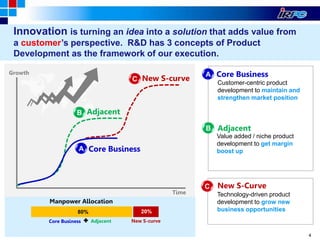
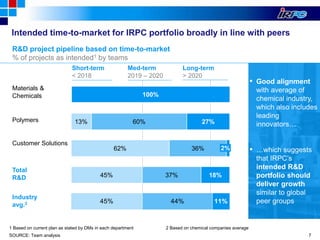
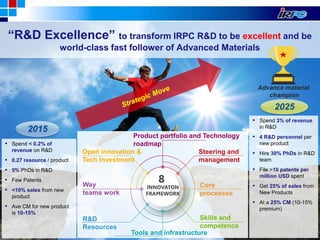
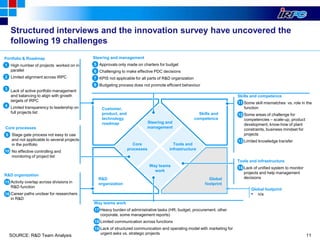
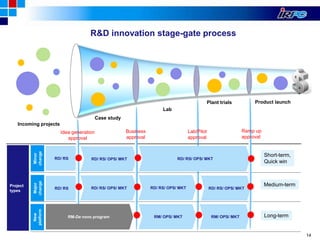
The document outlines IRPC's strategic plan for enhancing its research and development (R&D) capabilities, aiming for excellence and competitiveness through innovation while significantly increasing R&D investment. Key goals include developing a strong pipeline for new products, establishing an effective R&D framework, and fostering a culture of innovation to improve performance and market positioning. The plan emphasizes customer-centric product development and integration across functions to align with future growth targets.