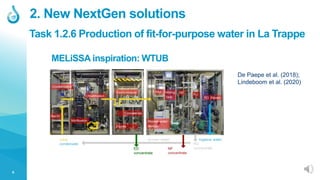
The document describes a biological wastewater treatment system called the Koningshoeven BioMakery located in La Trappe, Netherlands. The system uses a Metabolic Network Reactor (MNR) technology with 2-3,000 species of organisms to treat wastewater from a nearby beverage factory. The objectives are to combine the MNR with membranes to recover nutrients and water for reuse, and to produce fertilizer from recovered nutrients. Testing shows the MNR is able to reduce key water quality parameters but is sensitive to fluctuations in influent. Lessons learned include the need for closer interaction with the factory and redundant treatment to handle variability.