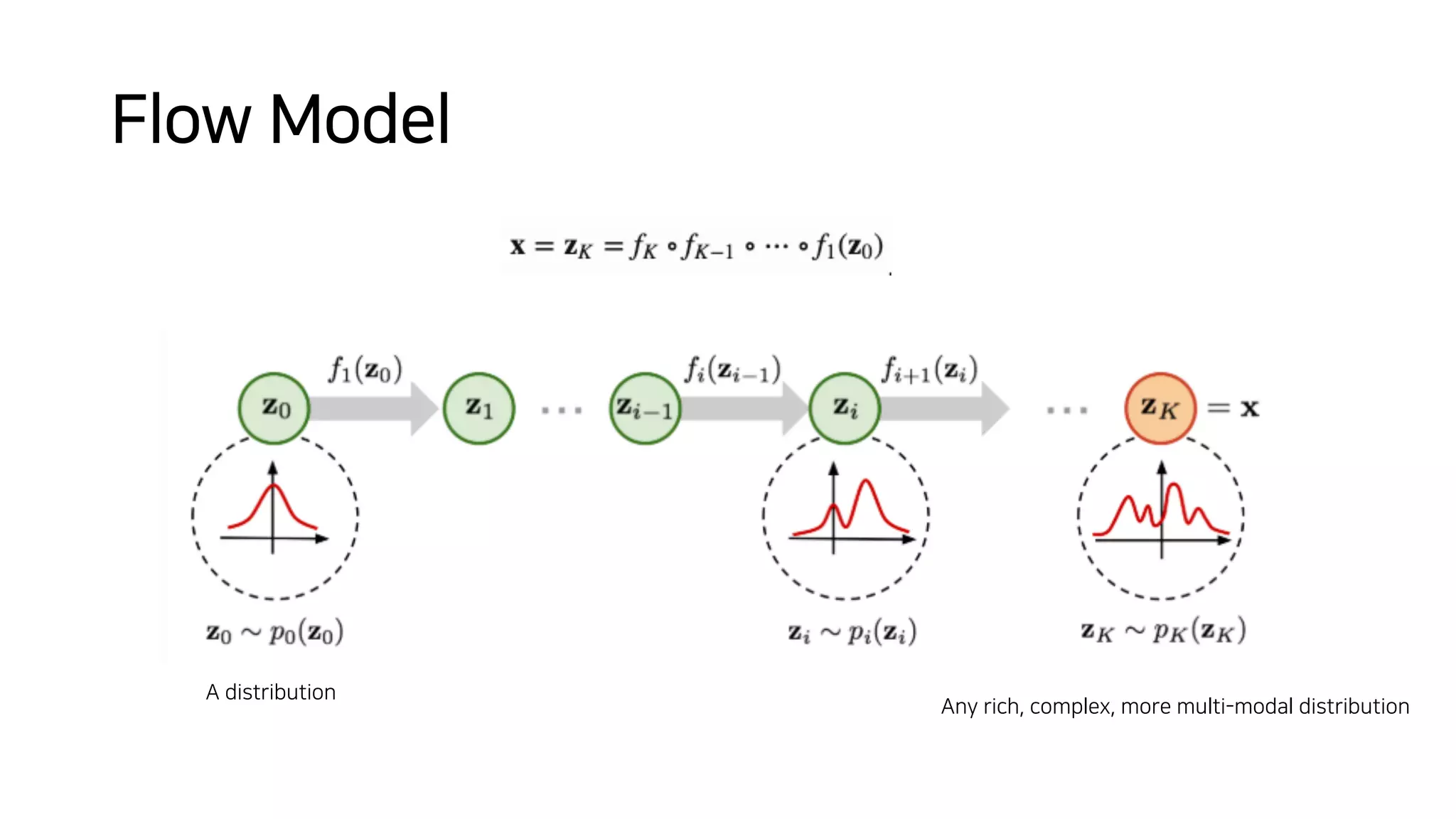
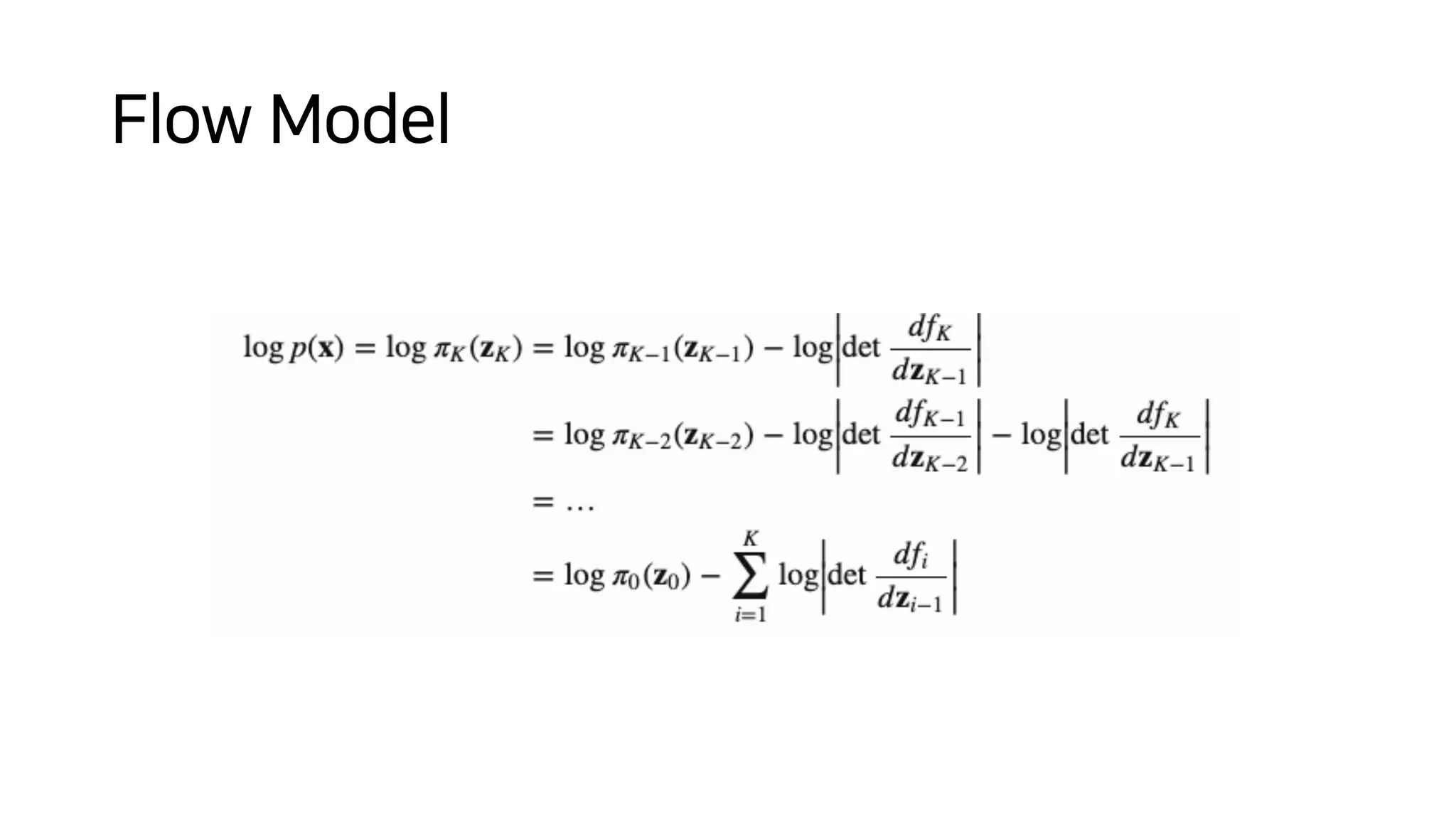
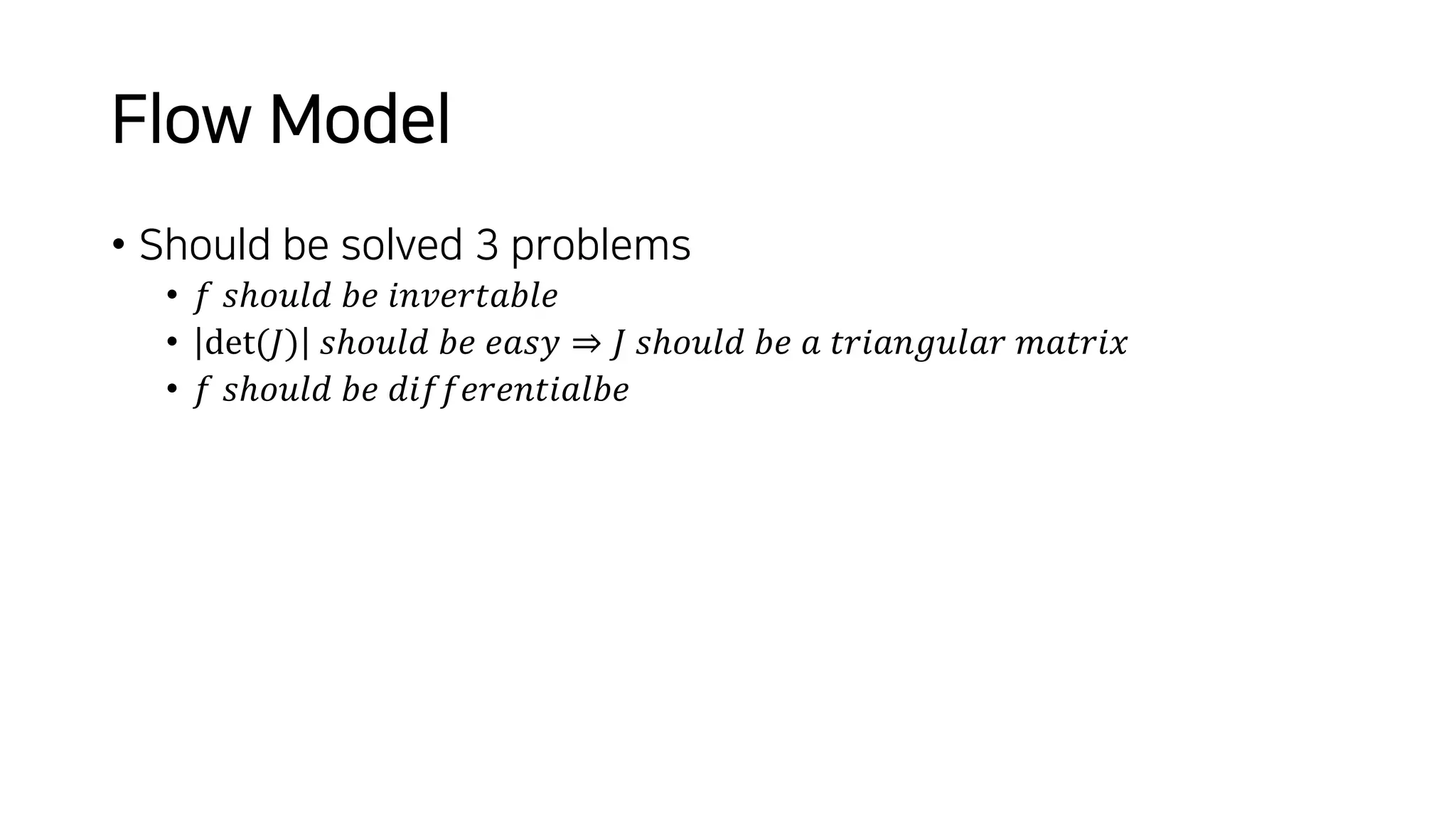
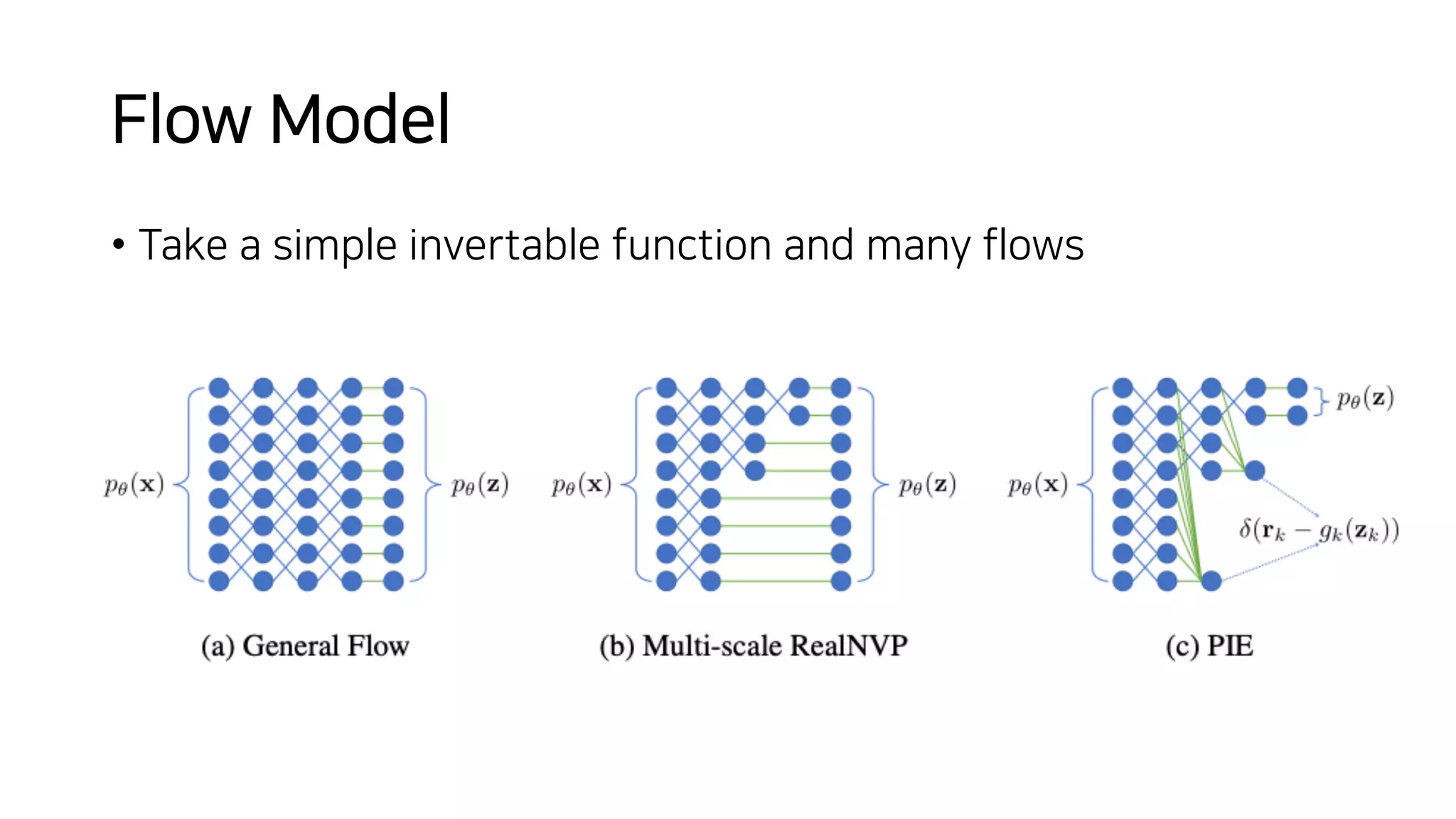
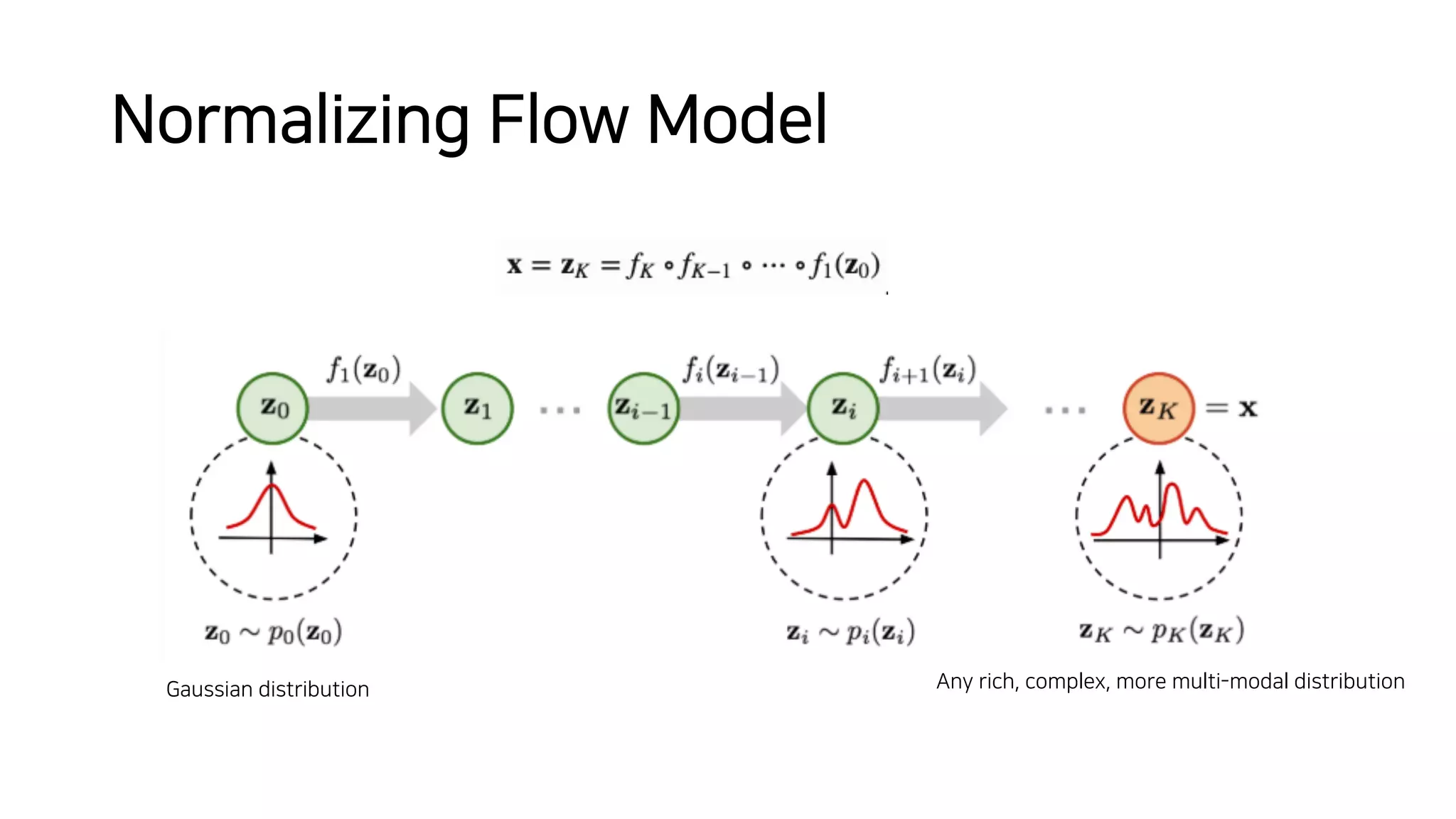
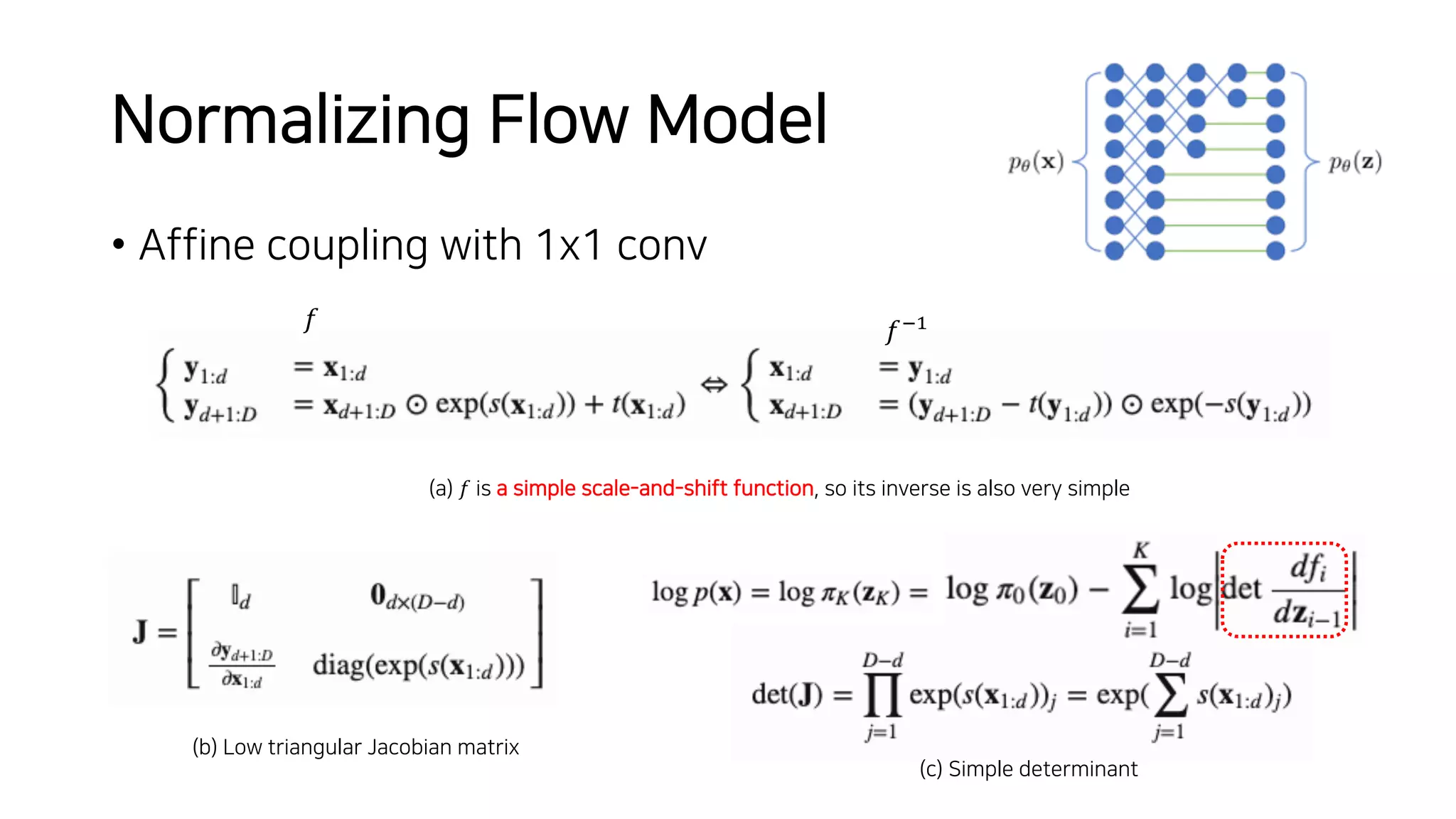
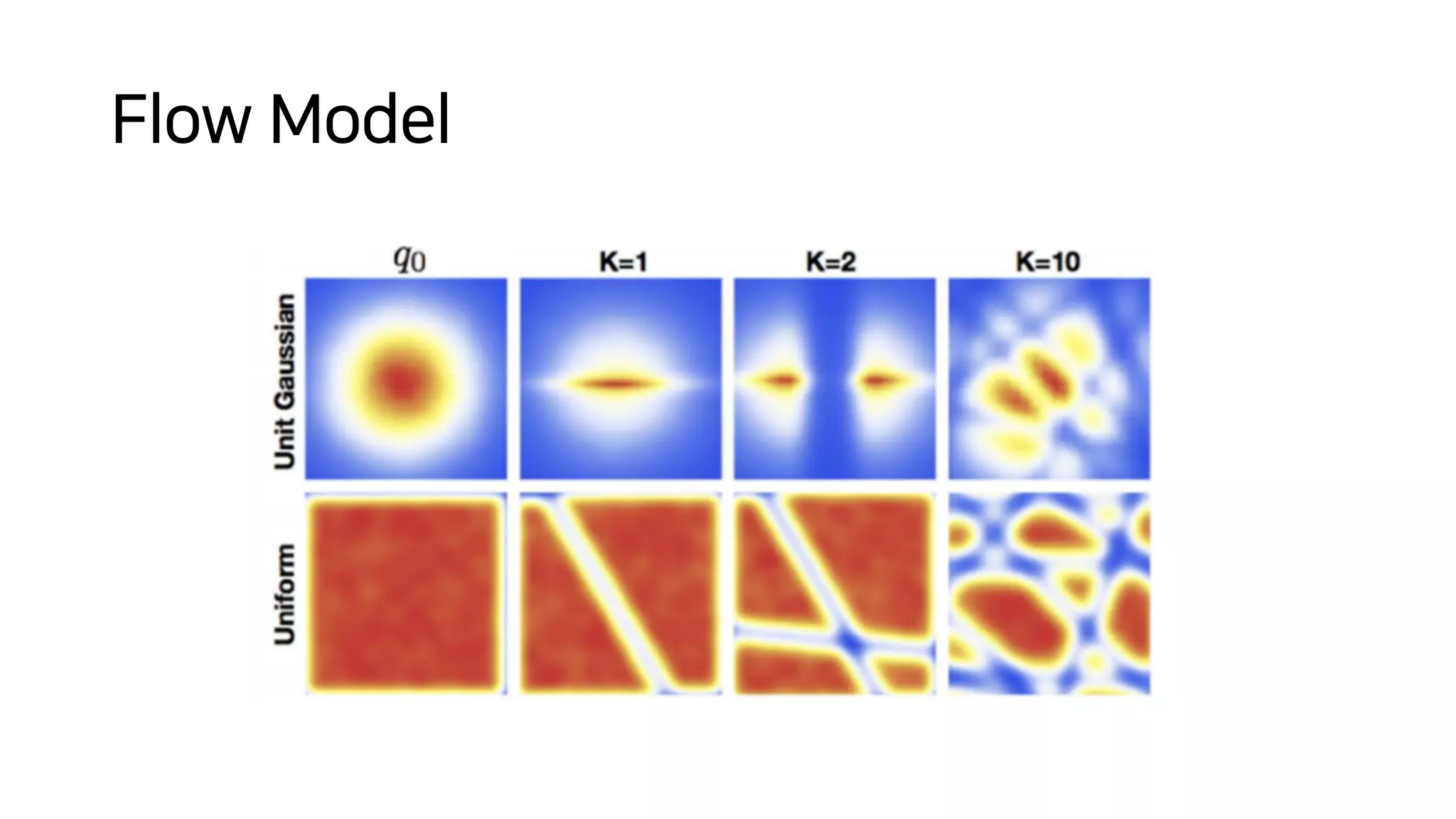
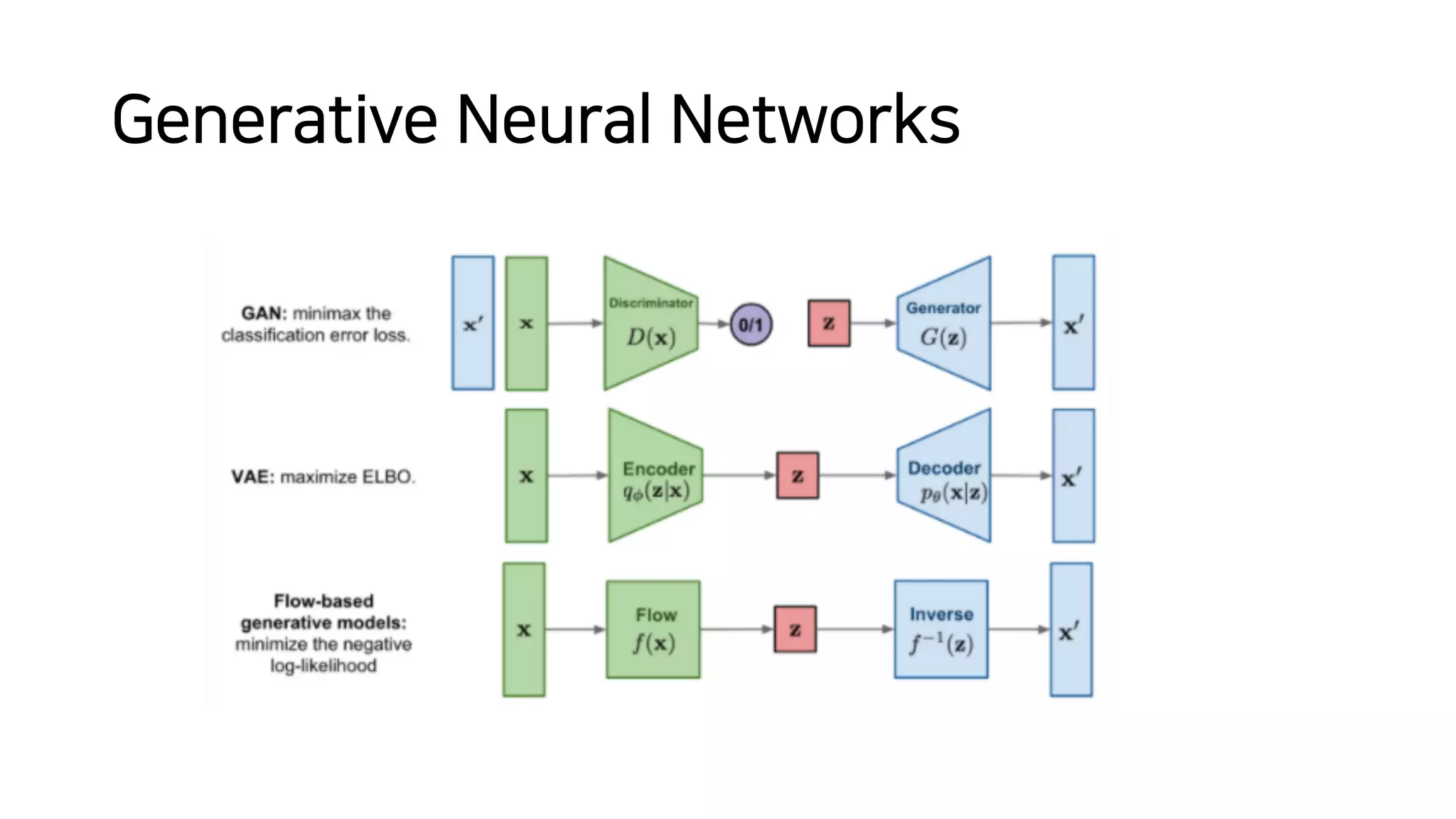
Normalizing flows can be used to transform a simple distribution like a Gaussian into a more complex target distribution through an invertible transformation. The transformation must be invertible to allow both generation and inference. It should also have an easily computable Jacobian determinant. Normalizing flow models achieve this by applying a series of simple invertible transformations with triangular Jacobians, such as affine coupling layers with 1x1 convolutions. This allows efficient and exact likelihood computation during both training and sampling from the modeled distribution.