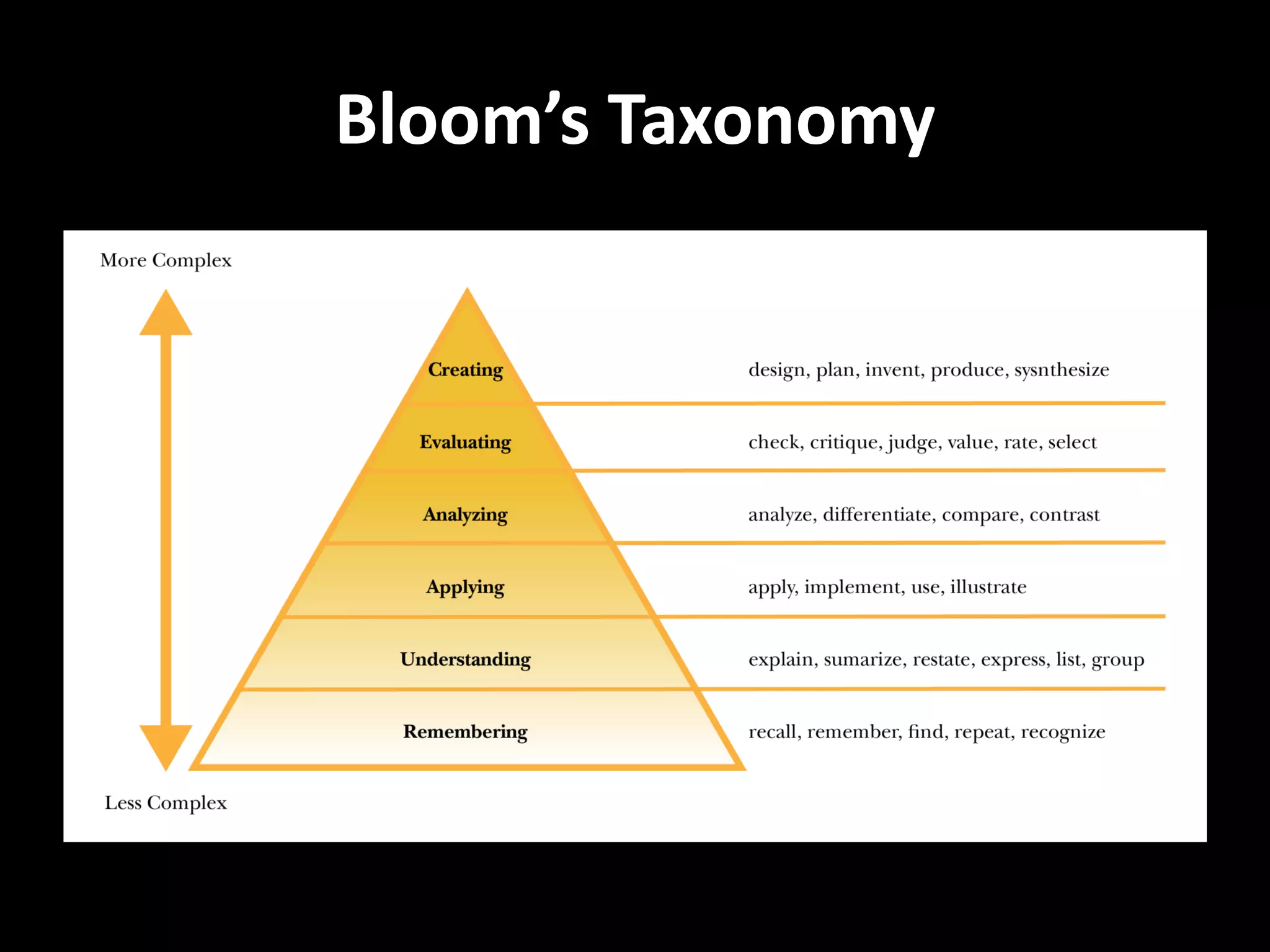
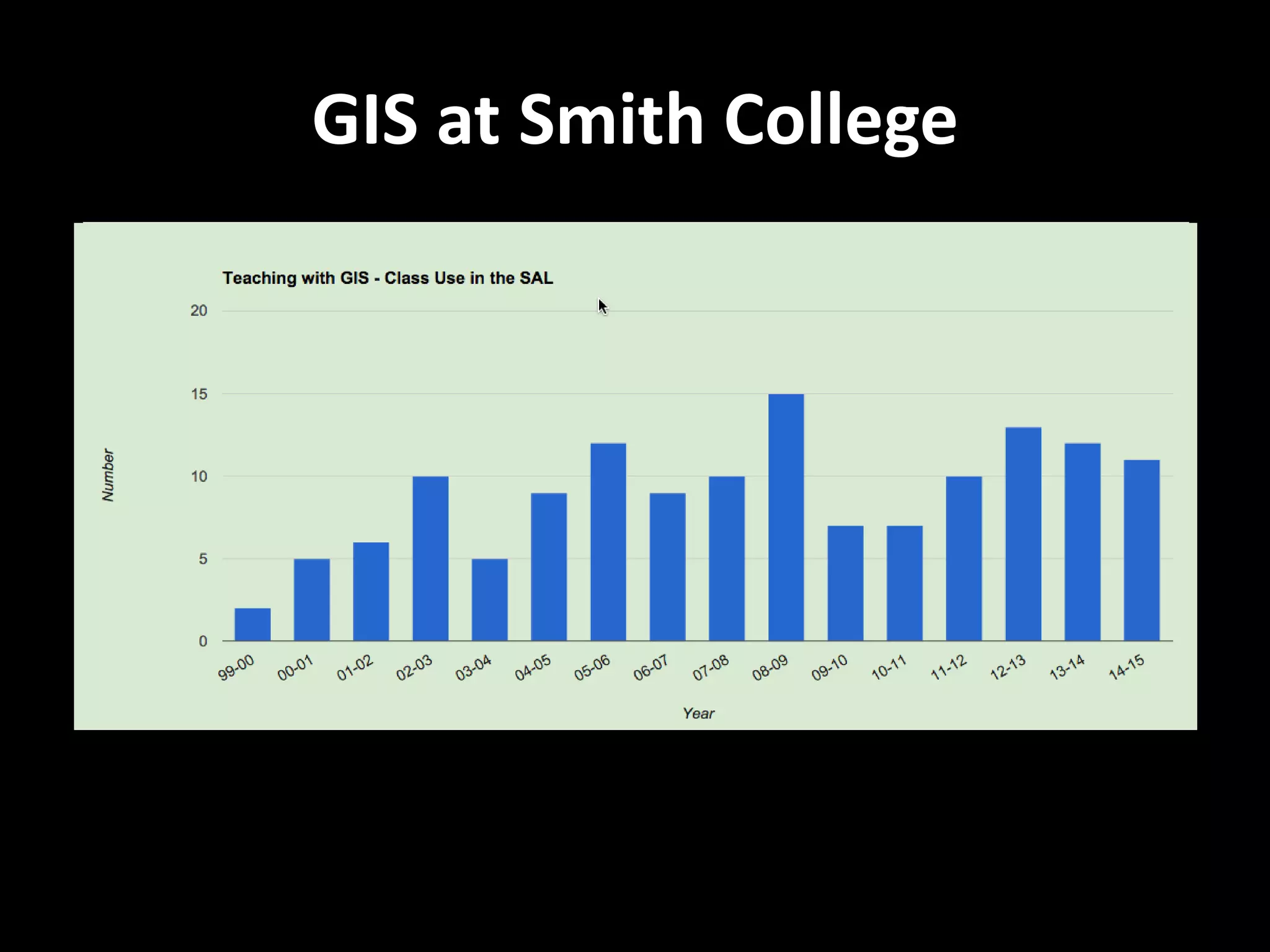
This document discusses GIS education and skills from the perspectives of professionals working in GIS. It summarizes GIS programs at Westfield State University and Smith College, including required courses and electives. The document also presents a survey of GIS professionals about the most important GIS skills and tools used in their daily work. Top skills identified include GIS analysis with spatial data, map creation, attention to detail, communication, and adaptability. The greatest challenge identified is applying coursework knowledge to solve real-world problems with specific workflows and processes.