This document discusses Nepal's Contribution Based Social Security Fund (CBSSF). It provides details on:
1) The laws and regulations governing CBSSF. Formal sector employees, informal sector workers, and self-employed individuals can register voluntarily or mandatorily.
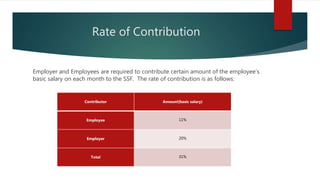
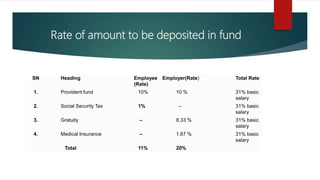
2) The schemes covered by CBSSF including medical treatment, accident and disability protection, dependent family protection, and old age protection. Contributions are allocated to each scheme.
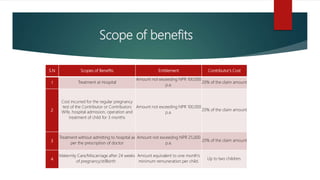
3) Benefits provided under each scheme such as medical cost coverage, accident compensation, pensions for dependents and retirees. The document outlines contribution rates, eligibility periods and excluded treatments.