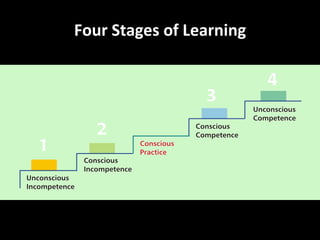
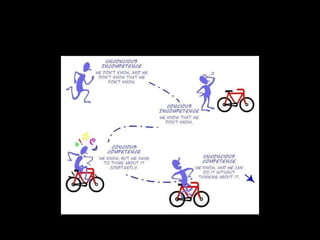
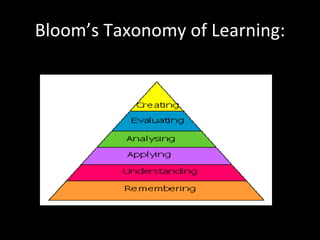
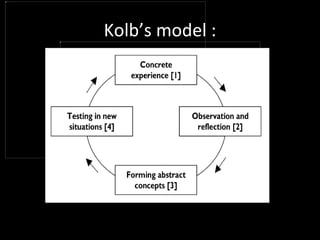
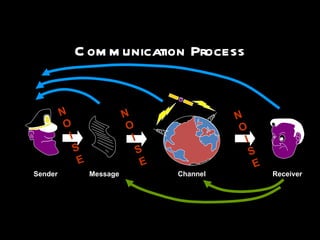
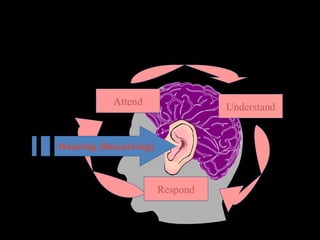
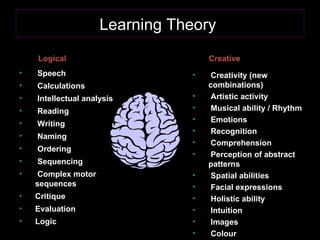
The document provides an overview of a training workshop on training skills and techniques. It discusses several models of learning including Bloom's Taxonomy, Kolb's Learning Model, and Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences. It also covers adult learning principles, a trainer's key behavioral competencies, and tips for facilitating discussion and ensuring participants learn effectively. The goal is to help trainers understand how people learn and how to structure training sessions using engaging methodologies.