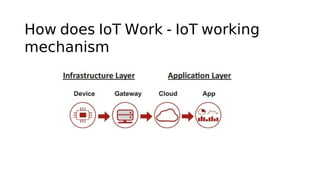
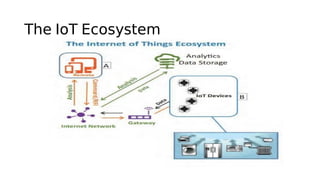
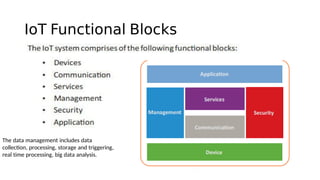
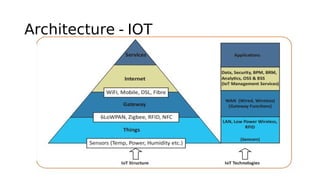
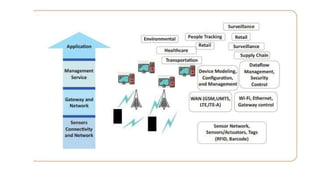
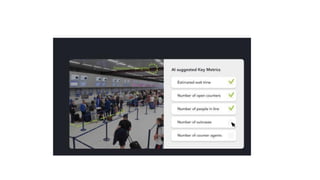
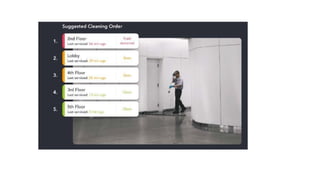
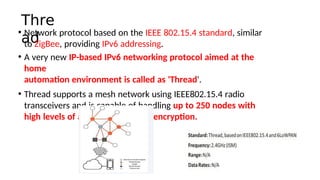
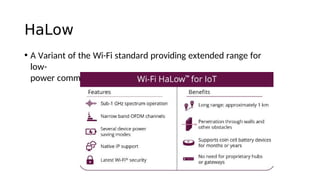
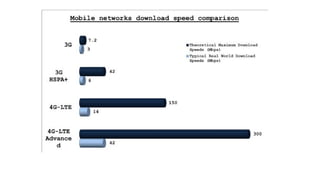
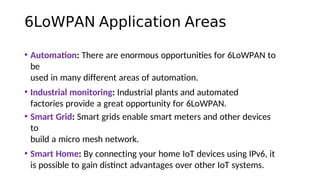
The document outlines the working mechanism of the Internet of Things (IoT), detailing the roles of devices, gateways, cloud infrastructure, and applications in collecting and processing data. It discusses various technologies and standards, such as Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Wi-Fi, that facilitate communication between IoT devices. Additionally, it highlights the importance of IP addresses and the scalability of IoT applications through machine learning and data analysis.