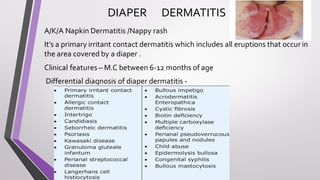
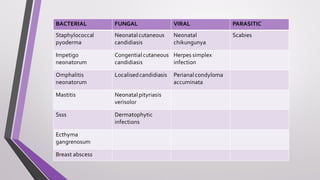
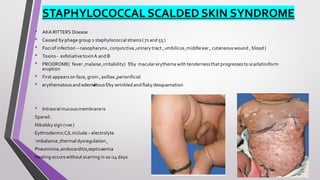
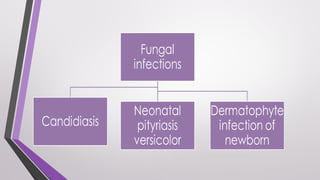
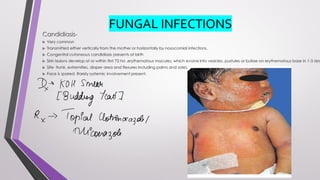
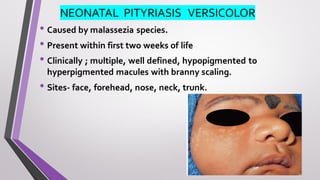
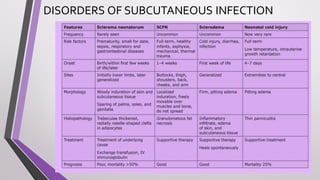
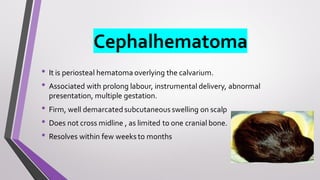
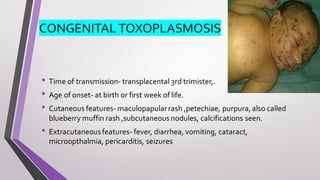
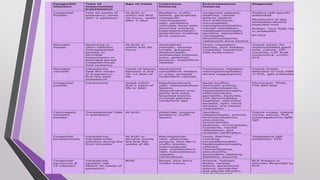
This document provides an overview of various neonatal skin diseases, including diaper dermatitis, bacterial, fungal, viral and parasitic infections, congenital infections, and iatrogenic injuries. It discusses conditions such as staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, impetigo neonatorum, congenital rubella, neonatal herpes, and complications of phototherapy that can present in newborns. The document also provides details on diagnosis and treatment of common neonatal skin diseases.