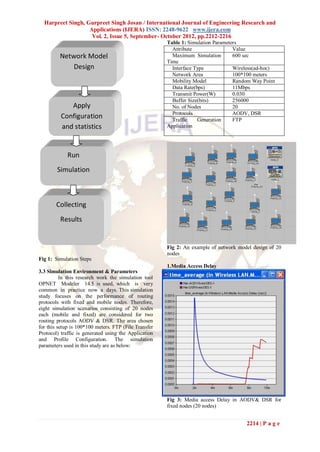
This document summarizes a research paper that evaluates the performance of two routing protocols, AODV and DSR, in wireless sensor networks. The paper analyzes the protocols based on two metrics: media access delay and network load. Through simulations with 20 nodes in OPNET, the paper finds that DSR has lower network load for mobile and stationary nodes, while AODV has lower media access delay for mobile nodes and initially for stationary nodes. Overall, the superior protocol depends on the scenario and performance metric considered.
![Harpreet Singh, Gurpreet Singh Josan / International Journal of Engineering Research and
Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 2, Issue 5, September- October 2012, pp.2212-2216
Performance Analysis of AODV & DSR Routing Protocols in
Wireless Sensor Networks
Harpreet Singh*, Gurpreet Singh Josan**
*(Department of Computer Science, Punjabi University, Patiala)
** (Asst.Prof. Department of Computer Science, Punjabi University, Patiala)
ABSTRACT
As deployment of sensor networks are issue without significant precedent in wireless
increasing either manually or randomly to network history .The nodes can be mobile or
monitor physical environments in different immobile, location-aware or location-unaware and
applications such as military, agriculture, homogenous or heterogeneous. Sensor nodes are
medical transport, industry etc. In monitoring of limited in energy supply and bandwidth. These
physical environments, the most important constraints combined with scalability determine the
application of wireless sensor network is design and management of sensor networks. The
monitoring of critical conditions. The most issues related to physical and link layers are unique
important in monitoring application like critical for all kind of sensor applications, therefore the
condition is the sensing of information during research on these areas has been focused on system-
emergency state from the physical environment level power awareness such as dynamic voltage
where the network of sensors is deployed. A big scaling, radio communication hardware, low duty
challenge to sensor networks is a fast, reliable cycle issues, system partitioning, energy aware
and fault tolerant channel during emergency MAC protocols.
conditions to sink (base station) that receives the One of the necessary requirements of a
events. Our focus is to discuss and evaluate the wireless sensor network is to deliver data reliably
performance of two different routing protocols against the dynamic and lossy nature of wireless
like Ad hoc On Demand Distance Vector (AODV) transmissions. In wireless sensor networks the
[1] and Dynamic Source Routing (DSR) for energy dissipation in transmission of data directly
monitoring of critical conditions with the help of depends on the routing algorithm. Hence, resource
important metrics like network load and media constraint Sensor Networks requires an optimum
access delay in different scenarios for both stable algorithm for routing.
and mobile nodes. On the basis of results derived
from simulation a conclusion is drawn on the 2. ROUTING PROTOCOL
comparison between these two different routing A routing protocol is a protocol that
protocols with parameters like media access delay specifies how routers communicate with each other,
and network load. disseminating information that enables them to
select routes between any two nodes on a computer
Keywords - Ad hoc On Demand Distance Vector network, the choice of the route being done by
(AODV), Dynamic Source Routing (DSR), Media routing algorithms. Each router has a priori
access delay, Network load, OPNET. knowledge only of networks attached to it directly.
A routing protocol shares this information first
1. INTRODUCTION among immediate neighbours, and then throughout
The advancements in wireless the network. This way, routers gain knowledge of
communication technologies enabled large scale the topology of the network. The term routing
wireless sensor networks (WSNs) [2] deployment. A protocol may refer specifically to one operating at
Wireless Sensor Networks consists of spatially layer three of the OSI model, which Similarly
distributed sensor to monitor physical or disseminates topology information between routers.
environmental conditions. As from the name rather As we are comparing AODV and DSR routing
than gathering sensed data through wired data buses protocols for mobile and stable nodes in wireless
WSN employs a wireless backhaul to transmit sensor networks are discussed below:
sensor reading to central location for aggregation
and further processing. AODV (Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector):
Wireless Sensor Networks can be generally AODV is a reactive routing protocol and a
described as a network of nodes that cooperatively route from one node to another node can be found
sense and may control the environment enabling when required. Each intermediate node in the
interaction between persons or computers and the network forwards the Route Request (RREQ)
surrounding environment. The design of energy message until it reaches the destination node. The
efficient communication protocols is a very peculiar
2212 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mw2522122216-121016014131-phpapp02/75/Mw2522122216-1-2048.jpg)
![Harpreet Singh, Gurpreet Singh Josan / International Journal of Engineering Research and
Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 2, Issue 5, September- October 2012, pp.2212-2216
destination node responds to the RREQ message by even when any one of the sensor node dies. Accurate
transmitting the Route Reply (RREP) message. and clear picture of the network can be obtained by
As the RREP flows through the network, it fixing the ST as smaller value even though it
determines the route from source node to destination consumes more energy due to frequent transmissions
node. The sequence number is increased by each [3].
originating node and used to determine whether the
received message is the most recent one. The older 3. SIMULATION AND ENVIRONMENT
routing table entries are replaced by the newer ones. In simulation the different types of
Active nodes in the networks are determined by scenarios are consider based upon mobile and fixed
broadcasting a “Hello” message periodically in the nodes on OPNET simulator. OPNET(Optimized
network. If a node fails to reply a link break is Network Engineering Tool) Modeler. 14.5 is used
detected and a Route Error (RERR) message is for the design and implementation of this work.
transmitted which is used to invalidate the route as it
flows through the network. A node also generates a 3.1 OPNET
RERR message if it gets message destined to a node OPNET is a network simulator that
for which a route is unavailable. provides virtual network communication
Types of messages in AODV: environment. It is appropriate for the research
1. Route Request (RREQ) message: It is used to studies, network modeling and engineering, R & D
form a route from one node to another node in a Operation and performance analysis. OPNET
network. Modular 14.5 [4] is chosen because it is one of the
2. Route Reply (RREP) message: It is used to leading environments for network modeling and
connect destination node to source node in a simulation. It offers easy graphical interface,
network. possibility to develop and run this simulation
3. Route Error (RERR) message: It is used to environment, validity of the simulation results. This
indicate any route broken or node failure. tool is highly reliable, robust and efficient [8]. It
4. HELLO message: It is used to determine the supports large number of built-in industry standard
activeness of the network. network protocols, devices, and applications.
The transmission of data depends on route discovery
and route maintenance in AODV. The route 3.1.1 OPNET Features
discovery depends on RREQ and RREP messages, if It provides virtual real time environment for
a node initiate’s request of route it will form route networks with GUI.
after getting the RREP. The route will be maintained Useful in evaluation of designs for new
by sending HELLO messages to neighbour nodes, if network models and architectures.
any link failure it will indicate using RERR message Good for performance study of existing
systems based on users conditions.
(TEEN) Threshold - sensitive Energy Efficient Easy for understanding the network
sensor Network protocol: behaviour in various scenarios.
TEEN is a reactive protocol proposed for
time-critical applications. BASE STATION 3.2 Simulation Steps
broadcasts the attribute, Hard Threshold (HT) and Simulation with OPNET is generally
Soft Threshold (ST) values to its cluster members. divided into four parts, network model design,
The sensor nodes starts sensing and transmits the applying statistics, run simulation and then to
sensed data when it exceeds HT. HT is the minimum view results and to analyze the results, if the
attribute range above which the values are expected. results are not correct then it has to be re-modeled
The transmitted sense value is stored in an internal and then to apply new statistics. The basic work
variable called Sensed Value. The cluster nodes flow of OPNET [5] can be seen in the flowchart
again starts sensing, when its value exceeds the ST. shown in figure 1.
The minimum change in the sensed value it switches
on its transmitter and transmits. The energy is
conserved since the sensor nodes in the cluster
senses continuously but transmits only when the
sensed value is above HT. The ST further reduces
the transmission which could have been occurred
when there is a little change or no change in sensed
attribute. As the cluster heads (CH) need to perform
extra computations it consumes more energy
compared to other nodes. The main drawback of this
protocol is that the transmission from nodes to CH
will not be there when the sensed value is not greater
than HT, hence the CH will never come to know
2213 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mw2522122216-121016014131-phpapp02/85/Mw2522122216-2-320.jpg)
![Harpreet Singh, Gurpreet Singh Josan / International Journal of Engineering Research and
Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 2, Issue 5, September- October 2012, pp.2212-2216
Fig 4: Media access Delay in AODV& DSR for
mobile nodes (20 nodes)
As it is clear from the figure 3 that media Fig 5: Network Load in AODV& DSR for fixed
access delay of AODV protocol is more than DSR in nodes
case of fixed nodes but only in the beginning, but as (20 nodes)
the time increases delay of DSR goes increases than
AODV. In figure 4 media access delay of DSR is
more than AODV while the nodes are mobile. So
AODV protocol performs better than DSR for higher
number of nodes in both fixed and mobile nodes
because delay is less except the initial state of
AODV in case of fixed nodes [5].
The Media Access Delay encountered by
the two routing protocols during the simulation
period for all scenarios. It is clear from figures that
DSR incurs the highest delay, especially on large
size of nodes. DSR exhibits large packet delay
because its routes discovery takes more time. Every
intermediate node tries to extract and record
information before forwarding a reply. AODV gives
the lower Media Access Delay as compared to DSR.
2. Network Load
Figures 5and 6 shows the Network load in
both the protocols for stable and mobile nodes. As
shown in the figure 5 that Network load of AODV is
more in case of fixed nodes as compare to the DSR
protocol [6]. It depends upon the number of nodes,
more the number of nodes more will be network
load in both the cases stable and mobile in DSR
protocol. While in the figure 6 Network load of DSR Fig 6: Network Load in AODV& DSR for mobile
is more in mobile nodes nodes
(20 nodes)
.
So according to the simulation the
performance analysis of DSR is better in aspect of
Network load for mobile and stable nodes in lower
number of nodes. In aspect of Media
2215 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mw2522122216-121016014131-phpapp02/85/Mw2522122216-4-320.jpg)
![Harpreet Singh, Gurpreet Singh Josan / International Journal of Engineering Research and
Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com
Vol. 2, Issue 5, September- October 2012, pp.2212-2216
access delay the performance of AODV is better for [6] Asha Ambhaikar H.R. Sharma
mobile nodes while for fixed nodes performance of V.K.Mohabey, “Scalability Performance of
DSR is better in the initial time but as the time MANET Routing protocols with Reference
increases performance of DSR goes down and to Variable Pause Time”, International
AODV perform better. Journal on Computer Science and
Engineering, Vol. 02, No. 09, PP. 3021-
4. CONCLUSION 3024,2010.
In this work the evaluation of the two [7] Arati Manjeshwar and Dharma P.Agarwal:
routing protocols for their responses to network “A Routing Protocol for Enhanced
scalability with respect to their network load and Efficiency in Wireless Sensor Networks”,
media access delay as their performance metrics. International Parallel and Distributed
DSR and AODV implemented in different scenarios Processing Symposium (IPDPS), 2001,
of executing stable nodes and mobile nodes IEEE.
networks. In each scenario all the nodes were used [8] Introduction to OPNET Modeler, 2007
as source nodes of sending data to a common base OPNET Technologies.
station. So according to the simulation the [9] Wikipedia, “ Introduction of Sensors”.
performance analysis of DSR is better in aspect of [10] Yogesh Chaba, Yudhvir Singh and Aarti,
Network load for mobile and stable nodes in lower “Performance analysis of Scalability and
number of nodes case. In aspect of Media access Mobility On Routing Protocols in
delay the performance of AODV is better for mobile MANET”, International Journal of
nodes while for fixed nodes performance of DSR is Information Technology and Knowledge
better in the initial time but as the time increases Management, Vol. 1,No. 2, PP. 327-336,
performance of DSR goes down and AODV perform Jul-Dec,2008.
better. On selected protocols, from the conducted [11] OPNET University Program:
study we conclude that in overall performance one http://www.opnet.com/services/university/
protocol is superior to other protocol. One protocol [12] Introduction to OPNET Modeler, 2007
may be far better in performance than other protocol OPNET Technologies.
in terms of media access delay and network load. [13] IETF Working Group MANET:
The size of the networks also matters for the http://www.ietf.org/html charters/manet-
performance of the protocol. chart er.html.
[14] Routing Protocol Performance Issues and
REFERENCES Evaluation
[1] Peng Liu, Y.Fun Hu, Geyong Min and Considerations:http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2
Guojun Dai,“Semantization improves the 501.txt.
Energy Efficiency of Wireless Sensor [15] Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector
Networks”,2010,IEEE (AODV) Routing: http://tools.ietf.org/ht
[2] Jun Zheng, Abbas Jamalipour, ml/rfc3561
“Classification of WSNs Routing
Protocol”, a chapter from Wireless sensor
networks: a networking perspective, John
Wiley & Sons, 2009.
[3] Hean Kuan Ong, Hean Loong Ong, Elok
Robert Tee and R. Sureswaran, “Scalability
study of ad-hoc wireless mobile network
routing protocol in sparse and dense
networks” Distributed Frameworks for
Multimedia Applications, 2006. The 2nd
International Conference, Pulau Pinang,
May 2006, IEEE.
[4] Suyang Ju and Joseph B. Evans, “Scalable
Cognitive Routing Protocol for Mobile Ad-
Hoc Networks”, IEEE Global
Telecommunications Conference, USA, 6-
10 Dec. 2010, IEEE.
[5] Prashant Singh, D.K. Lobiyal, “Scalability
of Routing in MANET”, 2010 Second
International Conference on
Communication Software and Networks,
Singapore, Feb 2010, IEEE.
2216 | P a g e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mw2522122216-121016014131-phpapp02/85/Mw2522122216-5-320.jpg)