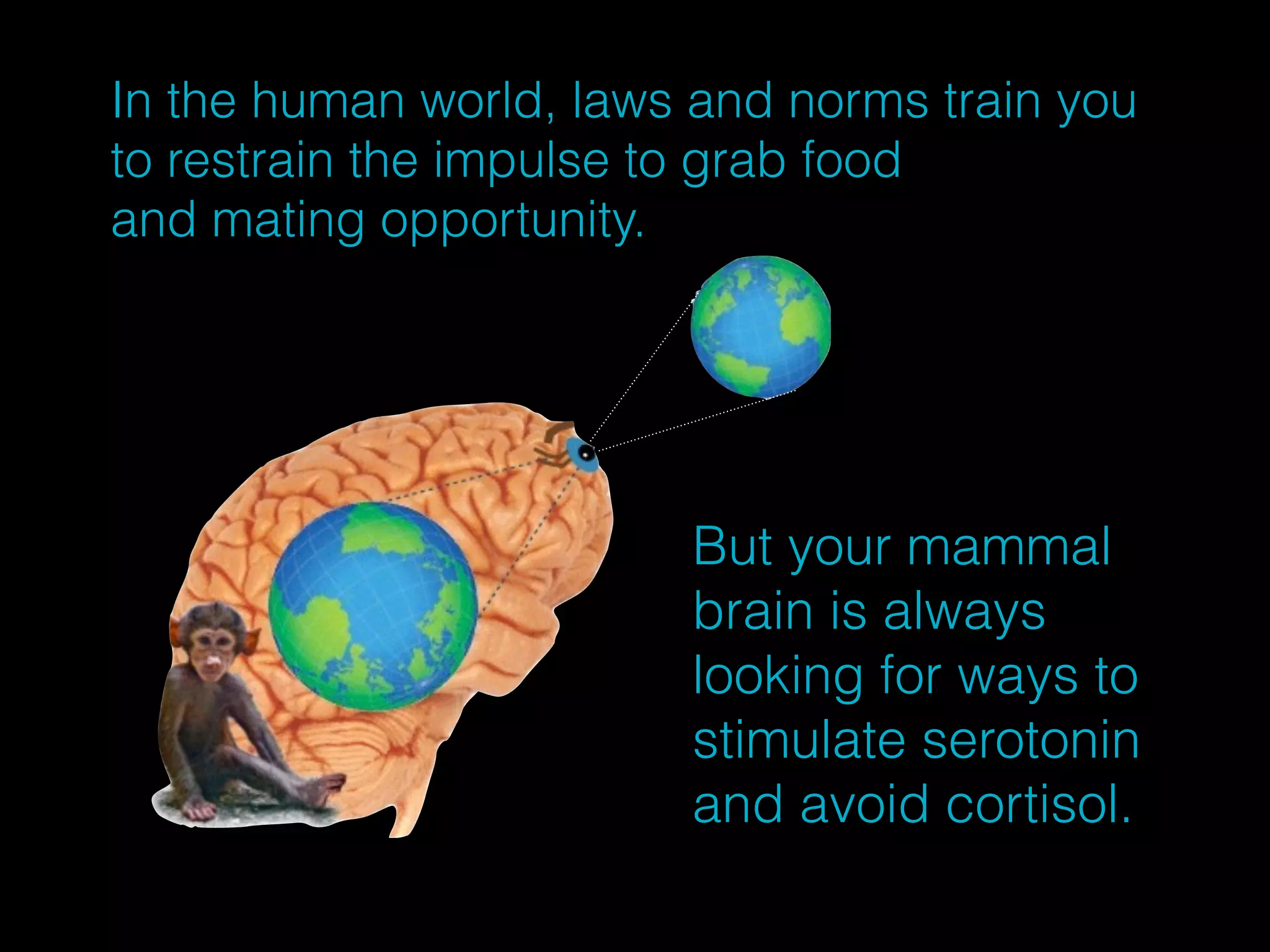
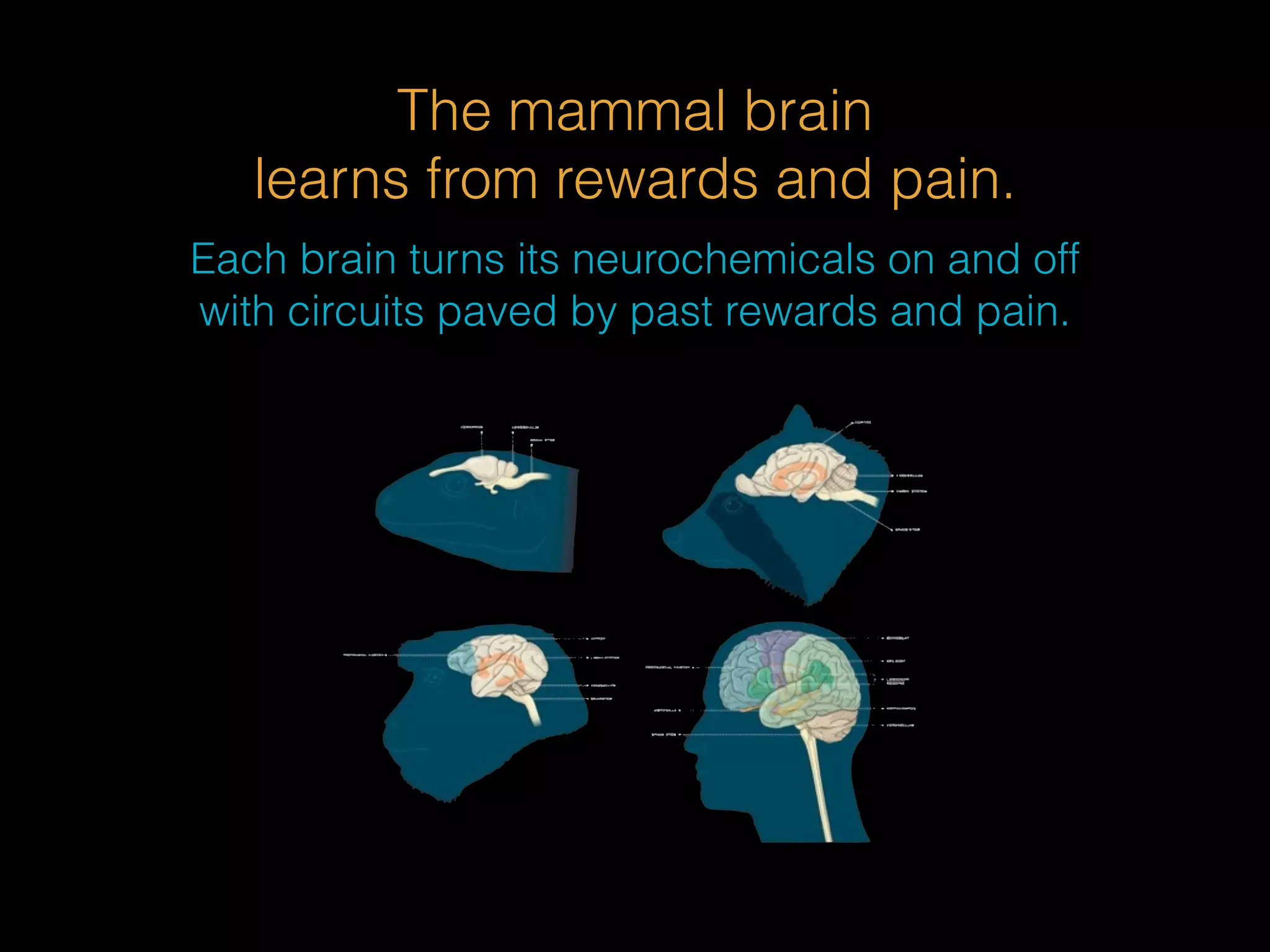
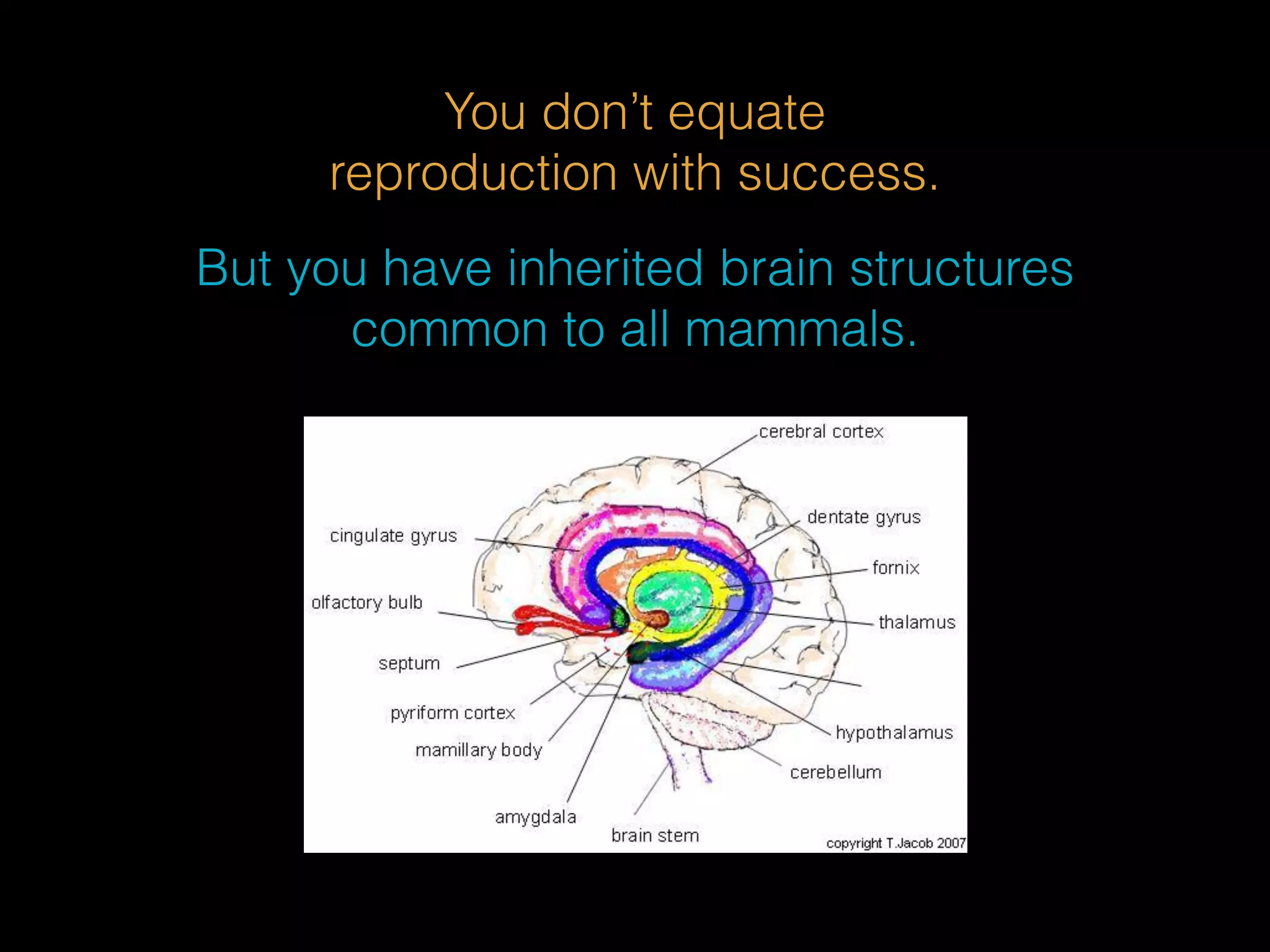
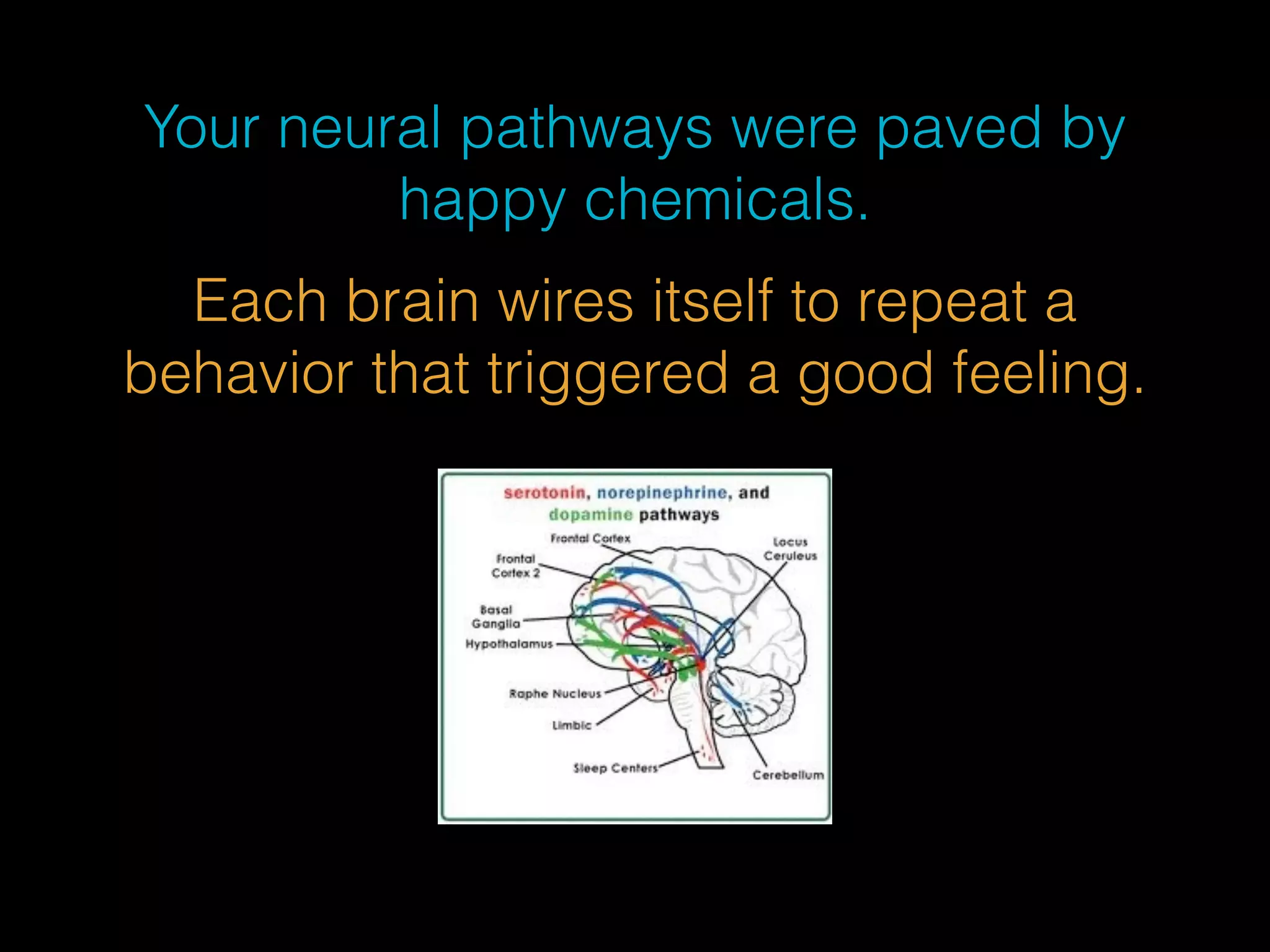
This document discusses the evolutionary psychology behind social hierarchies among mammals, emphasizing how social dominance influences serotonin and cortisol levels. It highlights that social comparison is a fundamental aspect of mammalian behavior linked to survival and reproductive success. The author suggests that managing our inner mammal—understanding the neurochemical triggers of social behavior—can help us navigate social relationships and achieve well-being.