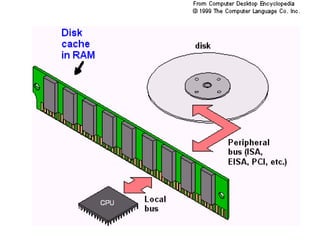
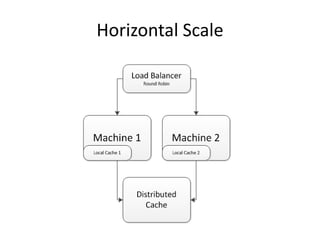
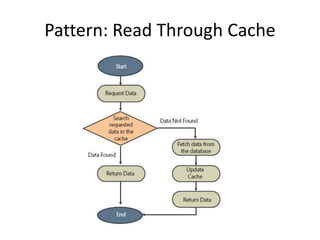
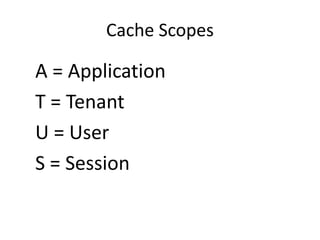
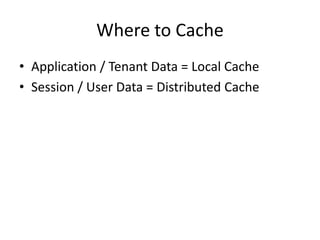
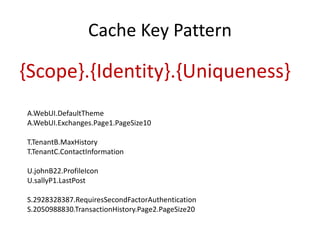
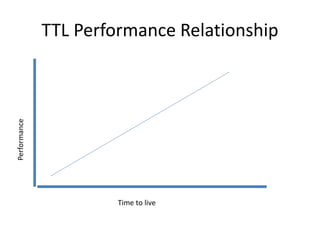
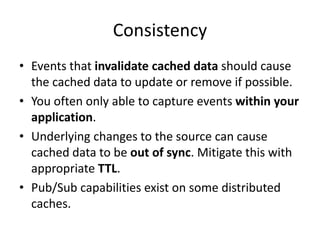
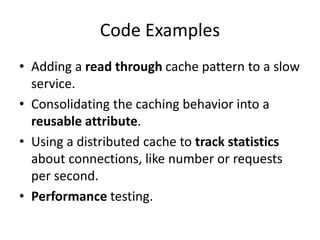
Distributed caching improves performance by storing data in multiple locations for faster retrieval. It works by storing copies of data on multiple machines to improve scalability and availability. There are different scopes for caching like application, tenant, user, and session data. The cache key identifies the data and includes the scope and uniqueness. The time to live determines how long cached data remains valid before being refreshed, with lower times improving consistency at the cost of performance. Code examples demonstrate caching patterns for services and tracking statistics across distributed caches.