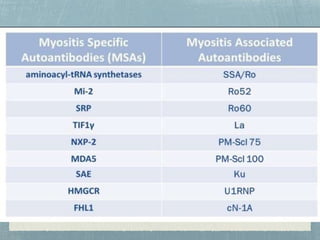
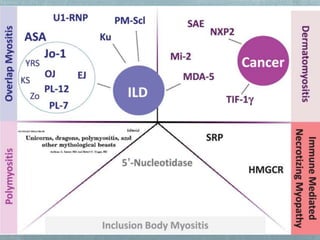
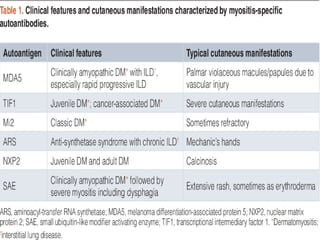
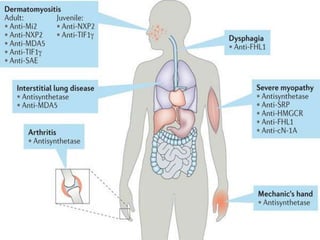
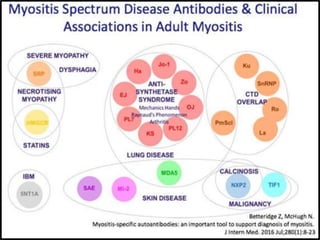
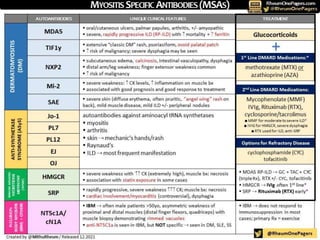
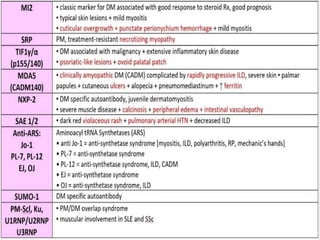
Inflammatory myopathy is a systemic autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle inflammation, weakness, and potential internal organ involvement, with main types including polymyositis and dermatomyositis. These conditions often have varying manifestations, such as skin rashes, muscle enzyme elevation, and can lead to complications like interstitial lung disease. Factors such as gender, age, and specific antibodies (e.g., anti-jo1) influence severity, prognosis, and associated risks like malignancy.