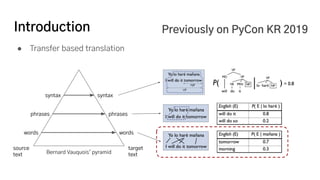
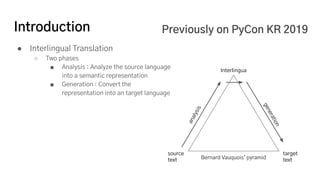
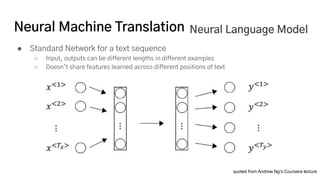
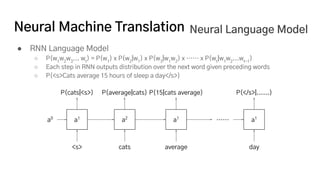
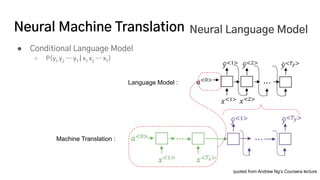
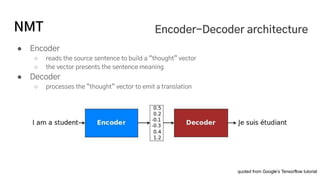
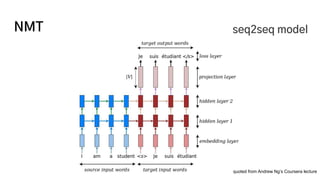
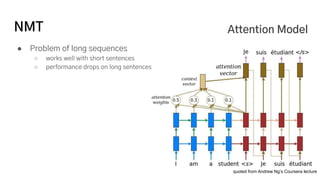
The document discusses the development of a machine learning-based automatic translator, focusing on neural machine translation (NMT) and its improvements over traditional methods. It outlines the architecture of NMT, including encoder-decoder models and attention mechanisms, as well as the challenges such as handling long sequences and local translation problems. The author also provides insights into dynamic programming applications in language processing, such as word segmentation and optimal sub-structure solutions.