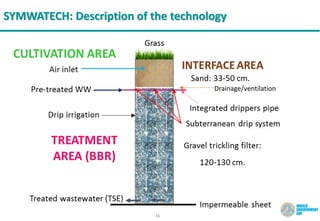
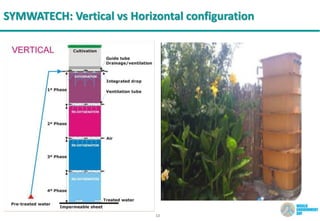
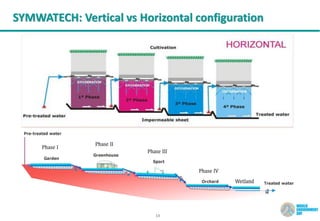
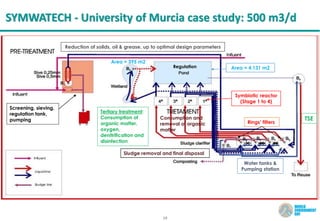
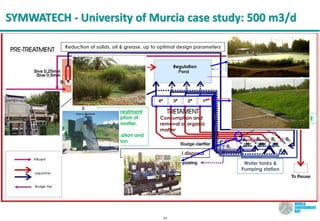
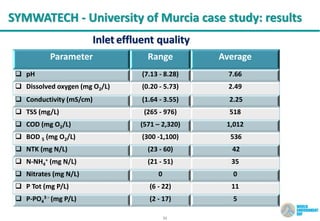
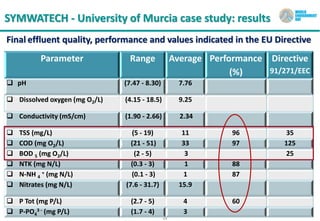
The document discusses symbiotic wastewater treatment technology as an innovative approach for water and energy conservation in Saudi Arabia. It provides background on the country's wastewater situation, goals for treatment and reuse, and key challenges. The symbiotic technology combines wastewater treatment and irrigation techniques in one system using biological reactors and drip irrigation. Case studies demonstrate high treatment efficiency up to 99.999% with significant reductions in costs, energy usage, and environmental impacts compared to conventional systems. The technology is presented as a scalable and flexible solution for wastewater management for various applications.



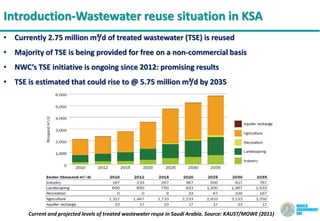

![7
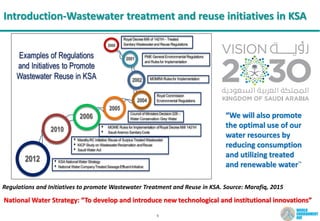
Introduction-Wastewater treatment and reuse potential in KSA
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
STP Capacity Treated Sewage TSE Reuse
Volume[1000m3/day]
Wastewater Treatment and Reuse Potential in KSA. Source: Ministry of Water and Electricity, 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a1a7377a-6e10-4e35-969b-690edbc40b5a-160606193149/85/Presentation-Symwatech-WED-05-06-16-final-7-320.jpg)