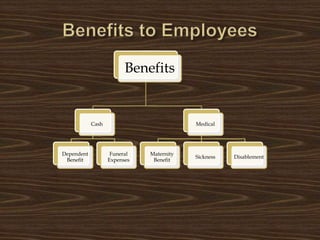
The document discusses the Payment of Gratuity Act which provides for gratuity payments to employees after 5 years of continuous service. Key details include:
- Gratuity is paid at the rate of 15 days wages for each completed year of service, up to a maximum of Rs. 3.5 lakhs.
- It is paid upon superannuation, retirement, resignation or death of the employee.
- In case of death, gratuity is paid to the employee's nominee or heirs.
- Gratuity can be partially or fully forfeited if an employee is terminated due to misconduct.