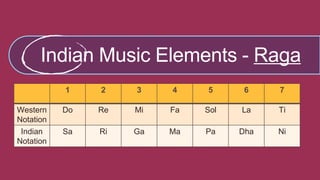
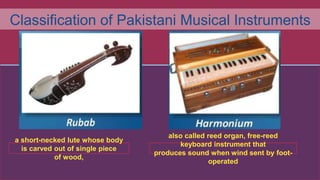
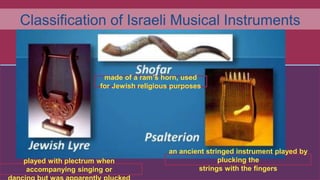
This document provides information about the classical music traditions of India, Pakistan, and Israel. It discusses the main vocal and instrumental styles of each region. For India, it describes Carnatic music of South India and Hindustani music of North India, and their main elements of raga and tala. For Pakistan, it outlines vocal styles like ghazal, qawwali, and secular singing. For Israel, it divides Jewish music into devotional and secular categories. The document also classifies the main types of musical instruments found across South Asia and the Middle East.