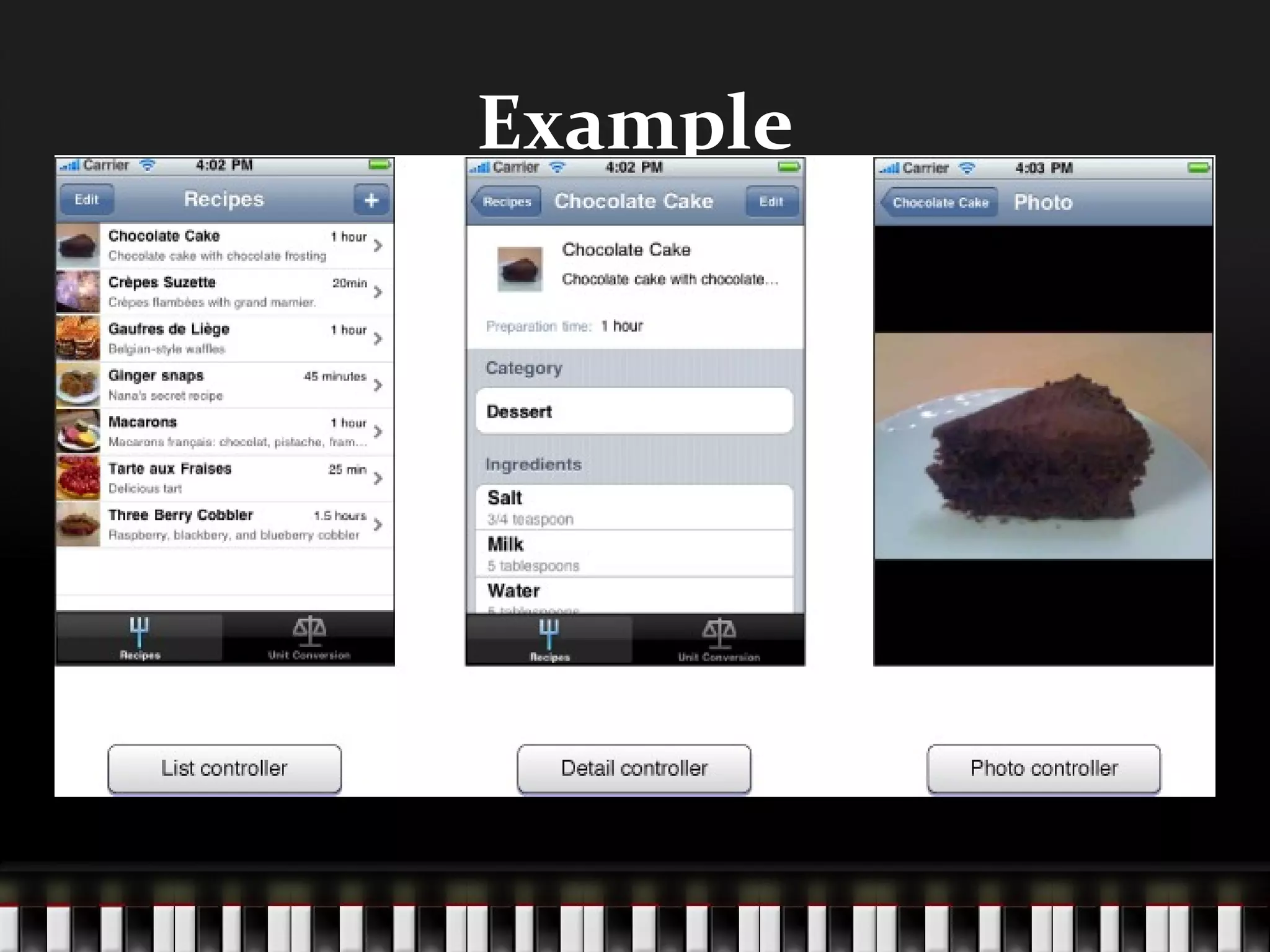
The document discusses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern which assigns objects in an application one of three roles: model, view, or controller. The pattern defines how these objects communicate with each other. MVC is central to a good design for Cocoa applications as it promotes reusability, extensibility, and is the basis for many Cocoa technologies. Model objects define the application's data logic. View objects display data and enable user interaction. Controller objects act as intermediaries between models and views.