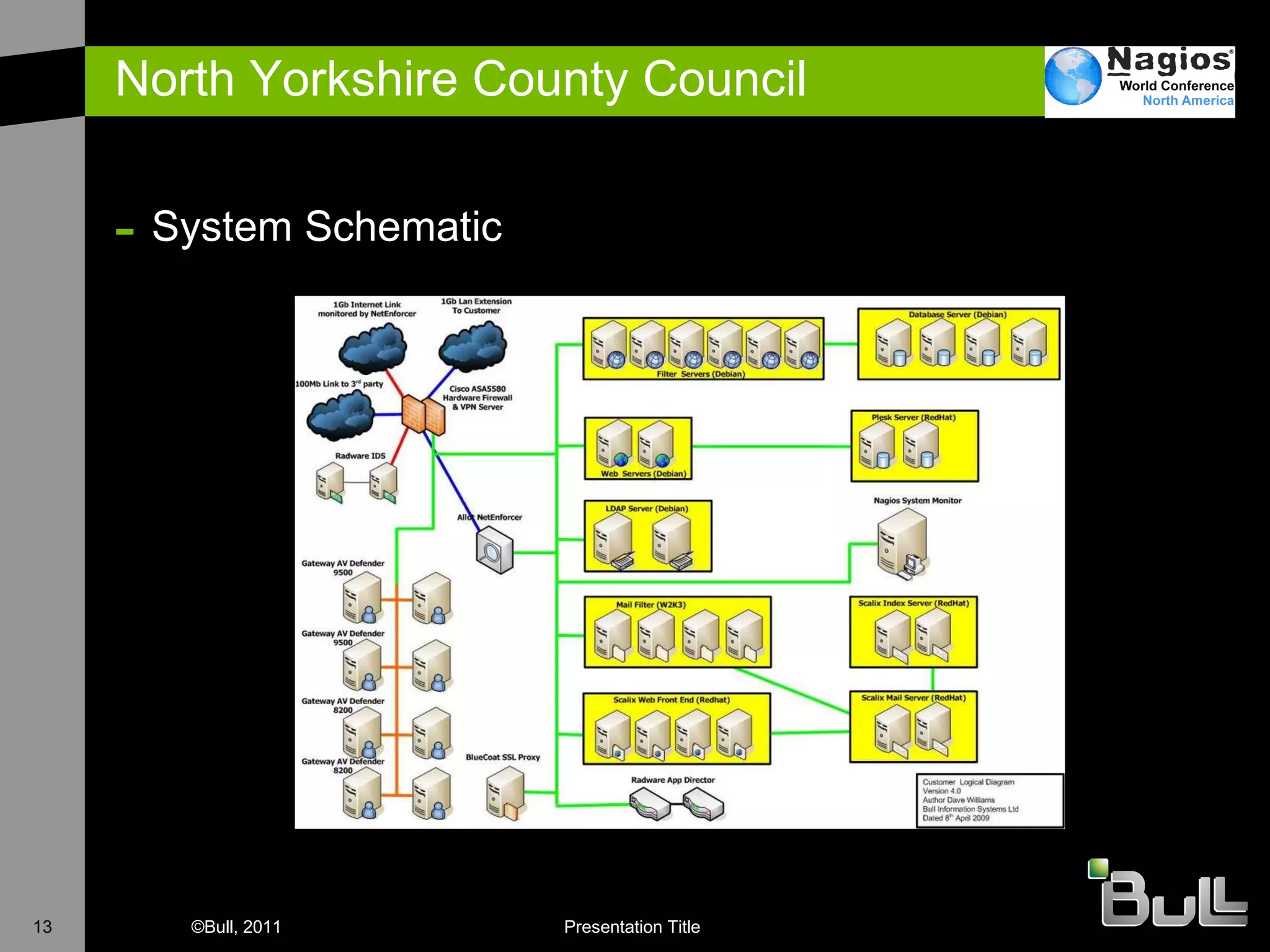
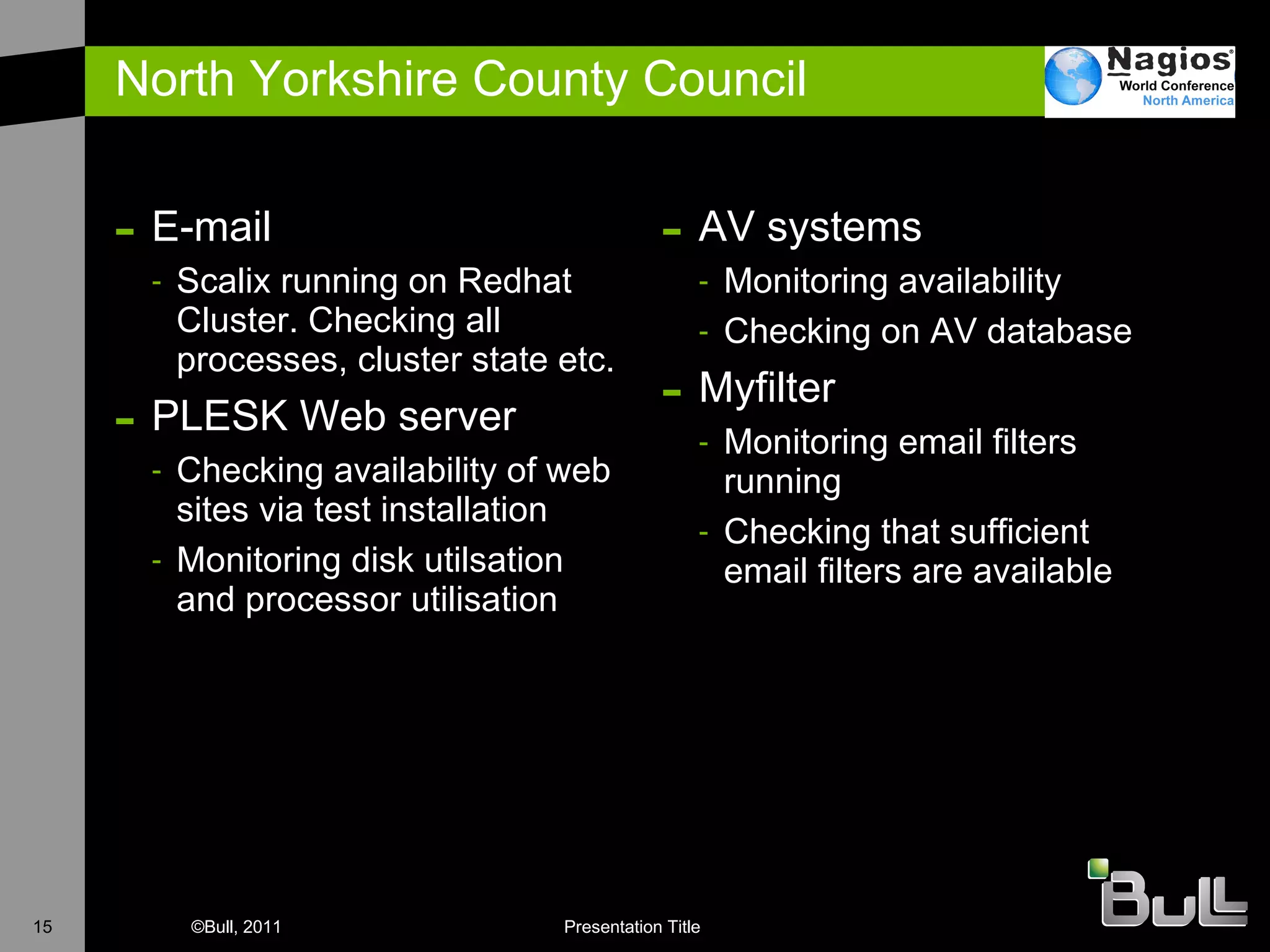
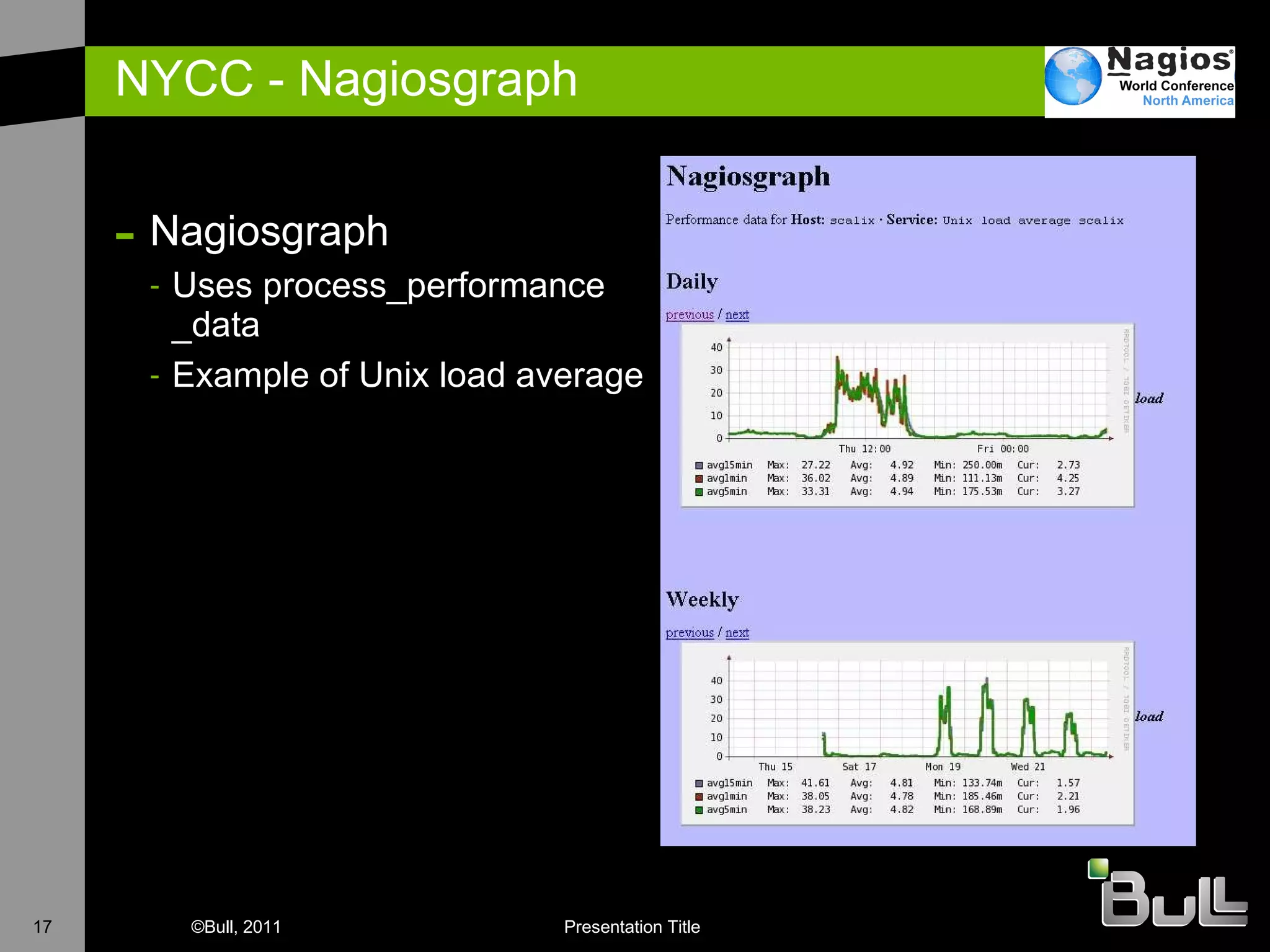
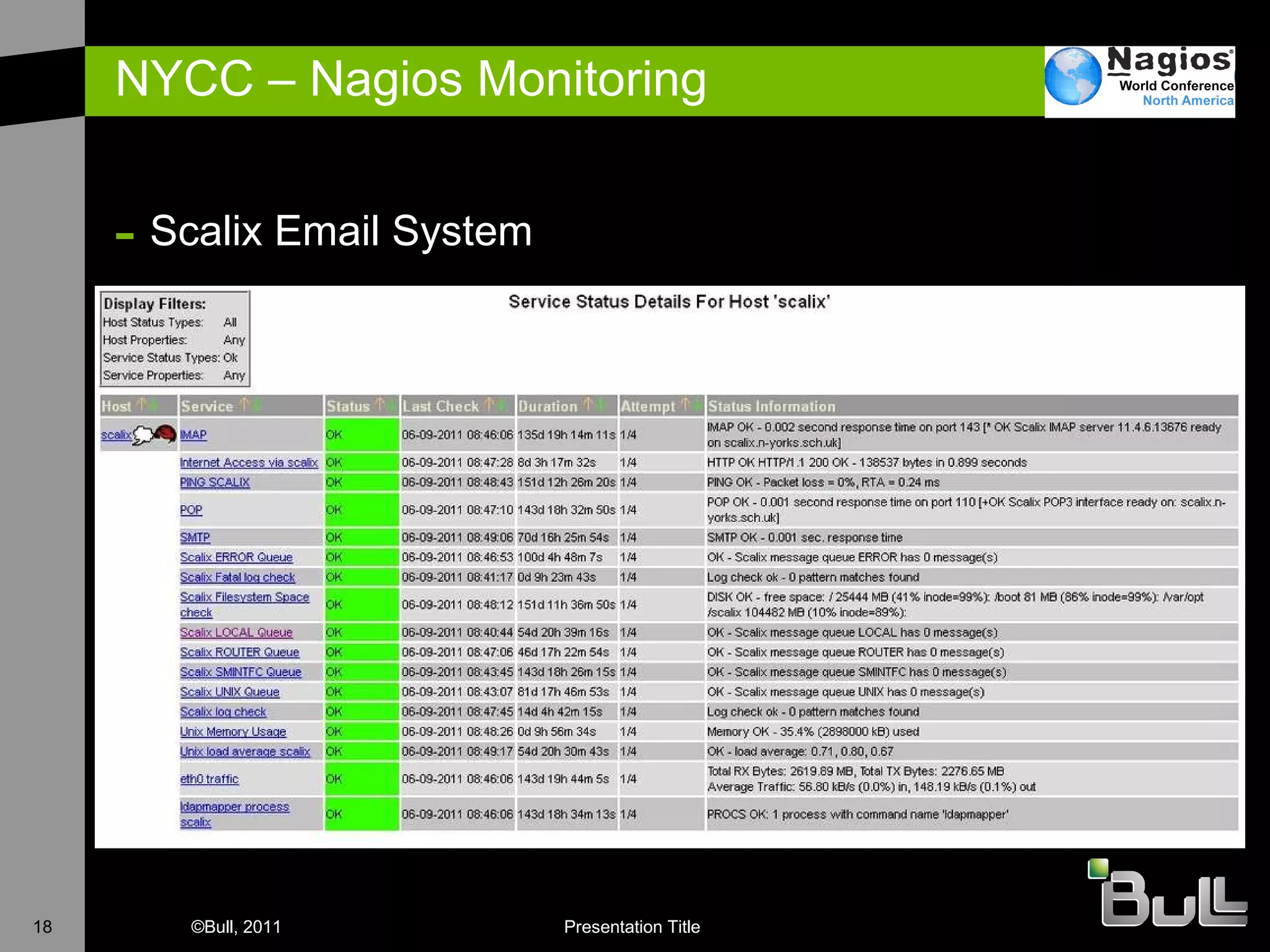
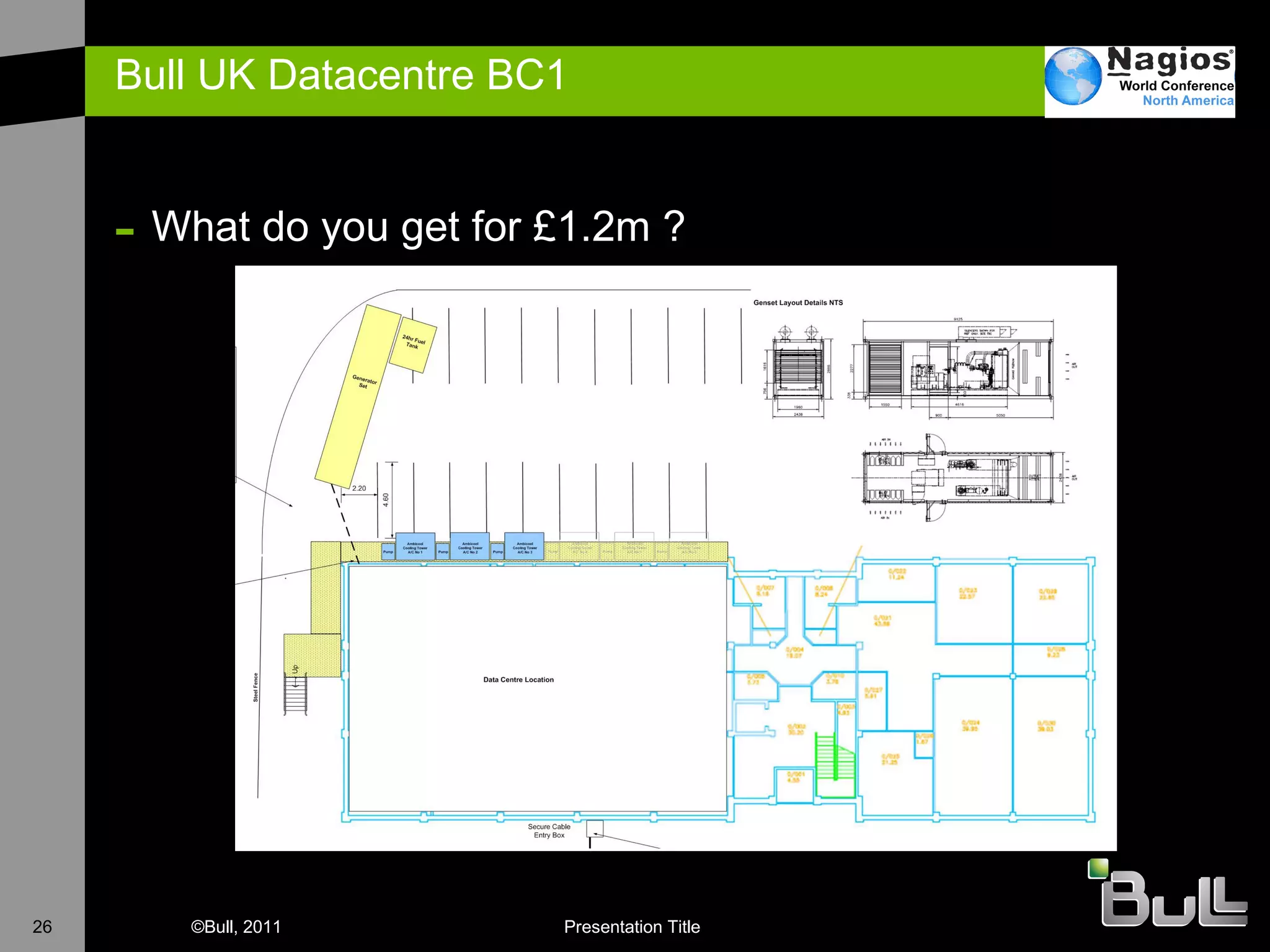
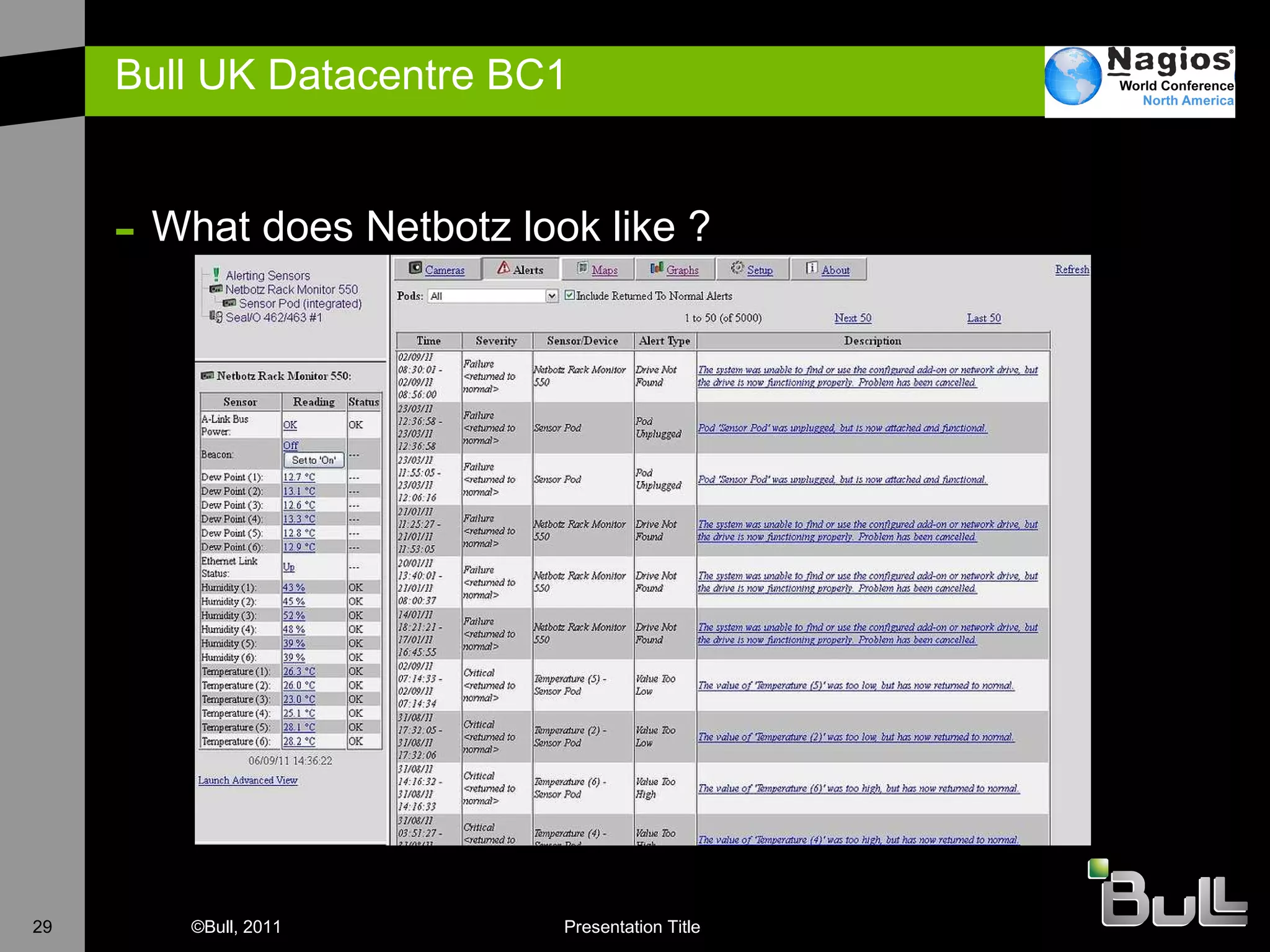
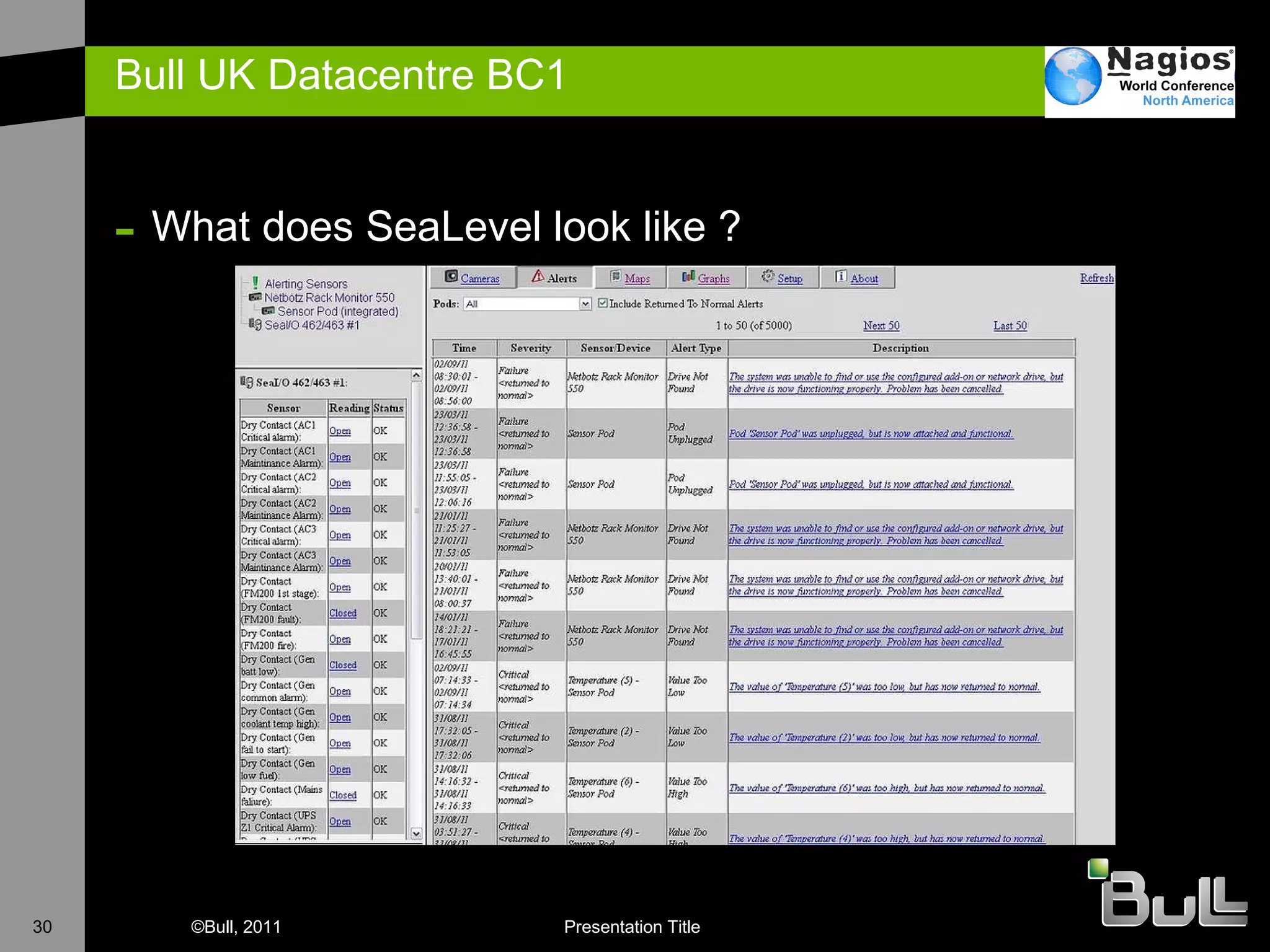
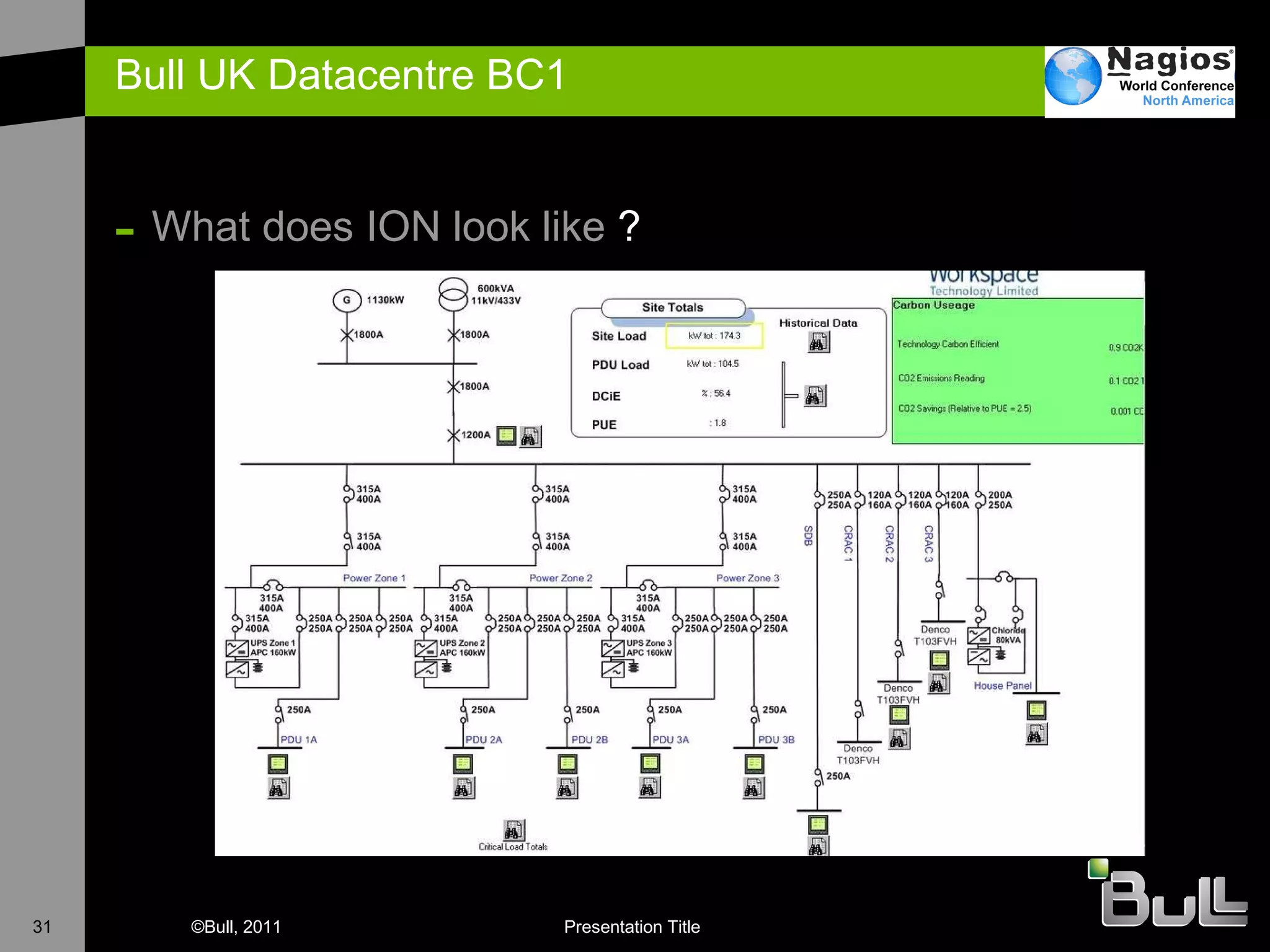
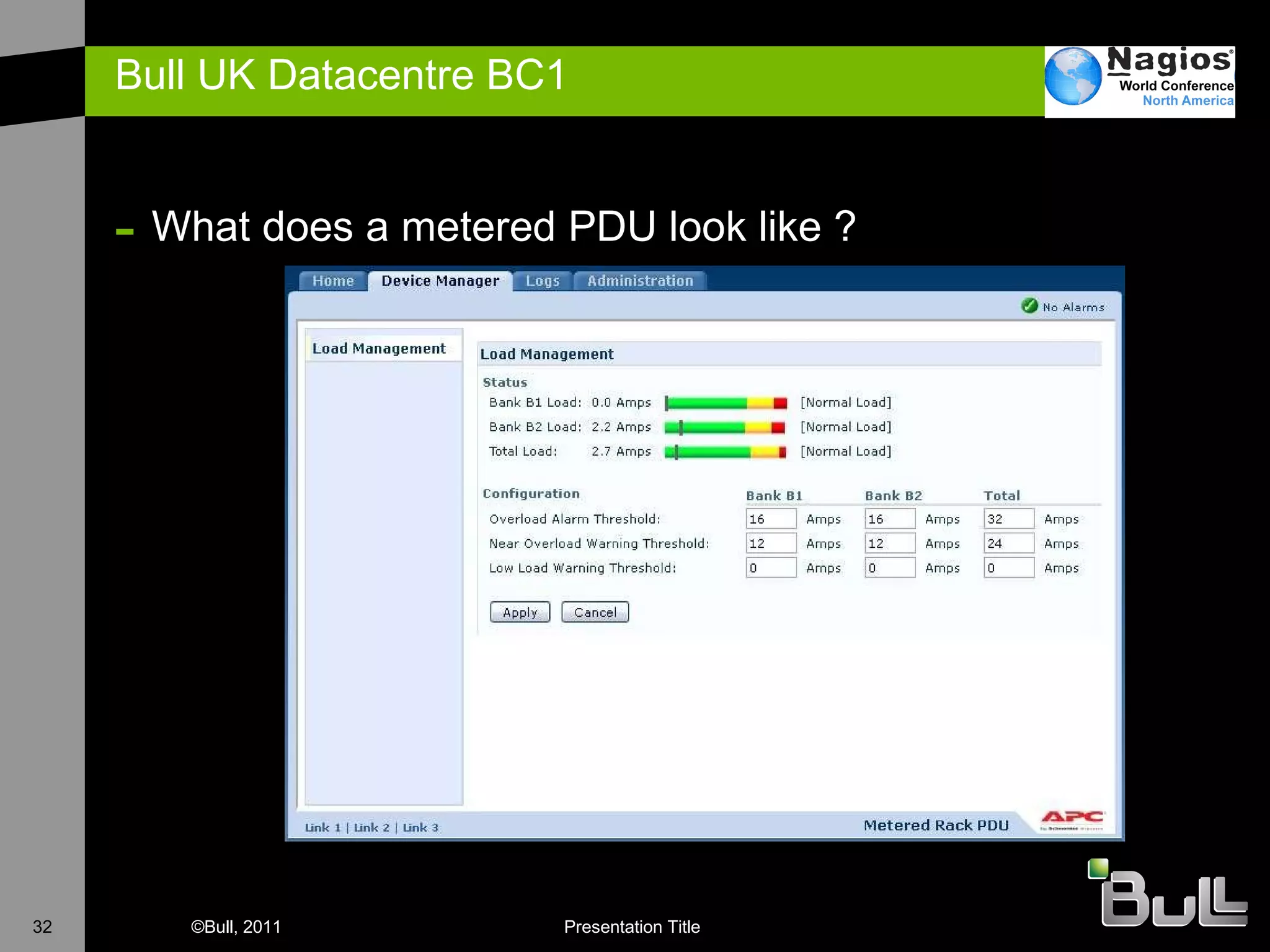
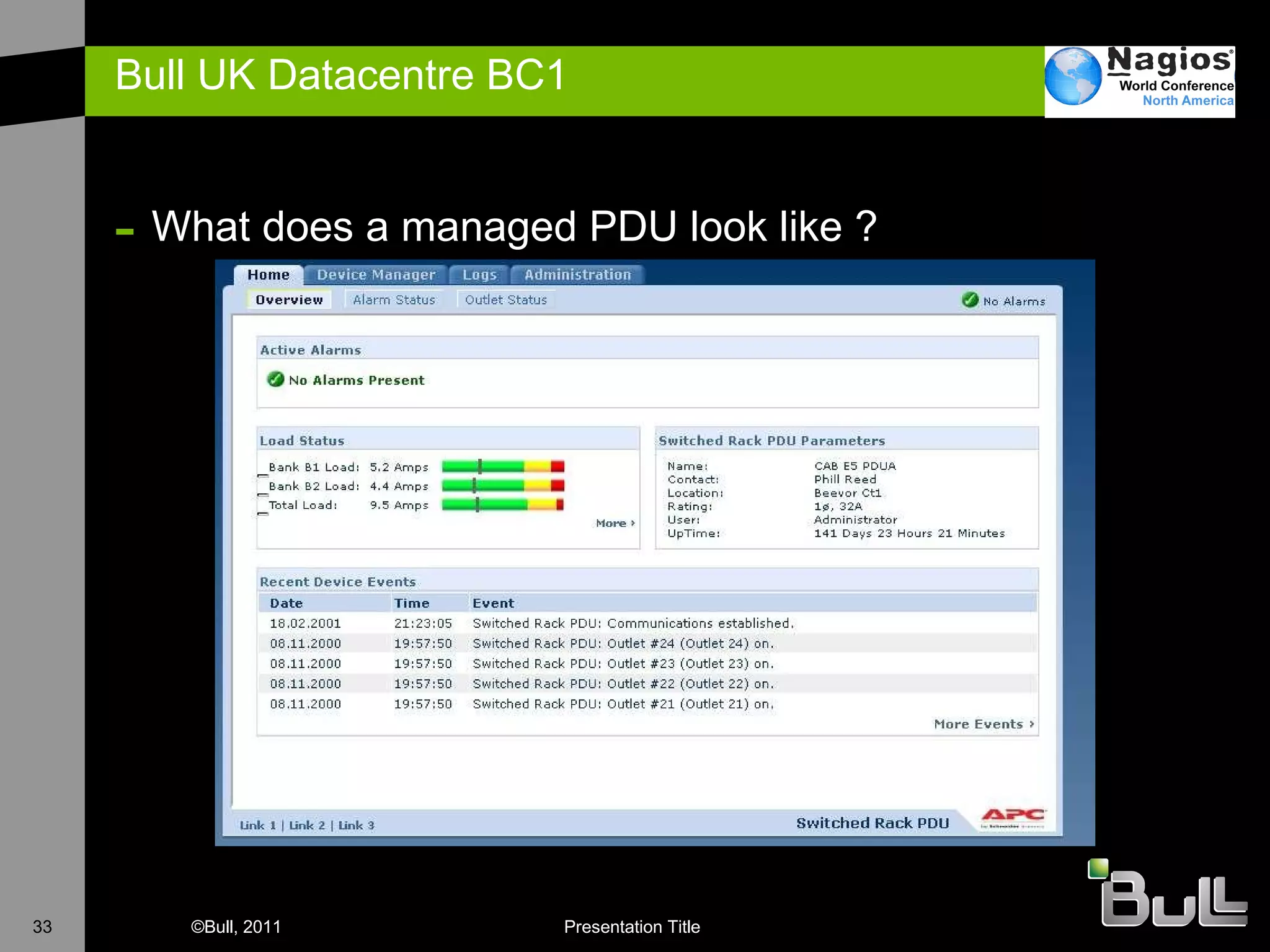
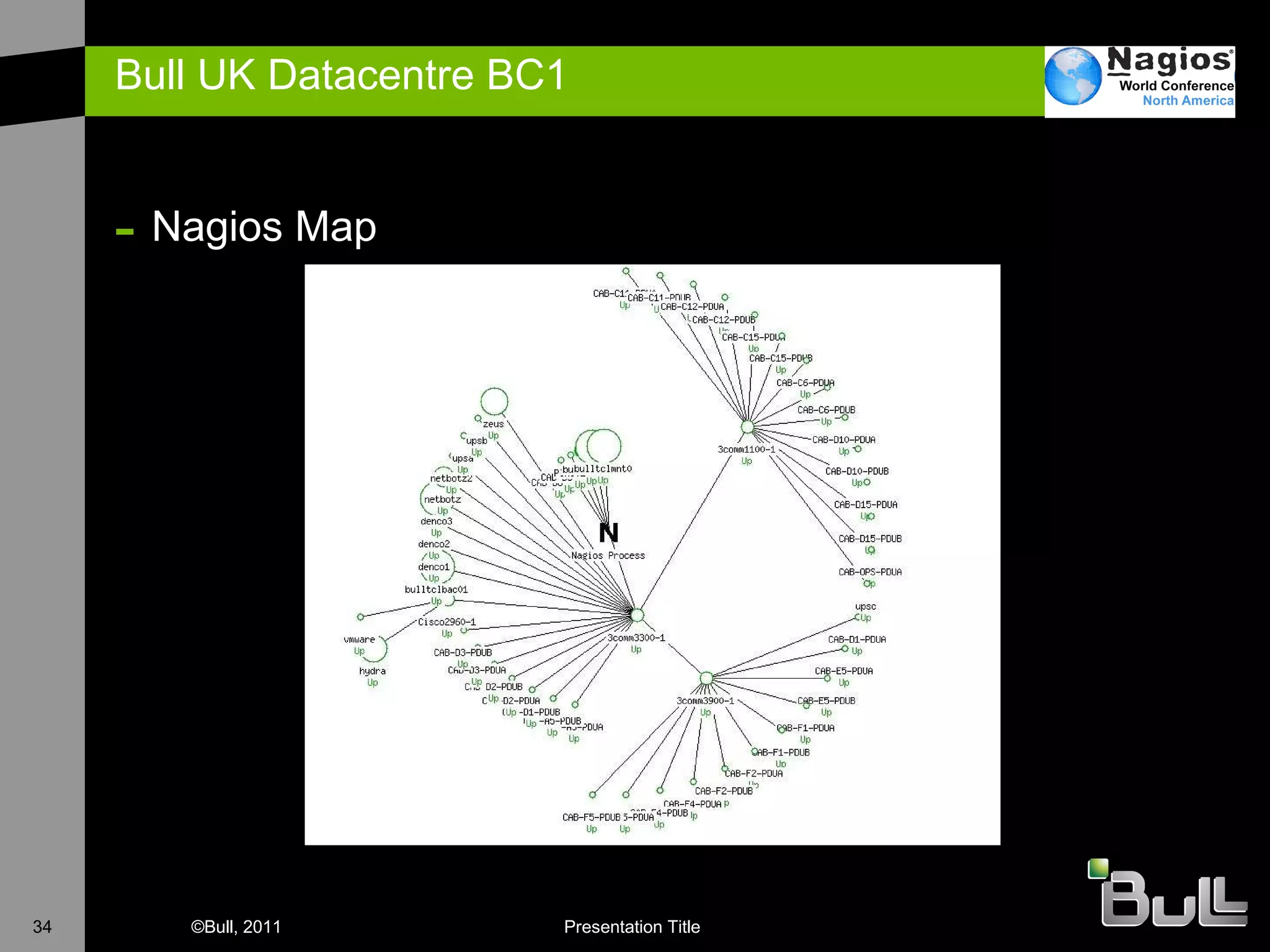
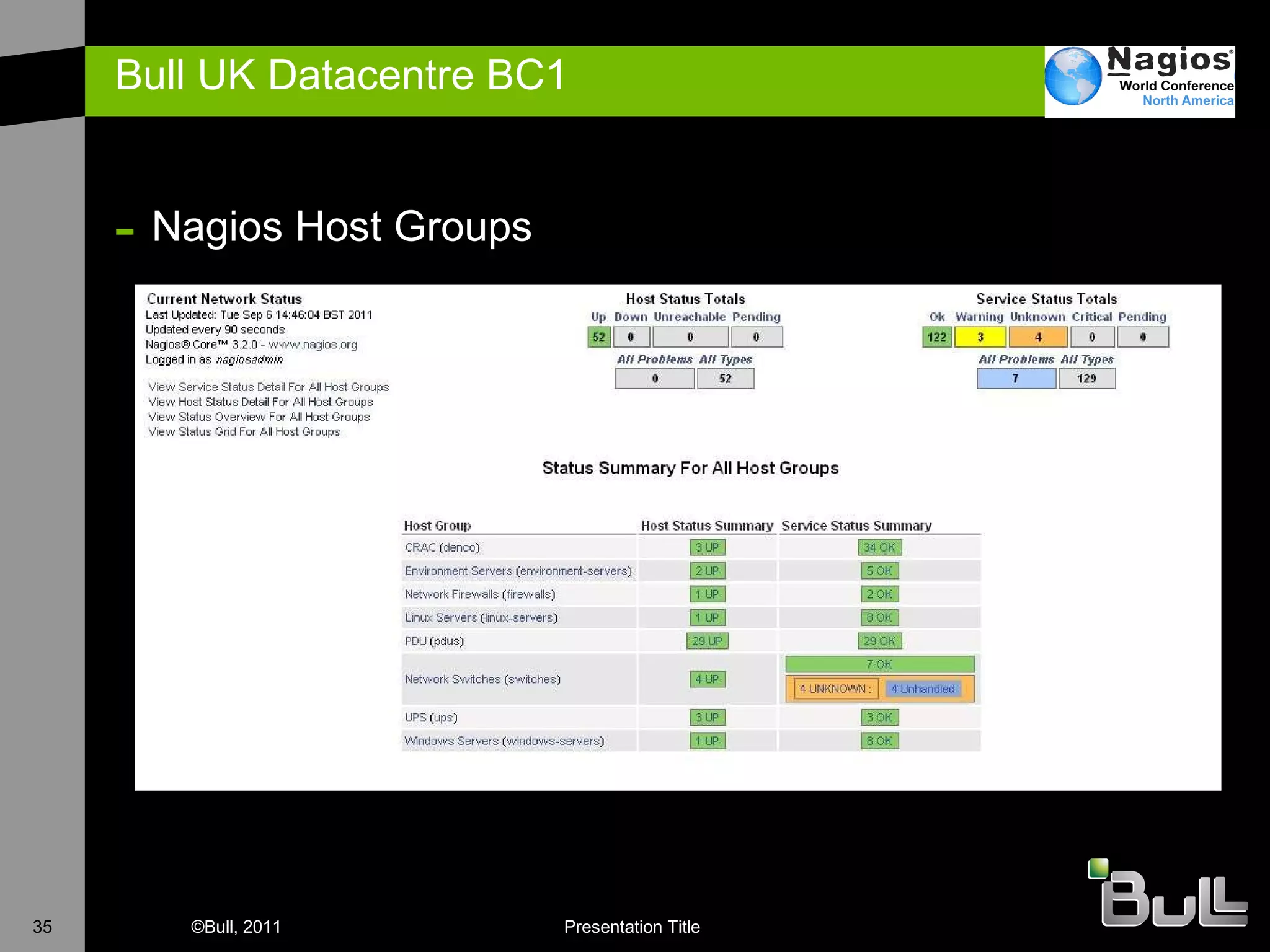
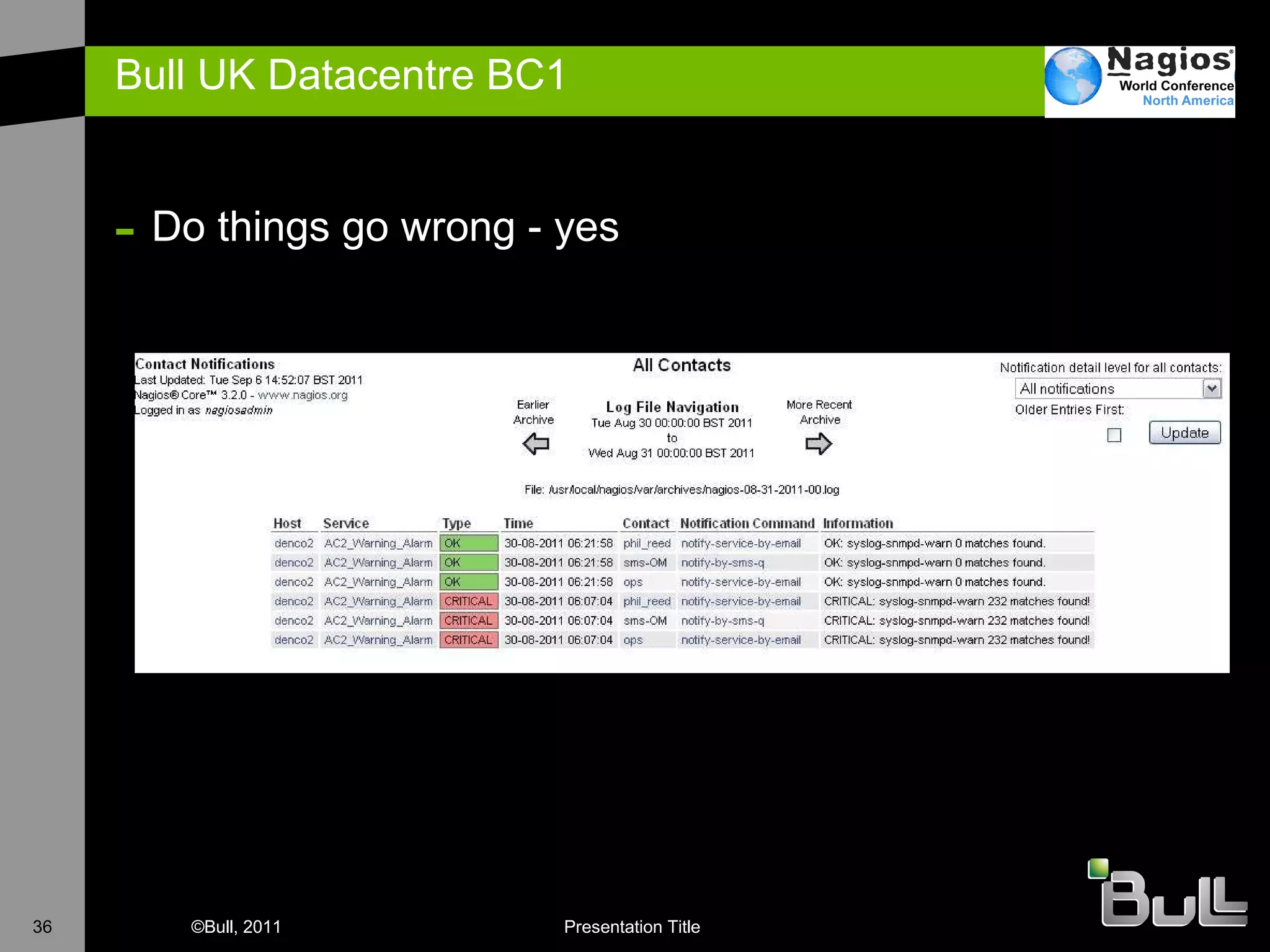
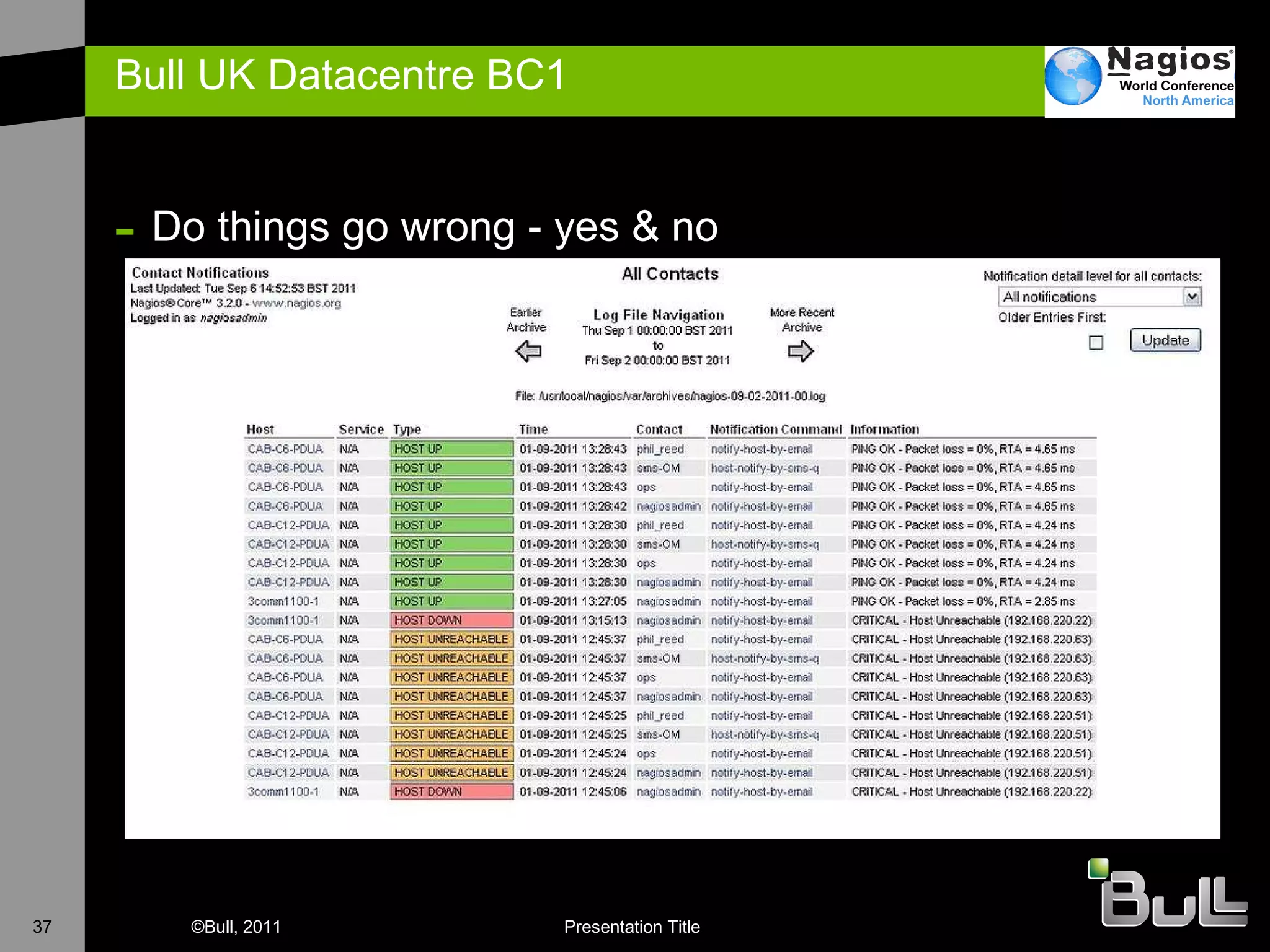
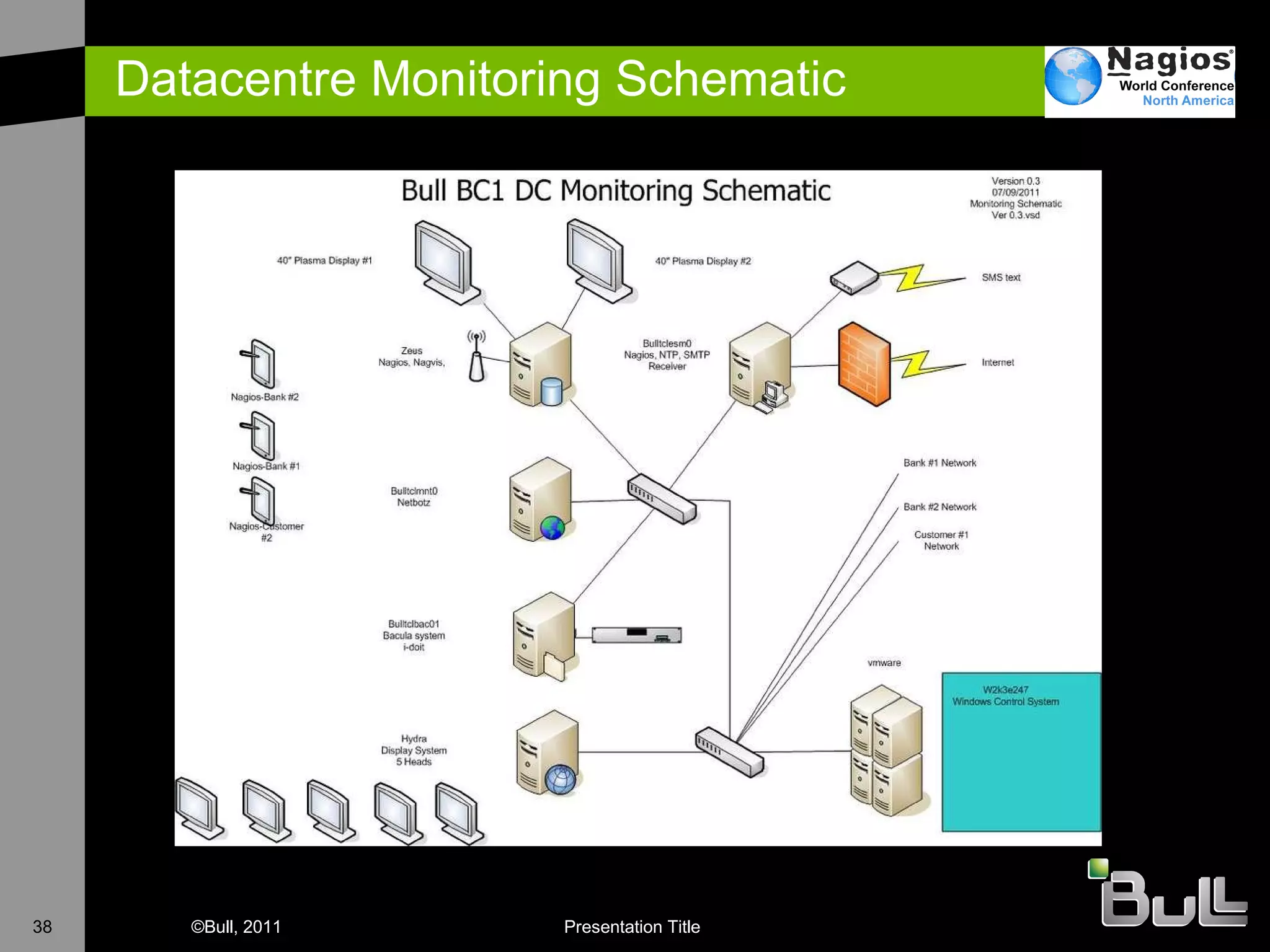
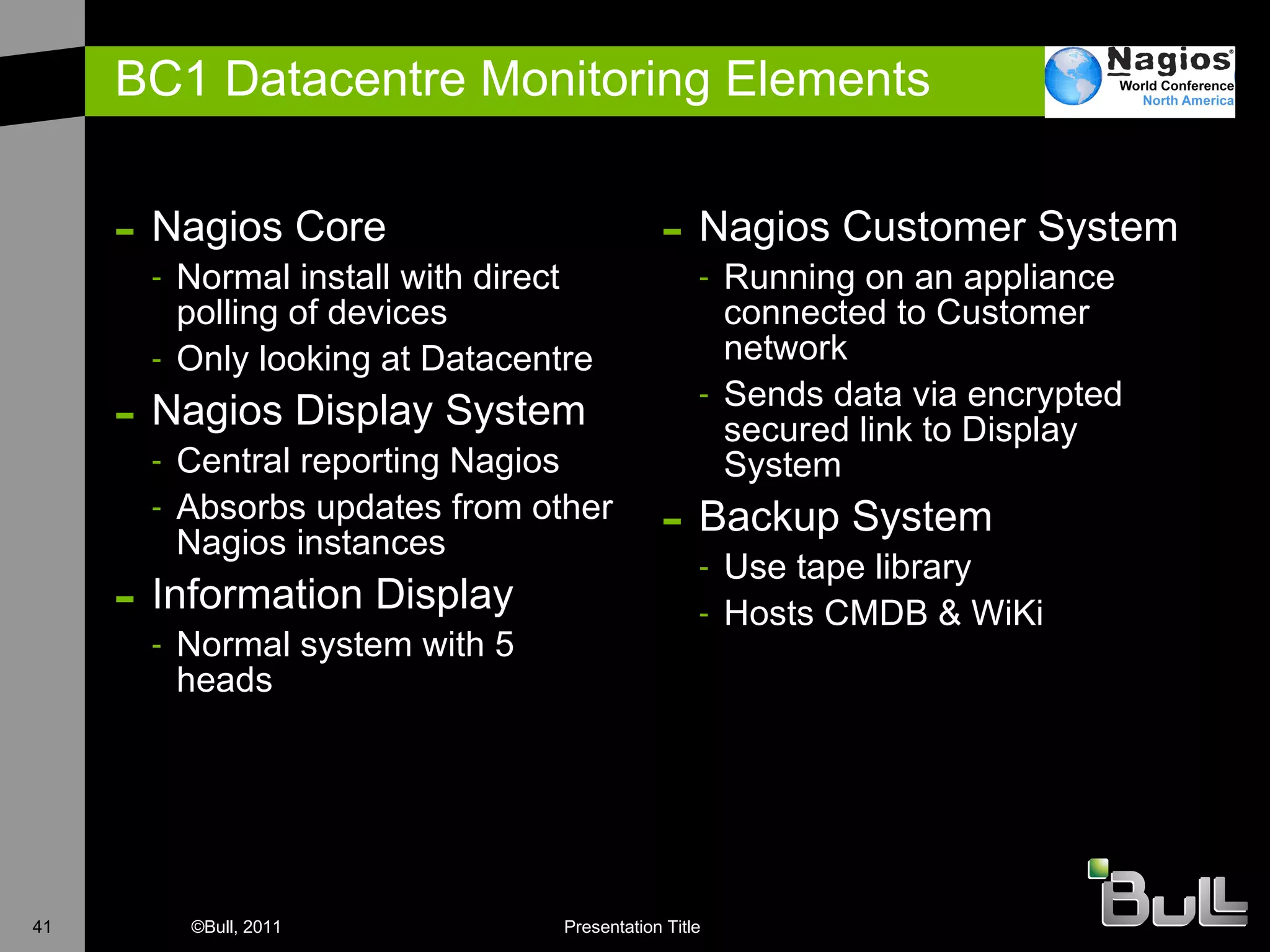
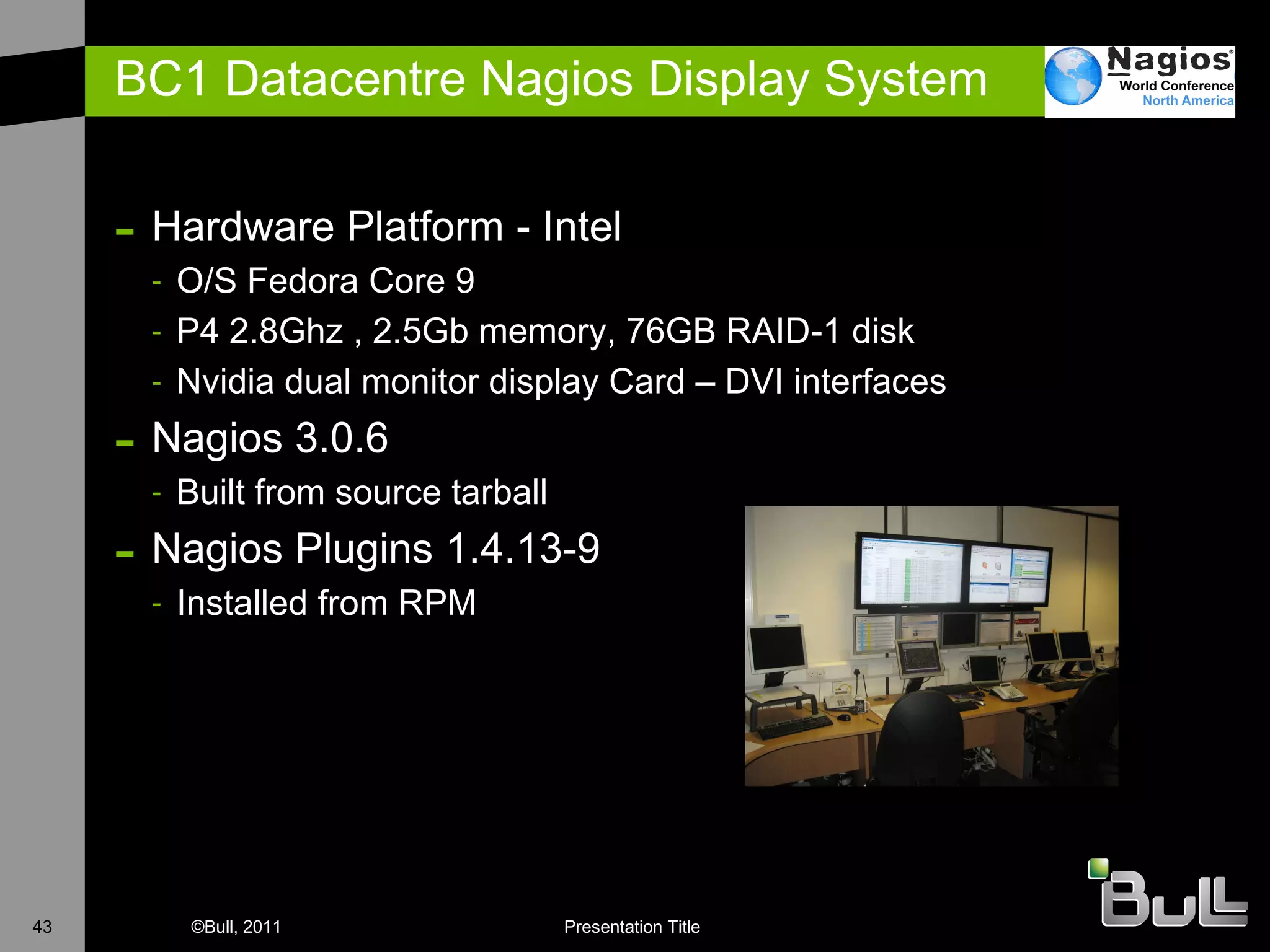
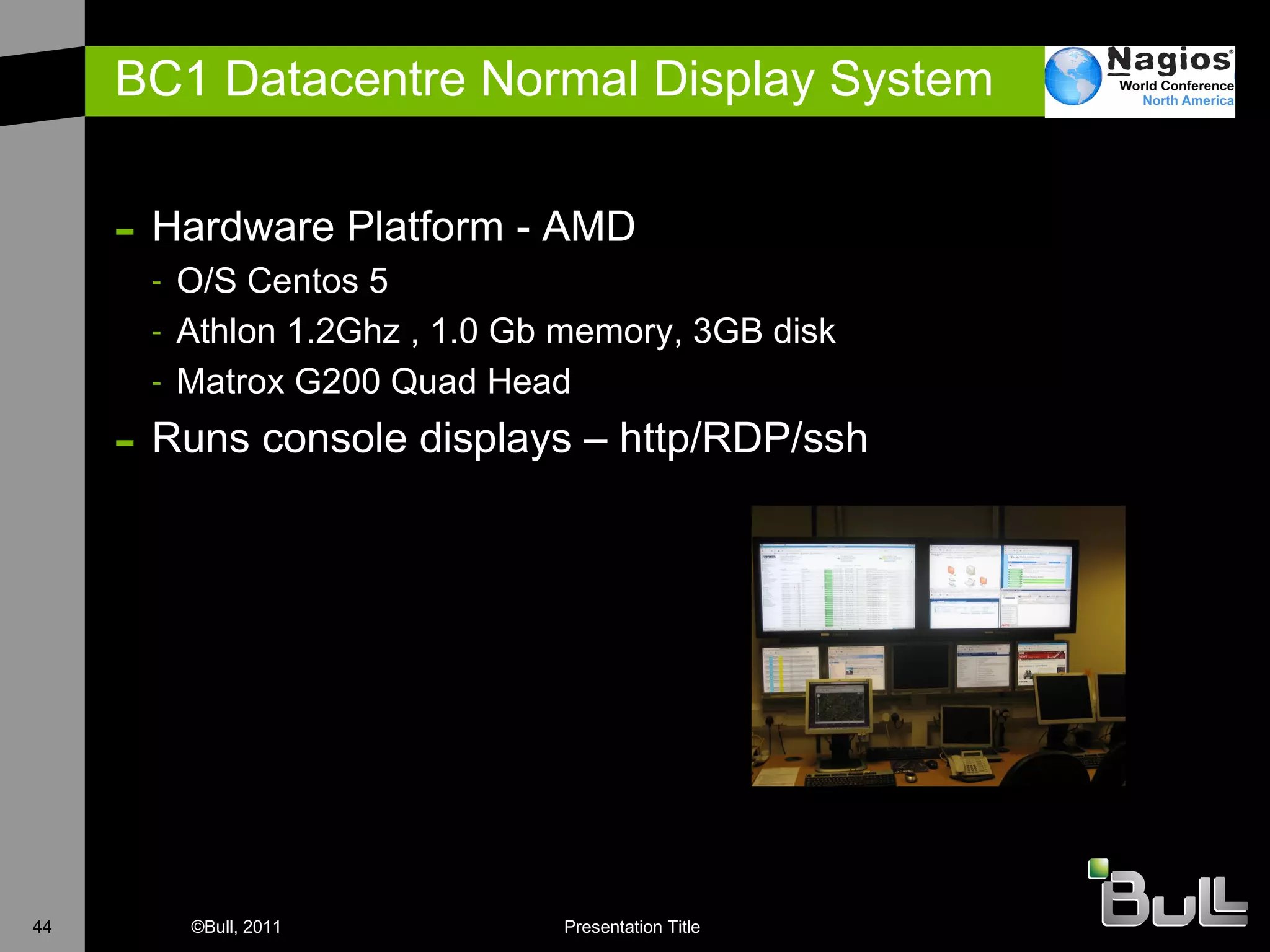
The document discusses the application of Nagios in real-world environments, particularly in monitoring systems for various organizations in the UK, including the Crown Office and Rother District Council. It covers system monitoring implementations, data center requirements, and energy efficiency metrics, emphasizing Nagios' ease of customization and effectiveness in monitoring diverse IT environments. Additionally, it outlines various tiers of data center classification and shares insights on strategic monitoring design and operational best practices.