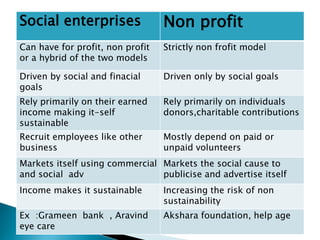
The document discusses non-profit organizations (NPOs), the third sector, and social enterprises. It defines NPOs as organizations that do not generate profits and exist to promote public welfare rather than revenue. NPOs are often tax-exempt and can receive tax-deductible donations. The third sector refers to non-governmental, non-profit organizations that undertake social activities. Social enterprises have both social and financial goals, relying primarily on earned income to be sustainable, unlike NPOs which rely mainly on donations. The key difference between social enterprises and NPOs is that social enterprises can generate profits to reinvest in their social mission.






![ The voluntary sector or community
sector (also non-profit sector or "not-for-
profit" sector) is the sphere of social activity
undertaken by organizations that are not for
profit[1] and non-governmental. This sector is
also called the third sector, in reference to
the public sectorand the private sector. Civic
sector is another term for the sector,
emphasizing the sector's relationship to civil
society.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nonprofitorganization-131010120114-phpapp01/85/Nonprofit-organization-7-320.jpg)
![ The Cabinet Office defined the ‘Third Sector’
as “the place between State and (the) private
sector”.[1]
In India this sector is commonly called the
"joint sector", and includes the industries run
in partnership by the state and Private Sector.
In a wider sense the initial investment is
made by the state and later the handling is
done by the private sector.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nonprofitorganization-131010120114-phpapp01/85/Nonprofit-organization-8-320.jpg)