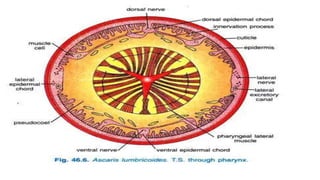
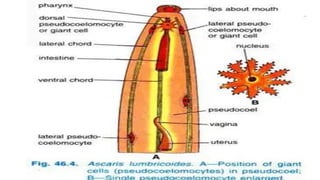
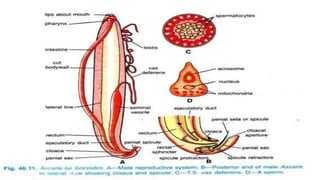
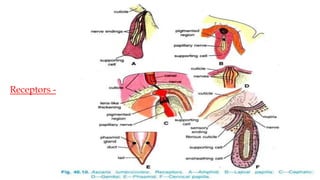
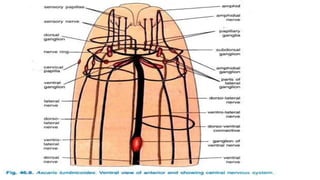
1. The document describes the anatomy and life cycle of the roundworm Ascaris. It details the body systems and structure including the cuticle, digestive system, reproductive system, and excretory system.
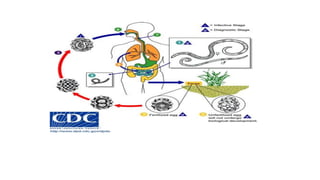
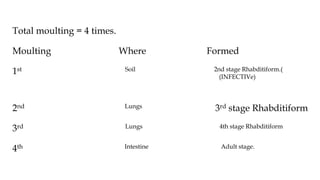
2. The life cycle of Ascaris involves eggs passing in feces, developing in soil, and infecting humans via contaminated food/water. The larvae hatch in the intestine and migrate through the lungs before reentering the stomach and small intestine where they mature into adults.
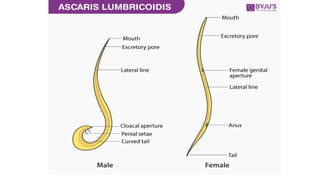
3. Key differences between male and female Ascaris include the male having a curved tail with cloaca while the female has a straight tail with an anus.