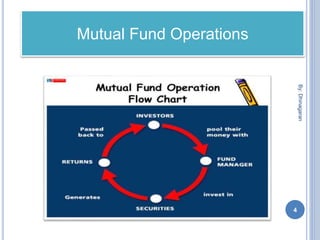
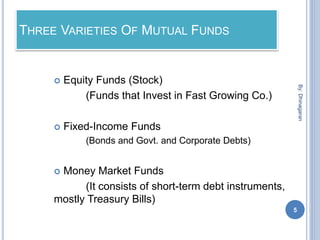
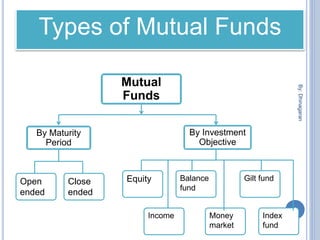
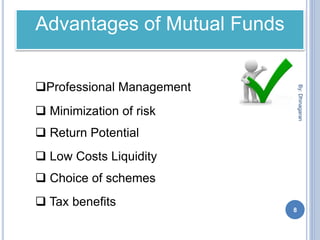
The document provides an overview of mutual funds, explaining their function as a vehicle for pooling investors' savings to invest in various capital market instruments. It details the history of mutual funds in India, types such as equity, fixed-income, and money market funds, and the advantages and disadvantages of investing in them. Additionally, it outlines investment strategies like systematic investment and withdrawal plans, and lists major mutual funds available in India.