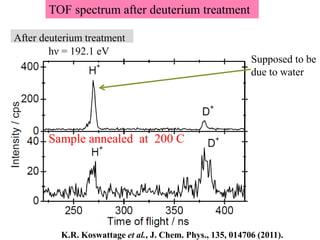
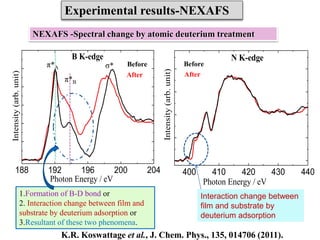
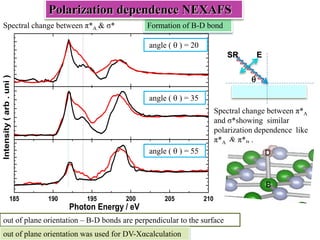
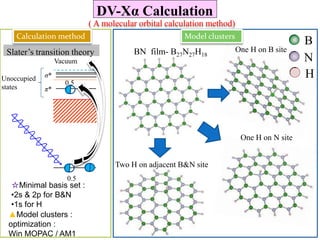
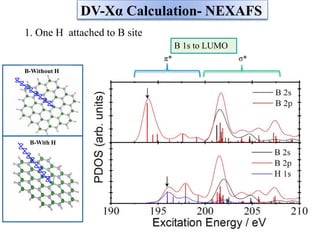
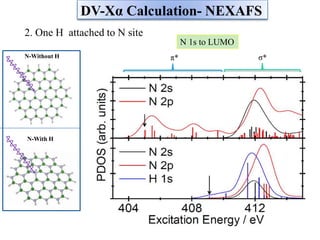
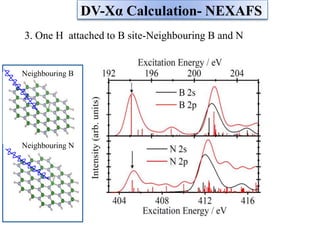
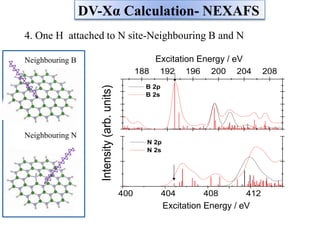
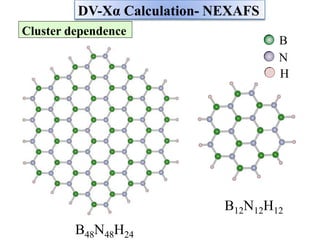
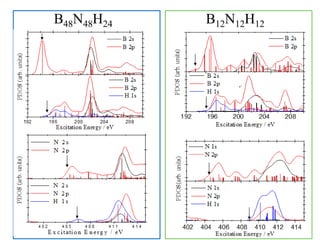
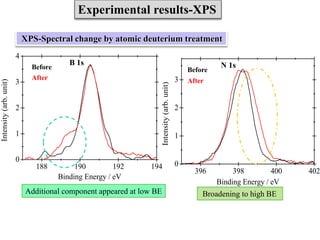
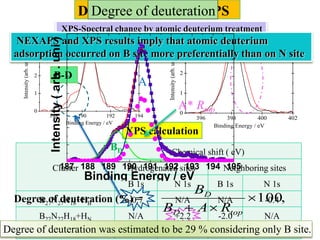
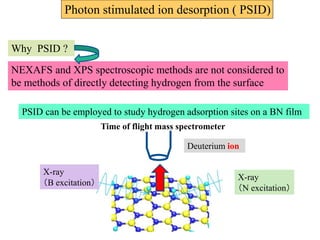
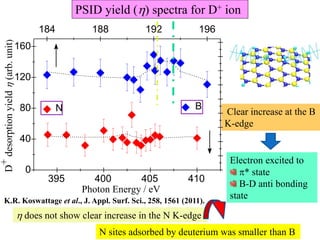
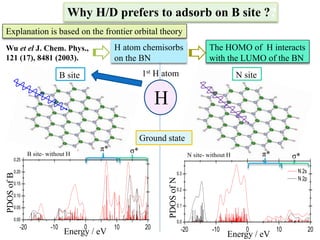
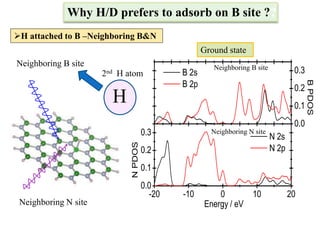
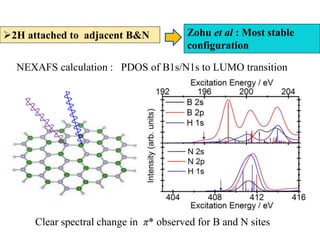
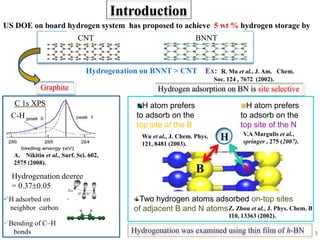
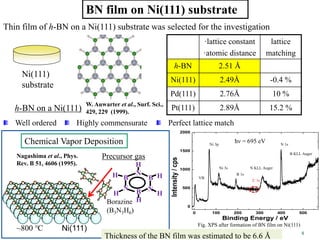
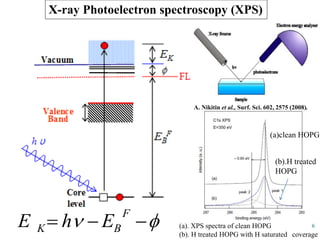
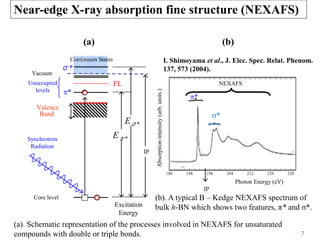
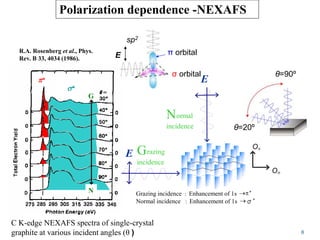
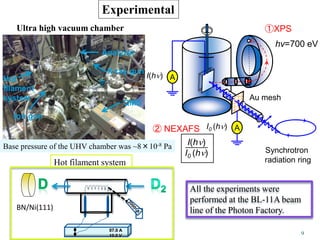
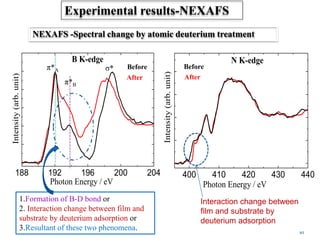
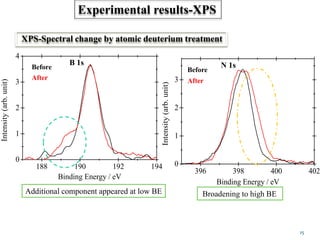
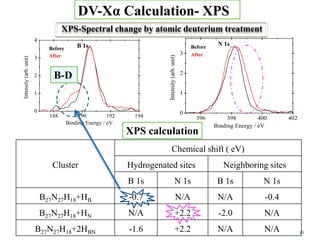
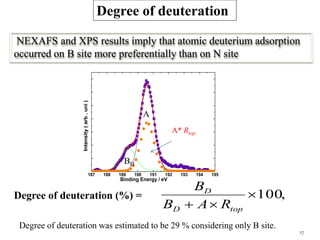
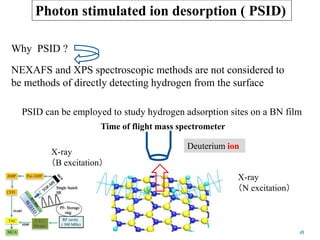
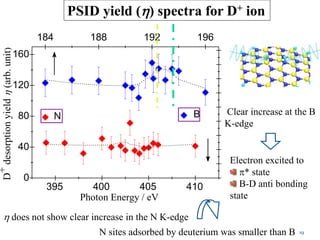
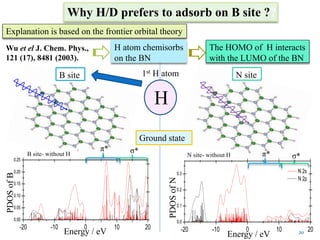
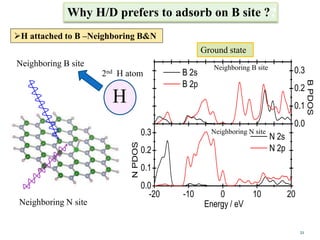
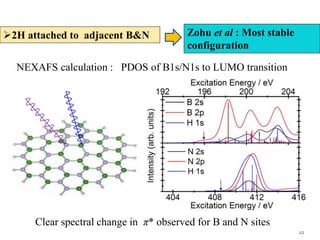
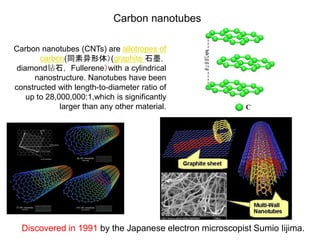
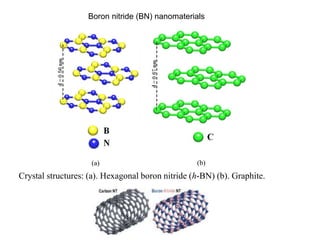
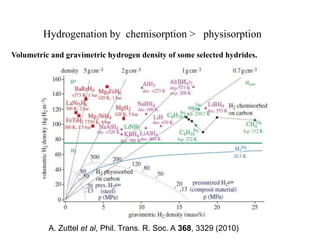
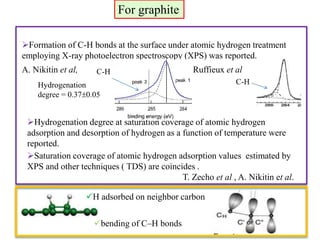
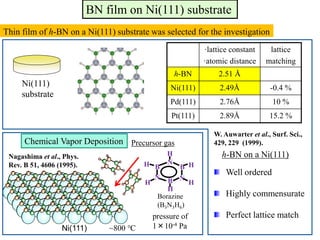
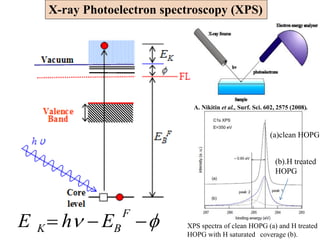
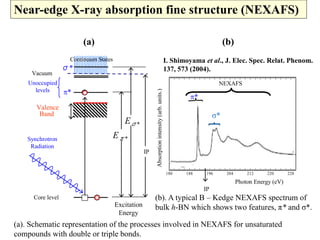
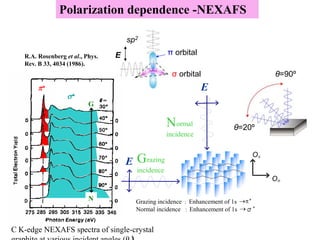
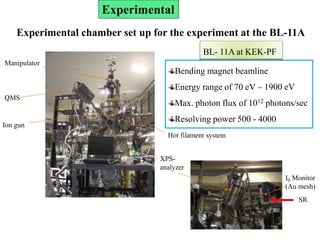
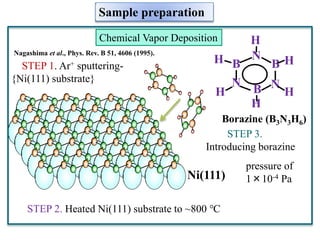
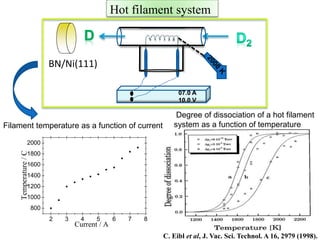
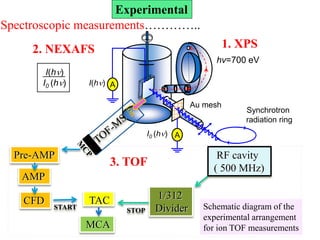
This document discusses a study on selective adsorption of atomic hydrogen on a hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) thin film. Various characterization techniques were used, including time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF), near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and photon stimulated ion desorption (PSID). The results from NEXAFS, XPS and PSID imply that atomic deuterium adsorption occurs preferentially on boron sites over nitrogen sites in the h-BN film. Density functional theory calculations provide further evidence that hydrogen atoms prefer to adsorb on boron sites due to favorable frontier orbital interactions









![Thin film of BN on Ni(111)
Ni (111)
BN thin film
IN1s IB1s
INi3s
t
Composition ratio & Thickness
sN
sB
sB
sN
I
I
hν
hν
N
B
1
1
1s1B
1s1N
)(
)(
][
][
s
s
)/exp(
)/exp(1
)(
)(
BNin3sNi
BNin1sB
Ni
B
Niin3sNi
BNin1sB
3sNi
1sB
3sNi
1sB
s
s
t
t
n
n
hν
hν
I
I
XPS spectrum of as-deposited
BN film on Ni(111)
Equations for estimation of Composition ratio & Thickness
Thickness of the BN film was estimated to be 6.6 Å
[B]/[N] was estimated to be 0.98
C 1s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nanomaterialstodevices-k-161209061754/85/Nano-Materials-to-Devices-K-R-Koswatta-49-320.jpg)