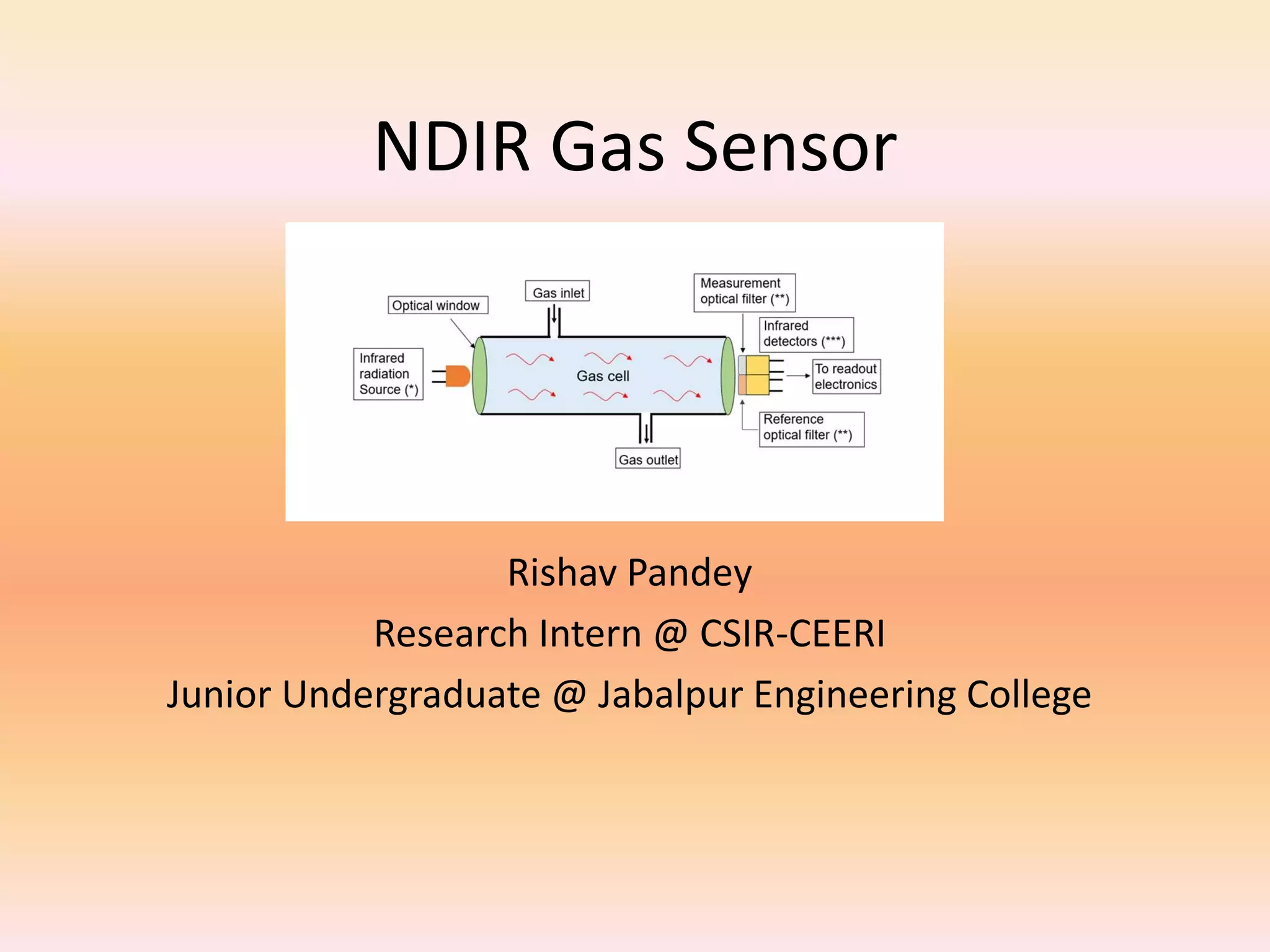
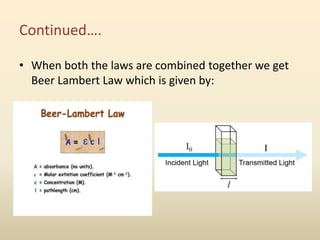
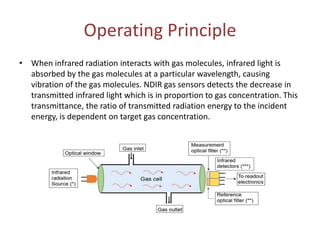
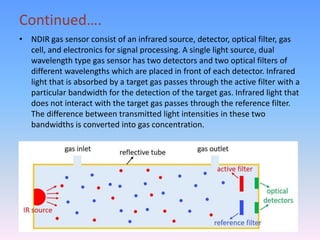
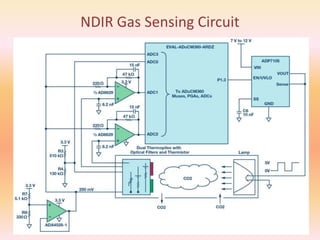
NDIR gas sensors use infrared light to measure carbon dioxide concentration. They work based on the principle that infrared light absorption by gas molecules decreases exponentially with increasing gas concentration (Beer-Lambert law). An NDIR gas sensor consists of an infrared light source, detector, gas cell, and optics. It measures the decrease in transmitted infrared light through the gas cell, which corresponds to the gas concentration present. The sensor electronics then convert the light intensity differences into a carbon dioxide concentration reading. NDIR gas sensors are commonly used to detect carbon dioxide due to their accuracy and reliability.