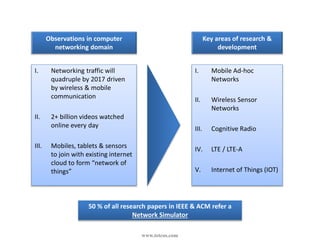
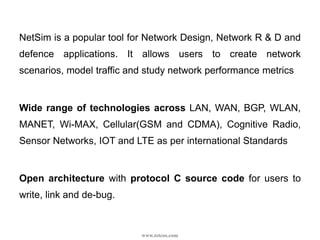
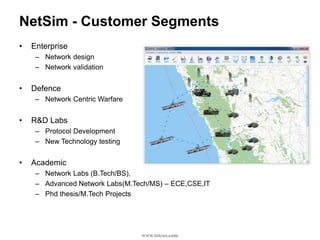
This document provides an overview of a webinar on using the NetSim network simulation platform to model Internet of Things (IoT) scenarios. The webinar covers why network simulation is useful, an introduction to NetSim and its capabilities, key IoT technologies like 802.15.4 and 6LoWPAN, designing an IoT scenario in NetSim, analyzing simulation metrics, editing protocol code, and research areas in IoT. It also includes information on contacting the company for technical support or commercial inquiries.