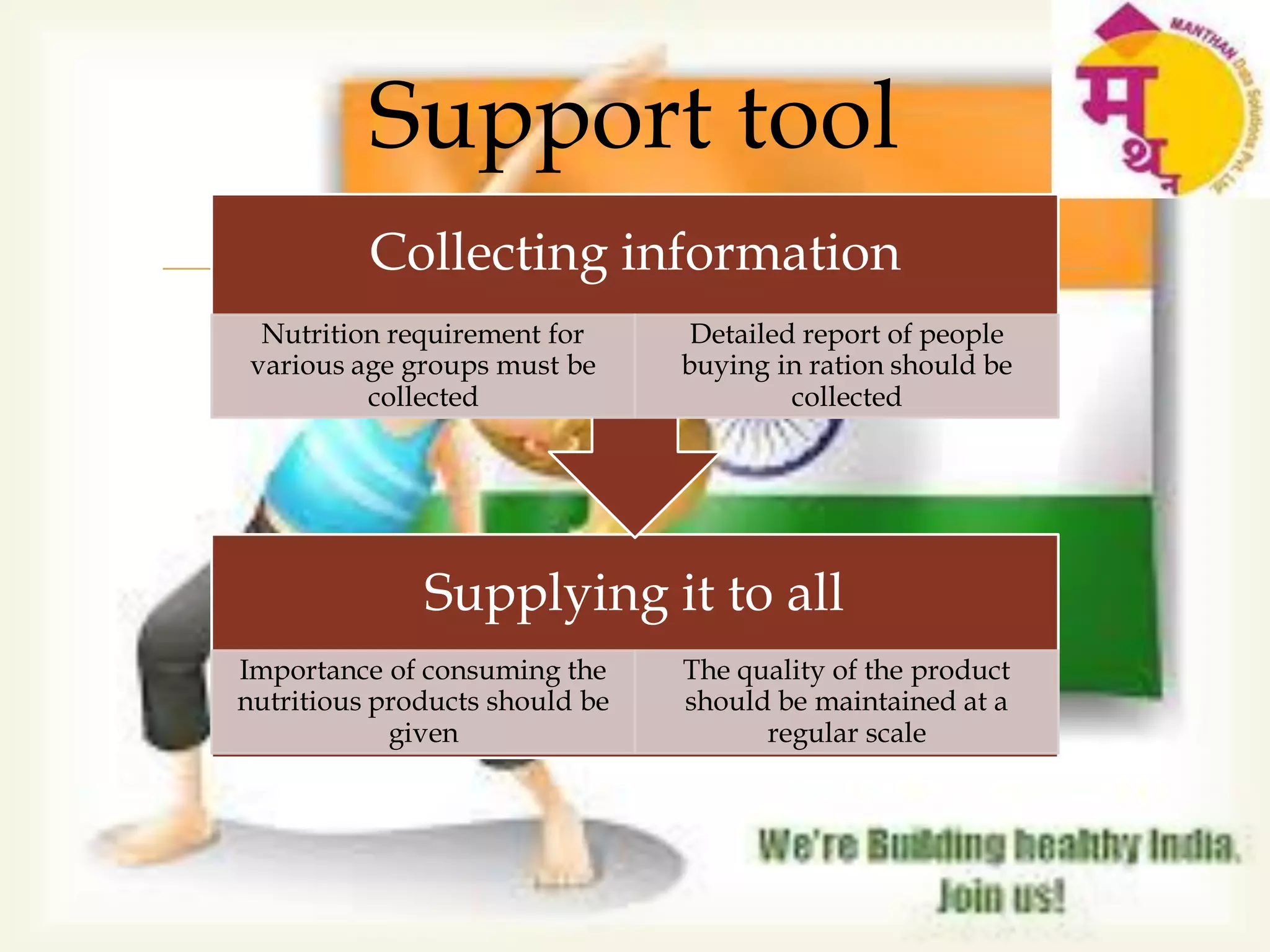
This document discusses malnutrition, its causes, impacts, and potential solutions. It defines malnutrition as an imbalance between nutrient intake and the body's needs. Malnutrition is directly or indirectly responsible for over 50% of child deaths globally. India has high levels of malnutrition, with 44% of children under 5 being underweight. Malnutrition during pregnancy increases risks for the child. Potential solutions discussed include promoting breastfeeding, nutrition education, food fortification, and ensuring access to nutritious foods.